-
Why Netflix's Long-Term Focus in New Warner Bros. Deal is a Win for Everyone
Netflix's new deal with Warner Bros., in which it agreed to a 28 day "DVD window" for new releases, in exchange for greater access to WB's films for its Watch Instantly streaming feature and reduced pricing on its own DVD purchases, is further proof that Netflix is squarely focused on the long-term. That's not only smart for Netflix, it's also a win for Hollywood studios and also for consumers.
With 11 million subscribers and growing, Netflix has emerged as one of Hollywood's most important home video customers. This dynamic has only increased recently due to slowing sales of DVDs (down another 13% in 2009) and Netflix's dominance in DVD rentals. Yet Netflix is viewed warily by Hollywood, primarily
 due to concerns that in the digital age, Netflix could gain too much power over Hollywood's fate. This concern was reinforced by Netflix's deal with premium cable channel Starz, a de facto end-run around Hollywood in which Netflix got streaming access to certain Disney, Sony and Lionsgate films.
due to concerns that in the digital age, Netflix could gain too much power over Hollywood's fate. This concern was reinforced by Netflix's deal with premium cable channel Starz, a de facto end-run around Hollywood in which Netflix got streaming access to certain Disney, Sony and Lionsgate films.As I've pointed out many times (as recently as this past Monday, in item #6), despite the Starz deal and the impressive adoption of Watch Instantly to date, Netflix faces a major challenge in building out its catalog of recent films for streaming use. Part of the challenge is Hollywood's "windowing" approach; in particular, other premium channels like HBO, Showtime and Epix have made significant financial commitments for electronic distribution during certain time periods that effectively preclude Netflix gaining streaming rights. Because much of Netflix's value proposition relies on its vast DVD selection (100K+ titles currently), if its streaming catalog continues to look meager by comparison, then Netflix's goal of migrating its users to streaming delivery over time will be seriously undermined.
That's where the new WB deal comes in. While the companies didn't disclose which titles or how many
 would be available, my guess is that the benefits of the deal, when it's fully implemented, will be noticeable to Netflix's subscribers or Netflix wouldn't have signed on. While WB is just one studio, if the new deal can be used as a template, Netflix could have a solid plan for gaining more films without paying big bucks. And the studios would get greater leverage against Redbox, which is viewed with even greater alarm by much of Hollywood.
would be available, my guess is that the benefits of the deal, when it's fully implemented, will be noticeable to Netflix's subscribers or Netflix wouldn't have signed on. While WB is just one studio, if the new deal can be used as a template, Netflix could have a solid plan for gaining more films without paying big bucks. And the studios would get greater leverage against Redbox, which is viewed with even greater alarm by much of Hollywood.Netflix's focus on the long term is smart strategy, and complements well the company's near-term emphasis on riding the convergence wave by embedding its Watch Instantly software in every conceivable living room device (e.g. PS3, Xbox, Roku, Bravia, Blu-ray players, etc.). It's also a strategy that benefits Hollywood. By creating a situation where studios preserve as much of their DVD sales as possible (allegedly 75% of a film's total DVD sales occur in the first 4 weeks following release), Netflix is helping Hollywood gracefully wind down and milk the DVD business.
Not surprisingly, consumers' first reaction to the deal was sour. Yesterday the Twittersphere was alight with grousing about the 28 day DVD window and how Netflix was "selling out its customers." Some even talked about canceling their Netflix service. I think most of this is idle chatter. Netflix has publicly said that just 30% of its DVD rentals come from recent releases (though it is likely that for Netflix's heaviest DVD renters, recent releases are far more important). In the end, Netflix is making a calculated bet that it can manage the potential subscriber consequences of creating the DVD window in order to benefit its larger goal of migrating its business to online delivery.
