-
Comcast's Digital Transformation Continues
A year ago, in "Comcast: A Company Transformed," I asserted that in the past 10 years Comcast has dramatically evolved from a traditional, plain vanilla cable TV operator to a digital TV, broadband Internet access and voice powerhouse. Comcast's Q3 '09 earnings, released last week, offered more proof that the company continues its transformation, capitalizing on consumers' shift to digital lifestyles.
As the chart below shows, Comcast's Q3 results were once again powered by higher digital TV penetration in its cable TV subscriber base, and additional broadband and voice subscribers.
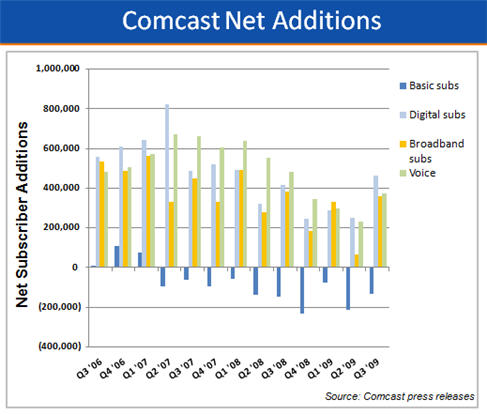
These gains offset the steady erosion in Comcast's total number of cable subs, which at the end of Q3 stood at approximately 23.8 million. Comcast has lost cable subs for 10 straight quarters (totaling 1.25 million) as competition from satellite and new telco video entrants takes its toll. Still, the company has been able to drive revenue per video subscriber steadily higher, to $116.91/month in Q3 '09, reflecting the value of product bundling and success in its business services area. As I said last year, Comcast has effectively moved "up-market," targeting consumers who are willing and able to afford a $100-$200 monthly bill to enjoy the modern digital lifestyle.
Even as the company continues to turn in solid financial performance, Comcast's slowing growth in the core areas of digital TV, broadband and voice are evident in the chart below, which converts the net additions to each service, plus the contraction in basic video subs, into trend lines. With the exception of a few sporadic blips up, over the past 3 years, all 3 areas have shown a steady deceleration in growth. For example, in the most recent 4 quarters (Q4 '08 - Q3 '09), Comcast added 3.4 million digital TV, broadband and voice subs, but this was down 38% vs. the 5.5 million digital TV, broadband and voice subs it added in the year earlier 4 quarters (Q4 '07 - Q3 '08). In the most recent 4 quarters, Comcast also lost 657,000 cable subs, vs. 436,000 in the earlier 4 quarter period, a 51% increase.

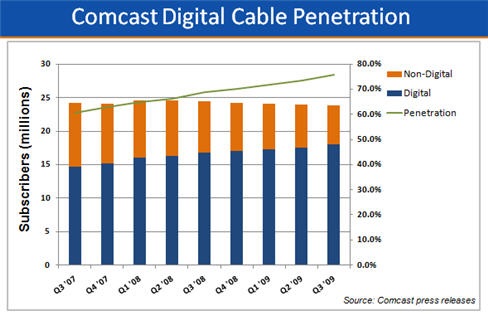
Meanwhile, a big bright spot over the last 3 years for Comcast has been the strong progress it has made in converting its subscriber base to digital TV. As the chart below shows, digital TV penetration now stands at nearly 76% of cable subs, up from about 69% at the end of Q3 '08, and about 61% at the end of Q3 '07. Between bundling, new digital channels, HD, VOD, an improved channel guide and DVR availability, Comcast has strengthened the value proposition for subscribers to convert to a digital set-top box, bringing the company higher revenues and a larger universe to deliver new services to, not to mention a stronger defense against possible cord-cutting.
With the slowdown in net additions occurring, Comcast has clearly begun contemplating where new growth, as well as expense reduction, will come from. Given its negotiations for a controlling stake in NBCU, for now it looks like the company's main strategy is deepening its stake in the content business. Since Comcast hasn't even formally acknowledged the negotiations, much less revealed what the financial and strategic benefits any deal might offer, it's too early to weigh the deal's pros and cons.
Should the deal happen though, it will certainly absorb significant management resources. Given how important an effective rollout of TV Everywhere is to the company, anything that distracts from this task would be a setback. Further, as I recently speculated in "How TV Everywhere Could Turn Cable Operators and Telcos Into Over-the-Top's Biggest Players," Comcast must also keep an eye on competitive drivers that might require it to serve video outside of its traditional geographical footprint (note, Comcast executives say there are no such plans). Doing so would be a herculean management challenge. Last week's research revealing that potentially 54% of Netflix's 11.1 million subscribers now use the service to stream video each month was a reminder that powerful national competitors are steadily building their IP-based delivery businesses through a variety of connected CE devices. These kinds of "over-the-top" services are inevitably competitive to Comcast and other incumbent video providers.
