-
It's Official: Netflix Has Entered a "Virtuous Cycle"
Looking at Netflix's Q4 '09 and full year '09 results released late last Wednesday, plus Netflix's performance over the last 3 years, I have concluded the company has officially entered a "virtuous cycle." For those of you not familiar with the term, a virtuous cycle is when a single change or improvement leads to a cascading series of follow-on benefits which both reinforce themselves and add further momentum to the original change (a hyper "one good thing leads to another" scenario, if you will). Virtuous cycles are extremely rare in business, and when they happen they have profound implications.
The start of Netflix's virtuous cycle is obvious: the company's introduction of its free "Watch Instantly" streaming feature in January, 2007. Streaming has fundamentally changed the Netflix service offering and consumers are increasingly aware of this. Traditionally, Netflix subscription plans were defined by limits - 1 DVD out at a time for $8.99/mo, 2-out for $13.99/mo or 3-out for $16.99/mo. But with the company's decision to remove the confusing original caps it placed on streaming consumption and move to an unlimited model, Netflix is now providing enormous new value at the same DVD rental price points. Netflix has also changed how it advertises its services, strongly emphasizing streaming (see its home page for example). The "unlimited streaming" message is breaking through and Netflix subscriber growth momentum over the last 3 years reflects this.
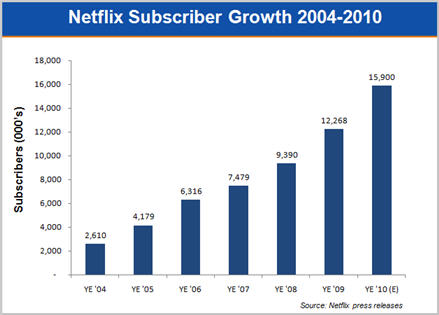
Subscribers grew to 12.3 million at the end of '09, 31% higher than YE '08. To get a sense of Netflix's momentum, '09 growth handily beat '08 (26%) and '07 (18%) growth. The 2.9 million subs added in '09 was 85% above the company's own 2009 beginning year forecast of 1.56 million sub additions. Looking ahead, the mid-point of Netflix's forecast for '10 is for another 30% growth in subs.
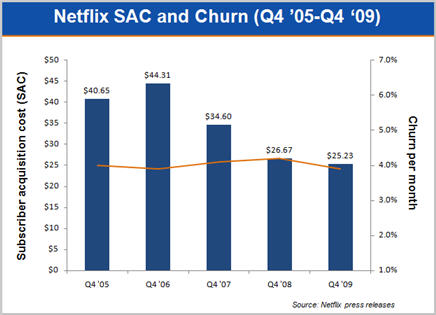
As the streaming benefits have resonated, it's very important to note that subscriber growth is actually getting progressively cheaper for Netflix to accomplish. As the following graph shows, Netflix's subscriber acquisition cost (SAC) has decreased by an impressive 43% from $44.31 in Q4 '06 to $25.23 in Q4 '09 (the 2nd lowest SAC in the company's history). Better still, the quality of these new subs seems high; average monthly churn in Q4 '09 was 3.9%, equal to the lowest churn the company has ever achieved. While Netflix isn't "buying" growth with low-quality additions (an old trick for subscription-oriented businesses), it is however putting more emphasis on the "1-out" service, which, with the addition of unlimited streaming, is an outstanding value for the low-end of the market. Netflix is eager to penetrate this segment, to whom $1 Redbox rentals are very attractive.
While Netflix's financials already reflect the virtuous cycle impact streaming is having on the business, it is likely there is much more to come as streaming takes further hold. Netflix revealed that 48% of its subscribers streamed at least 15 minutes/mo in Q4 '09, up from 41% in Q3 '09 and 26% in Q4 '08 (Incidentally, I think it's conceivable that 80% or more of recently-added subscribers are streaming). But it's just in the last year that Netflix streaming has begun to make the move from computer-only consumption to TV-based consumption, truly making it a mainstream experience. Netflix has inked deals with all the major game consoles (with a Wii marketing campaign beginning in '10), plus numerous CE devices, Blu-ray players, etc. Just ahead is a future where Wi-Fi will be ubiquitous in all new TVs and Netflix's deals with all the major TV manufacturers will ensure it is even more front and center for consumers.