If Netflix is right, and it can sign on additional studios to similar deals, then ultimately consumers will win. That's because, as Netflix proves in the value of streaming, it will be able to offer improved terms to studios, resulting in Netflix getting better and better access to films. But this will be a gradual process that unfolds over time. Whereas consumers always "want everything yesterday," the reality is that if Hollywood and Netflix can avoid disruption and instead preserve most of their economics by gracefully transitioning their businesses to digital delivery, consumers stand a better chance of continuing to receive the kind of premium-quality (i.e. expensive to produce) films they value. The demise of the newspaper industry is a cautionary example of what happens when disruption instead prevails and an industry's traditional economics are destroyed.
We are still on the front end of seismic shifts that will alter how Hollywood's films are distributed to consumers. By focusing on the long-term, as evidenced by its WB deal, Netflix is playing an important role in increasing the odds of a successful transition.
What do you think? Post a comment now.
Categories: Aggregators, FIlms, Studios
Topics: Netflix, Starz, Warner Bros.
-
YouTube Movie Rentals: An Intriguing But Dubious Idea
Last week the WSJ broke the news that YouTube is in talks with Lionsgate, Sony, MGM and Warner Bros. about launching streaming movie rentals. On the surface this is an intriguing proposition: the 800 pound gorilla of the online video world tantalizing Hollywood with its massive audience and promotional reach. However, when you dig a little deeper, I believe it's a dubious distraction for YouTube, which is still trying to prove that it can make its ad model work.
I appreciate all the possible reasons YouTube is eyeing movie rentals. To evolve from its UGC roots, the company has been anxious for more premium content to monetize. But with Hulu locking up exclusive access
 to ABC, Fox and NBC shows for at least the next year and a half or longer, full-length broadcast TV shows are largely unavailable. And now TV Everywhere threatens to foreclose access to cable TV programs. All this makes movies even more attractive.
to ABC, Fox and NBC shows for at least the next year and a half or longer, full-length broadcast TV shows are largely unavailable. And now TV Everywhere threatens to foreclose access to cable TV programs. All this makes movies even more attractive. Then there's Google's uber mission to organize the world's information. YouTube executives are savvy enough to know that not all content can be delivered solely on an ad-supported basis - not yet nor possibly ever (for more about the challenges of effectively monetizing broadcast TV shows, let alone movies, see my prior posts on Hulu). To succeed in gaining access to certain content, offering a commerce model is ultimately essential. Since YouTube has already put in place some key commerce-oriented infrastructure pieces like download-to-own and click-to-buy, rolling out a rental option is less of a stretch. Lastly, YouTube can position itself to Hollywood as a more flexible partner and viable alternative to Apple's iTunes.
Regardless, YouTube movie rentals are still a dubious idea for at least 3 reasons: they're a distraction from YouTube's as yet unproven ad model, there are too many competitors and too little opportunity to differentiate itself and the revenue opportunity is relatively small.
Focus on getting the ad model working right - Given its market-leading 40% share of all online video streams, I've long believed that YouTube is the best-positioned company to make the online video ad model work. YouTube has made solid progress adding premium content to the site that it can monetize, but it still has a lot of work ahead to make its ads profitable. As I wrote in June, Google's own senior management cannot yet clearly articulate YouTube's financial performance, causing many in the industry to worry about YouTube's sustainability. Some might assert that YouTube can keep tweaking the ad model while also rolling out rentals but I disagree. With the ongoing ad spending depression, YouTube must stay laser-focused on making its ad model work, and also on communicating its success.
Too many competitors, too little differentiation - It's hard to believe the world really needs another online option for accessing movies, and mainly older ones at that. There's Hulu, iTunes, Netflix, Amazon, Xbox and soon cable, satellite and telcos rolling out movies on TV Everywhere, just to name a few. Maybe YouTube has some secret differentiator up its sleeve, but I doubt it. Rather, it will be just one more comparably-priced option for consumers. And in some ways it will actually be inferior. For example, unlike Netflix and Amazon, YouTube's browser-centric approach means watching movies on YouTube will remain a suboptimal, computer-based experience. Unless YouTube is willing to pay up big-time, there's also no reason to believe it will get Hollywood product any earlier than proven services like Netflix and iTunes.