As Comcast has transformed itself into a digital powerhouse it has positioned itself extremely well for continued market leadership. How it chooses to allocate its vast resources, and then how well it executes on its choices will determine how much of its significant potential is realized.
What do you think? Post a comment now.
Categories: Cable TV Operators
Topics: Comcast
-
4 Items Worth Noting for the Nov 2nd Week (Q3 earnings review, Blu-ray streaming, Apple lurks, "Anywhere" coming)
Following are 4 items worth noting for the Nov 2nd week:
1. Media company and service provider earnings underscore improvements in economy - This was earnings week for the bulk of the publicly-traded media companies and video service providers, and the general theme was modest increases in financial performance, due largely to the rebounding economy. The media companies reporting - CBS, News Corp, Time Warner. Discovery, Viacom and the Rainbow division of Cablevision - showed ongoing strength in their cable networks, with broadcast networks improving somewhat from earlier this year. For ad-supported online video sites, plus anyone else that's ad-supported, indications of a healthier ad climate are obviously very important.
Meanwhile the video service providers reporting - Comcast, Cablevision, Time Warner Cable and DirecTV all showed revenue gains, a clear reminder that even in recessionary times, the subscription TV business is quite resilient. Cable operators continued their trend of losing basic subscribers to emerging telco competitors (with evidence that DirecTV might now be as well), though they were able to offset these losses largely through rate increases. Though some people believe "cord-cutting" due to new over-the-top video services is real, this phenomenon hasn't shown up yet in any of the financial results. Nor do I expect it will for some time either, as numerous building blocks still need to fall into place (e.g. better OTT content, mass deployment of convergence devices, ease-of-use, etc.)
2. Blu-ray players could help drive broadband to the TV - Speaking of convergence devices, two articles this week highlighted the role that Blu-ray players are having in bringing broadband video to the living room. The WSJ and Video Business both noted that Blu-ray manufacturers see broadband connectivity as complementary to the disc value proposition, and are moving forward aggressively on integrating this feature. Blu-ray can use all the help it can get. According to statistics I recently pulled from the Digital Entertainment Group, in Q3 '09, DVD players continue to outsell Blu-ray players by an almost 5 to 1 ratio (15 million vs. 3.3 million). Cumulatively there are only 11.2 Blu-ray compatible U.S. homes, vs. 92 million DVD homes.
Still, aggressive price-cutting could change the equation. I recently noticed Best Buy promoting one of its private-label Insignia Blu-ray players, with Netflix Watch Instantly integrated, for just $99. That's a big price drop from even a year ago. Not surprisingly, Netflix's Chief Content Officer Ted Sarandros said "streaming apps are the killer apps for Blu-ray players." Of course, Netflix execs would likely say that streaming apps are also the killer apps for game devices, Internet-connected TVs and every other device it is integrating its Watch Instantly software into. I've been generally pessimistic about Blu-ray's prospects, but price cuts and streaming could finally move the sales needle in a bigger way.
3. Apple lurks, but how long will it stay quiet in video? - The week got off to a bang with a report that Apple is floating a $30/mo subscription idea by TV networks. While I think the price point is far too low for Apple to be able to offer anything close to the comprehensive content lineup current video service providers have, it was another reminder that Apple lurks as a major potential video disruptor. How long will it stay quiet is the key question.
While in my local Apple store yesterday (yes I'm preparing to finally ditch my PC and go Mac), I saw the new 27 inch iMac for the first time. It was a pretty stark reminder that Apple is just a hair's breadth away from making TVs itself. Have you seen this beast yet? It's Hummer-esque as a workstation for all but the creative set, but, stripped of some of its computing power to cost-reduce it, it would be a gorgeous smaller-size TV. Throw in iTunes, a remote, decent content, Apple's vaunted ease-of-use and of course its coolness cachet and the company could fast re-order the subscription TV industry, not to mention the TV OEM industry. The word on the street is that Apple's next big product launch is a "Kindle-killer" tablet/e-reader, so it's unlikely Steve Jobs would steal any of that product's thunder by near-simultaneously introducing a TV. If a TV's coming (and I'm betting it is), it's likely to be 2H '10 at the earliest.