To make streaming attractive, Netflix has had to essentially build a second content library. As I've suggested in the past, this isn't easy, as the company must navigate a thicket of pre-existing Hollywood rights and business relationships. Most notably, Netflix has run into the premium cable networks (HBO, Showtime, Starz and Epix) which have a monopoly on Hollywood's output for their release window. Netflix's deal with Starz was an important first step but still, I've been skeptical that Netflix would land streaming deals with the others.I'm now gaining more confidence that this will indeed happen, especially for these networks' original productions. Netflix is simply getting too big to ignore. It represents a whole new revenue opportunity for premium channels, plus an important loyalty-building outlet. Further out though, while Netflix CEO Reed Hastings says he wants the company to be a distributor for these premium channels, I think it's nearly inevitable that Netflix will compete head-on with them for Hollywood's output. Economics dictate that eventually it makes more sense for Netflix to bid directly for Hollywood rights than work through a premium channel middleman.
In fact, Netflix already has tons of Hollywood relationships, and its recent deal with Warner Bros, creating a 28-day DVD window is emblematic of how Netflix looks at streaming content acquisition going forward. In that superb deal, which was ludicrously criticized by some, Netflix simultaneously helped a critical partner sustain its DVD sales window, while gaining cheaper access to more DVD copies on day 29 and increased streaming rights for catalog titles. As Hastings pointed out on the Q4 earnings call, given the inconsistencies in DVD release strategies, most consumers have little-to-no idea when a title becomes available on DVD, so, while still early, opening up the 28 day window has caused no subscriber complaints. And the company's analysis of subscriber "Queues" indicates, just 27% of requests are for newly-released titles.
Importantly, Netflix's strategy is to pour savings from its DVD deals into streaming content acquisition. As I noted recently, Netflix's detailed subscriber data and usage analysis gives it a huge asymmetric advantage in negotiating additional streaming licenses from Hollywood. Netflix can surgically concentrate its resources on only those titles it knows its subscribers will value. Over time, as DVD sales continue to collapse, Netflix will be there to offer its subs a broader and broader rental selection.
The biggest challenge to Netflix for streaming content acquisition is how much it chooses to spend. Netflix's relatively small size among giants like Comcast and others is what prompted me to suggest over a year ago that Microsoft would acquire Netflix. I'm officially retracting that prediction now, as 2009 demonstrated how much streaming progress Netflix can make on its own. In fact, I think all rumors of a possible Netflix acquisition are off-base; I see the company remaining independent for some time to come.
Netflix is now riding a serious wave and its executives recognize the mile-wide opportunity ahead of it. The product is immeasurably stronger and more appealing with unlimited streaming included. That's in turn leading to impressive sub growth with much-reduced SAC and improving churn. The number of devices bridging Netflix to the TV is growing and portends ubiquity at some point down the road as these devices further leverage Netflix's platinum consumer brand. Streaming content selection is improving, bringing side benefits of reduced DVD postage and inventory costs. With millions of subscribers Netflix now has both the economics and the scale to be a very significant player in the video ecosystem.
Last but not least is a very favorable competitive climate. Aside from a hobbled Blockbuster, astoundingly, Netflix doesn't have any other direct DVD subscription/online streaming hybrid competitor (Amazon and Apple, are you paying attention?). And while Comcast and other multichannel video programming distributors ("MVPDs") are rolling out TV Everywhere services (5 years later than they should have, in my opinion), these are still early stage, and still encumbered by archaic regional limitations. Indeed, Netflix's growth may well cause these companies to consider their own over-the-top plans, as I've suggested.
For years I have been saying that broadband video is the single most disruptive influence on the traditional video distribution value chain. Netflix's success with streaming and the consequences that are yet to play out are resounding evidence of this. Above and beyond YouTube, Hulu, Amazon, Apple and others, Netflix is by far the most important video distributor to watch.
What do you think? Post a comment now (no sign-in required)
Categories: Aggregators, Devices
Topics: Comcast, Netflix, Warner Bros.