Revenue upside is small - It's hard to estimate how many movie rentals YouTube could generate, but here's one swag, which shows how limited the revenue opportunity likely is. Let's say YouTube ramped up to .5% of its 120M+ monthly U.S. viewers (assuming it had U.S. rights only to start) renting 1 movie per week (not a trivial assumption considering virtually none of YouTube's users have ever spent a dime on the site and there are plenty of existing online movie alternatives). YouTube's revenue would be 600K rentals/week x $4/movie (assumed price) x 30% (YouTube's likely revenue share) = $720K/week. For the full year it would be $37.4M. With YouTube's 2009 revenue estimates in the $300M range, that's about 12% of revenue. Nothing to sneeze at, but not world-beating either, especially as compared to YouTube's massive advertising opportunity.
Given these considerations, I contend that YouTube would be far better off trying to become the dominant player in online video advertising, replicating Google's success in online advertising. Like all other companies, YouTube has finite resources and corporate attention - it should focus where it can become a true leader. There's enough quality content and brands willing to partner with YouTube on an ad-supported basis to keep the company plenty busy, and on the road to eventual financial success.
What do you think? Post a comment now.
Categories: Advertising, Aggregators, FIlms, Studios
Topics: Hulu, Lionsgate, MGM, Sony, Warner Bros., YouTube
-
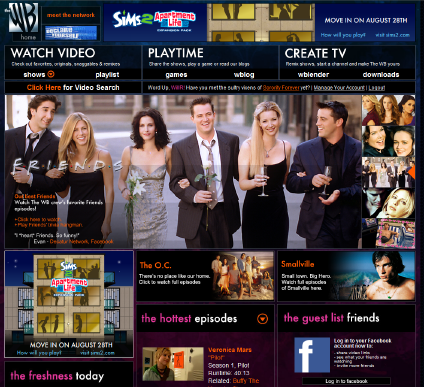
TheWB.com Launches Public Beta - Nice Execution, Fuzzy Strategy
TheWB.com's curtain is finally going up, with the site set to officially open for public beta at 11am Pacific Time today. Along with fellow analysts and press, I was given a sneak peek at the site and so I'm able to offer some initial impressions. At first blush, and after having some of my specific questions answered by a WB spokesman, my reaction is that the site is executed well, but that its strategy seems fuzzy.
As many of you know, TheWB TV channel went off the air in September, 2006. In April, 2008 Warner Bros. Television Group announced that it would launch TheWB.com as an online network. The new site contains a mix of about 20 classic WB and Warner Bros. programs and a slew of forthcoming original web-only programs created by big-name talent. Many of the classic programs have cult-like followings and will no doubt find an ardent online audience.
In addition, TheWB site has some nifty features such as a mashup capability called "WBlender" powered by Adobe Premiere Express, video search powered by Digitalsmiths (including full scene-by-scene indexing of all programs which allows search at the dialogue, character, location, episode, session and series level) and a pretty deep Facebook app allowing users to share content back and forth.
While these features all will eventually raise the bar for other sites, certain aspects are not yet fully implemented. For example, WBlender today only offers users a paltry 30 or so pre-selected clips and just 6 soundtracks to mash. Later this year the selection will widen when the WBlender is married to the video search feature, allowing all scenes from all shows to be mashed together. It's not clear whether users will be able to clip specific segments themselves from favorite episodes or not.
Overall, the site's execution is solid except for a few minor personal quibbles that aren't worth spending time on here. I believe a far bigger issue is the site's fuzzy strategy. A WB spokesman told me that "TheWB.com is not meant to be an archival library of every episode of every show ever made, but rather an entertainment destination that gives our viewers a lot of great entertainment, along with a reason to come back again tomorrow." This is meant to give "our programmers the ability to create themed programming blocks that mesh with our audience's sensibilities."Yet how TheWB.com actually translates this strategy into which programs and episodes are available on the site at any given time is where I think it's going to generate considerable user frustration, not to mention a lack of competitiveness with its own syndication outlets.