4. Get ready for the "Anywhere" revolution - Yesterday I had the pleasure of listening to Emily Green, president and CEO of tech research firm Yankee Group, deliver a keynote in which she previewed themes and data from her forthcoming book, "Anywhere: How Global Connectivity is Revolutionizing the Way We Do Business." Emily is an old friend, and 15 years ago when she was a Forrester analyst and I was VP of Biz Dev at Continental Cablevision (then the 3rd largest cable operator), she was one of the few people I spoke to who got how important high-speed Internet access was, and how strategic it would become for the cable industry. 40 million U.S. cable broadband homes later (and 70 million overall) amply validates both points.
Emily's new book explores how the world will change when both wired and wireless connectivity are as pervasive as electricity is today. No question the Internet and cell phones have already dramatically changed the world, but Emily makes a very strong case that we ain't seen nothing yet. I couldn't help but think that TV Everywhere is arriving just in time for video service providers whose customers increasingly expect their video anywhere, anytime and on any device. "Anywhere" will be a must-read for anyone trying to make sense of how revolutionary pervasive connectivity is.
Enjoy your weekends!
Categories: Aggregators, Books, Broadcasters, Cable Networks, Cable TV Operators, Devices
Topics: Best Buy, Bl, Cablevision, CBS, Comcast, DirecTV, Netflix, News Corp, Rainbow, Time Warner Cable, Time Warner. Discovery, Viacom
-
More on Comcast's "Excalibur" Project
Last week's piece in Cable Digital News, "Comcast Forges Excalibur for IPTV" generated a number of emails to my inbox. Despite an oddly misleading title using the primarily telco-oriented term "IPTV," the substance of the article caught lots of people's attention. It explained that Comcast, America's largest cable operator, has set up a new division, "Comcast Converged Products" (CCP) and that Comcast "...would put all IP services, including video, into a common provisioning and management system."
VideoNuze readers who contacted me interpreted Excalibur as being the basis for a potential out-of-market, over-the-top (OTT) plan by Comcast. These folks were referencing a post I wrote in September, "How TV Everywhere Could Turn Cable Operators and Telcos Into Over-the-Top's Biggest Players," in which I
 asserted that the next phase of TV Everywhere - "TVE 2.0" as I called it - could well find incumbent service providers invading each others' geographical turf with an IP/broadband-only service. While this type of move would represent a major break from traditional industry norms, I suggested that it may be irresistible for growth reasons and inevitable for competitive reasons.
asserted that the next phase of TV Everywhere - "TVE 2.0" as I called it - could well find incumbent service providers invading each others' geographical turf with an IP/broadband-only service. While this type of move would represent a major break from traditional industry norms, I suggested that it may be irresistible for growth reasons and inevitable for competitive reasons. I talked to a Comcast spokesperson yesterday to learn more about Excalibur and to ferret out any indications that it could indeed be the basis for a Comcast OTT play. According to the spokesperson, Excalibur's mission is to "use IP to deliver cross-platform interactive services." The spokesperson noted that it would be a mistake to think of these as solely video-oriented. Comcast already uses IP technology extensively in its network and Excalibur is meant to find ways to "improve the consumer experience across platforms." One example cited was a feature like checking your voicemail from the Comcast.net portal.
When pressed for specifics on CCP deployments, new products or timelines, the spokesperson said there are no specific plans at this time. The spokesperson did confirm that Sam Schwartz (formerly the head of Comcast Interactive Capital) has been appointed president of CCP, but said the "core Excalibur team" is smaller than the 100 people that CDN reported. I referenced my recent OTT post and the spokesperson had no comment on my speculation Comcast would go out of footprint.
Admittedly that doesn't add a lot of new detail about Excalibur. From my perspective, I'm dubious that the company would reassign Schwartz to anything that wasn't highly strategic. While using IP to enhance the customer experience is worthwhile, Comcast has major competitive battles brewing that are critical to focus on. Yesterday's news that Apple is floating a $30 subscription offering is a reminder that the Steve Jobs lion will pounce at some point. Similarly, Netflix, which just reported superb Q3 results, broad usage of its streaming feature, an integration with PS3 (and a rumored one with the Wii) is looking more and more like a national cable competitor, leveraging myriad CE devices. Others to be mindful of include YouTube, Hulu and Amazon. These are of course in addition to fierce satellite and telco rivals.
Given all of this, Comcast's smartest move would in fact be to reassign its savviest tech-oriented executive, given him/her a large team and task him/her with ensuring the company's competitiveness in the face of new entrants. In particular, gaming how to compete with Apple should be near the top of the list. Apple has shown an uncanny ability to reinvent markets with its easy-to-use, ultracool devices. While gaining access to cable programming is far from a slam-dunk, Apple's ability to innovate is unmatched, potentially making it a totally new kind of cable competitor.
Last week, coming out of the CTAM Summit, I expressed concern that the cable industry was not fully recognizing online video as a bona fide new medium, which it needs to embrace and capitalize on. For now Excalibur's real agenda is murky; time will tell how aggressive it is.
What do you think? Post a comment now.
Categories: Cable TV Operators
Topics: Apple, Comcast, Excalibur, Netflix
-
VideoNuze Report Podcast #38 - October 30, 2009
Daisy Whitney and I are pleased to present the 38th edition of the VideoNuze Report podcast, for October 30th, 2009.
This week Daisy first shares her observations from the recent iMedia Summit, where Julie Roehm, the former CMO of Wal-Mart shared insights about the factors driving brands to shift their ad spending to digital media. Daisy also highlights reasons Roehm gave for why the shift isn't necessarily happening as quickly as it should.
Then I dig into 2 of my posts from earlier this week, "Seeking Cable's Formula for Success in Broadband Video," part 1 and part 2, which were based on panels I moderated at the CTAM Summit (an annual conference of cable industry marketers) in Denver. On the one hand my sense is that the cable industry is trying to get its arms around consumers' shift to broadband video usage, but on the other, I think it is focusing too much on its existing TV platform and not enough on embracing broadband video as a new medium. Listen in to learn more.
Click here to listen to the podcast (14 minutes, 38 seconds)
Click here for previous podcasts
The VideoNuze Report is available in iTunes...subscribe today!
Categories: Advertising, Cable Networks, Cable TV Operators, Podcasts
Topics: CTAM Summit, iMedia, Podcast
-
Seeking Cable's Formula for Success in Broadband Video - Part 2
Yesterday I moderated the closing general session panel of the CTAM Summit, which included Paul Bascobert (Chief Marketing Officer, Dow Jones & Company), Matt Bond (EVP, Content Acquisition, Comcast), Andy Heller (Vice Chairman, Turner Broadcasting System, Inc.), Jason Kilar (CEO, Hulu), David Preschlack (EVP, Disney and ESPN Networks Affiliate U.S. Sales and Marketing) and Peter Stern (EVP & Chief Strategy Officer, Time Warner Cable). The session offered a prime opportunity to better understand the cable industry's strategy for success in the broadband video era.
In yesterday's post I asserted that the cable industry's main challenge is balancing its desire to preserve its highly successful subscription/ad-supported business model, while meeting consumers' increasing demands for flexibility. At a very high level the two goals are not incompatible; in particular the concept of TV Everywhere could well be a killer app in serving both. Rather, for me, yesterday's session reinforced my concern that the industry is still too focused on the TV platform, and not sufficiently acknowledging consumers' behavioral shifts to online consumption. These are not my sentiments alone; walking the halls of the Colorado Convention Center, various industry participants expressed their concern, in one way or another, that the industry is still not fully in synch with changing times.
On the panel Peter made great points citing data that a very high proportion of online viewing is in the home, and that the amount of time spent viewing online video is still tiny compared to traditional TV viewing. The latter point is one I often make as well, though I believe an equally important point is the remarkable rate at which online video's viewership has grown over the last several years.
On the surface, I agree with Peter's insistence that 80% of the industry's focus should be on improving the TV experience, as that's where consumers primarily watch today, and where the industry has its greatest strength. In fact in yesterday's post, I lamented the industry's underinvestment in VOD as resulting in gaps that competitors are exploiting. These gaps, whether in discoverability, content availability, ease-of-use or monetization desperately need to be closed.
Digging deeper though, a core issue I have with Peter's approach (which is common in the industry btw) is that it doesn't seem to acknowledge that online video is its own medium and should be prioritized as such. Online video is not something that should be thought of as being incorporated into the TV experience. Rather, I believe millions of users see online video as its own medium, with breakthrough benefits such as anywhere access, searchability, sharing, interactivity, personalization and so on.
These benefits help explain why online video's adoption rate has been so rapid. Consider that YouTube delivers almost three times as many streams (10 billion) in a single month as Comcast delivers VOD sessions (3.6 billion) in an entire year. Or that with more than 4.5 million of its subscribers streaming at least 1 program or movie in the 3rd quarter, Netflix already likely has more streaming users than any cable operator (except Comcast) has VOD users.