Three shows "Friends," "Buffy the Vampire Slayer" and "Angel" illustrate the point. With "Friends" just 7 episodes are currently available on the site, inexplicably from 7 different seasons. If there's a thematic thread, it is neither stated on the site, nor intuitive to me. If I want to watch a specific episode from a particular season, I'm out of luck. Meanwhile TheWB.com shortchanges "Angel" and "Buffy" fans by offering just the first 5 episodes of each, while Hulu, as one example, already offers 22 and 34 episodes each program, respectively.
I think it will quickly become evident that TheWB.com's strategy to "program" its online network is at odds with the on-demand desires of users seeking unfettered access to the full catalog of all programs. Here we see legacy linear TV thinking being grafted onto a high-potential online platform, with the result being a confusing sub-par user experience.
I know I've said this before, but I continue to believe that Hulu is the reigning broadband video user experience king. Having cracked the code on how to deliver fast growth and user loyalty, TheWB.com would be wise to go to school on Hulu and borrow liberally from lessons it has already learned and acted on well.
Still, in fairness, this is still just the beta of TheWB.com. There's a lot to be excited about here, but getting the site's strategy aligned with user expectations is a key building block to eventual success.
What do you think? Post a comment now.
Categories: Broadcasters
Topics: Hulu, TheWB.com, Warner Bros.
-
Non-Linear Presentation + Long-form Premium Video = Big Opportunity
I continue to be surprised that more long-form premium content providers have not pursued initiatives to slice and dice their programs into a non-linear user presentation. This is what "The Daily Show" has done at its site, deconstructing every episode into searchable clips. I think it's a big opportunity to drive more fan engagement, new ad inventory and provide insight about new programming ideas.
While this idea is a natural for archived sports and news programming, I think the model applies to scripted programs as well. Here's an example:
As I've written before, my wife and I were huge fans of "The West Wing" during its seven-year run on NBC.
 While we now own the full DVD collection, periodically I'll talk to someone about the show and reminisce about a specific moment from years back. (In fact, TWW seems cosmically related to the current election cycle, given the show's last narrative around 2 candidates - one younger and one older - battling to succeed Bartlet.) This spurs many of those, "boy, I'd love to see that scene right now!" moments.
While we now own the full DVD collection, periodically I'll talk to someone about the show and reminisce about a specific moment from years back. (In fact, TWW seems cosmically related to the current election cycle, given the show's last narrative around 2 candidates - one younger and one older - battling to succeed Bartlet.) This spurs many of those, "boy, I'd love to see that scene right now!" moments.So wouldn't it be awesome if NBC or Warner Bros. (its producer), or whoever has the rights, were to create a site where all the episodes were archived and fully indexed for searching? This would go far beyond the show's current lame-o web site. I could type in "Bartlet speeches," "Josh meltdowns" or even "C.J.-Danny fights" and instantly see collections of relevant clips.
Before you accuse me of being geeky, stop and consider that we all have our favorite programs and love to relive memorable lines and moments. I'd argue that a really vibrant community could be built at these sites, attracting traditional advertisers eager to continue their audience relationships. Then of course there's the opportunity to embed clips into Facebook and MySpace pages, extending the community further. And think about what this ongoing loyalty would do to drive up the value of broadcast syndication rights.
The big challenge here is indexing the archive. The process must rely heavily on accurate metadata generation, but in a highly scalable, cost-effective manner. That's a mouthful of requirements, so clearly this isn't easy stuff. Various players are trying to crack this nut; two which I've previously written about are Gotuit (which is announcing a partnership with Move Networks today) and EveryZing, but there are others too. Recently I've had briefings with 2 companies that are investing in this area and will have news in the coming months.
Long-from premium providers are facing an onslaught of competition from short-form alternatives while also commonly experiencing a shortage of available inventory. Non-linear presentations of their content addresses both these issues, while delighting loyal fans. I see this as an emerging and sizable opportunity.
Am I missing something here? Post a comment now!
Categories: Advertising, Broadcasters, Technology
Topics: Daily Show, EveryZing, Gotuit, Move Networks, NBC, Warner Bros., West Wing
-
iTunes Film Deals Not a Game-Changer
In the last few days there's been a lot of attention paid to Apple's deals with Disney, Fox, Warner Bros, Paramount, Universal, Sony, Lionsgate, Imagine and First Look Studios giving iTunes day-and-date access to these studios' current films.
As an advocate of the broadband medium, naturally I'm delighted to see studios put broadband distribution
 on a par with DVD release. The deals should rightly be interpreted as another step in the maturation of the broadband medium.
on a par with DVD release. The deals should rightly be interpreted as another step in the maturation of the broadband medium. However, these deals, in and of themselves, do not constitute a game-changing event for paid downloads of feature films. That's because until there's mass connectivity between PCs and TVs and much-improved portability, consumers' willingness to buy is going to be significantly muted. Consumers' inability to easily watch a feature film on their widescreen TV or easily grab-these- movies-to-go (as with DVDs) are a huge drag on the download value proposition, easily swamping its new convenience benefits.
I believe that lack of mass connectivity between PCs and TVs is the last major hurdle to unlocking broadband video's ultimate potential. It is also the firewall that's preserving a lot of incumbents' business models (cable operators, broadcasters, etc.). No question, Apple and iTunes are powerful marketing partners for the studios, and their download revenue will certainly increase from its current modest base. But not even Apple's mighty brand (and certainly not its anemic AppleTV device) is enough to compensate for broadband's current deficiency.
The good news is that there's a frenzy of energy directed at solving the PC-to-TV connectivity issue. Though no approach has yet broken through, I'm still betting it's only a matter of time until one does. When that happens, studios will reap the major benefits. Until then, these deals represent progress, but not game-changing events.
Categories: Aggregators, Downloads, FIlms, Studios
Topics: Apple, Disney, FOX, iTunes, Lionsgate, New Line, Paramount, Sony Pictures, Universal, Warner Bros.
-
Warner Bros. International Television's On-Demand Rollout Seems On Track
A piece in Variety yesterday describing WBITD's aggressive new strategy to mine on-demand opportunities in cable, satellite and broadband underscores how technology is driving new distribution options and revenue opportunities, while at the same time posing new challenges to traditional business models.

The article, entitled "WB Shows Go On-Demand" outlines how WBITD is launching "Warner TV" branded on-demand initiatives in Europe and Asia. That Warner will be offering its library of films and TV programs Warner entirely on-demand is a clear acknowledgement that consumer behavior has shifted beyond the "appointment viewing" paradigm of linear TV.
This shift, along with scarce channel capacity and resistant service providers, have all contributed to the fact that launching new cable networks here in the U.S has all but dried up. The recently unveiled Fox Business Channel is a huge exception; behind the scenes there are scores of people who aspired to launch their own cable networks who have now shifted their focus to on-demand, or increasingly to broadband.
Jeffrey Schlesinger, WBITD's president put his finger on why the on-demand and broadband models make so much sense, "The costs here are much lower than creating a linear channel. You don't have as much on-air promotion that you have to do. You don't have as much scheduling or advertising sales infrastructure. You don't have to worry about commercial insertion."
Building a new programming franchise today is more about nimbleness and experimentation than big structure and deliberative scheduling. WBITD seems to recognize this and also seems to be willing to test lots of different models depending on the opportunities and circumstances it encounters in each local market.
Of course the key balancing act for WBITD here is pursuing these new initiatives without disrupting existing revenue streams and relationships. That's the first thing I hear from all content providers who have a vested interest in existing models, but a hunger for new revenues. WBITD is sensitive to this: its plan is to offer library titles or a secondary window on current programming,
Add WBITD to your "watch list" of companies pioneering how distribution will work in the broadband era.
Categories: International
Topics: Warner Bros.
Posts for 'Warner Bros.'
Previous |