My conclusion is that the cable industry would be best served by understanding these differences and what they say about consumers' shifting desires and behaviors. Then the industry should aggressively embrace these differences to capitalize on this new medium in ways far beyond just providing the underlying broadband access, as it does today. TV Everywhere, as it is currently conceived, is just a starting point. To be clear, I'm not suggesting the industry should not also be optimizing the TV experience. But rather than devoting 80% of its energies to this, it should be equally balancing its investments so that it is concurrently trying to optimize the online (and mobile) video experience as well.
A point that Paul made seemed right on the money to me: when the WSJ thinks of different platforms, "context is key." Trying to serve their users' needs, given what they want at a particular moment and their physical situation drives the WSJ's product strategy. But note, just as the WSJ's online edition is the poster child for success in paid subscriptions (which the WSJ has now extended to paid mobile applications), it is also celebrating this week its new (and first-time) status as America's most widely-circulated newspaper. The takeaway for the cable industry: you can simultaneously invest and succeed in both new and traditional media, they are not mutually exclusive.
Prior to yesterday's panel, in an acceptance speech for receiving CTAM's 'Grand TAM' annual award, Bob Miron, the chairman of cable operator Advance/Newhouse, correctly acknowledged the rise of freely-available broadband video as a significant new challenge to the cable industry's traditional business model. Based on his 50 years in the business, his prescription for success was to remember the "customer is king." In myriad ways - some overt and some subtle - the cable industry's customers are telling it that broadband video is a new medium they highly value. To succeed in the broadband video era the cable industry must fully acknowledge, embrace and capitalize on this.
What do you think? Post a comment now.
Categories: Cable Networks, Cable TV Operators
Topics: Comcast, Netflix, Time Warner Cable, WSJ, YouTube
-
Seeking Cable's Formula for Success in Broadband Video
Yesterday VideoNuze hosted a breakfast at the annual CTAM Summit where I moderated a discussion titled, "How Cable Succeeds in the Broadband Video Era." Panelists included Ian Blaine, CEO, thePlatform, Rebecca Glashow, SVP, Digital Media Distribution, Discovery Communications, Bruce Leichtman, President & Principal Analyst, Leichtman Research Group and Chuck Seiber, VP, Marketing, Roku. Following are some of my observations from the discussion.
Against a backdrop of rapidly rising broadband video consumption, cable operators and networks are trying to strike a balance between preserving their traditional, and highly profitable business model, while still keeping pace with consumers' desire for more flexible and on-demand viewing options. A nagging question is whether full-length cable programs should be made available online for free, solely supported by advertising (the Hulu model), or if the cable industry's dual subscription/advertising model should be extended online (the TV Everywhere concept).
On the panel, Rebecca likely reflected many cable networks' current thoughts, saying, "We are in an ecosystem with our distribution partners that works....It (the free model) is going to kill all of our business; it's certainly going to kill our ability to produce high quality programming." These sentiments echo concerns I've raised about the viability of ad-supported long-form video. Even as Rebecca was critical of the free model, she noted that Discovery is taking a measured approach to TV Everywhere.
Chief among Rebecca's concerns regarding TV Everywhere is the need to accurately measure online viewership, crucial for ensuring that if viewership were to shift to online, that Discovery's ratings would not be hurt in the process. As Rebecca further pointed out, measurement issues have limited the appeal of cable operators' Video-on-Demand offerings.
Bruce went a step further to suggest that cable operators should learn from VOD's shortcomings when crafting their TV Everywhere plans. Bruce said that VOD rollouts "were led by engineers on a node-by-node basis" when they should have been led by marketers, and that "some operators introduced VOD only with trepidation." He believes that the problems that VOD had in the early days, "are still impacting consumers' perception of the on-demand platform."
Another VOD lesson I would add is that operators must also make TV Everywhere monetizable for their content partners. VOD has suffered significantly from operators not investing in dynamic ad-insertion capabilities, making VOD a marginal opportunity for ad-supported cable networks. A day earlier on another CTAM Summit panel, Steve Burke, Comcast's COO highlighted the fact that Comcast is now generating 300 million VOD sessions/month. But he also noted that Comcast has only just launched a dynamic ad-insertion capability, and in just one of its operations. It continues to bewilder me why Comcast wasn't investing in dynamic ad insertion when it was doing 10 million VOD sessions/month, years ago. How much further along might the VOD platform be, had robust advertising been possible?
As a result, it's fair to wonder whether operators will invest in TV Everywhere sufficiently to make it attractive as a new distribution platform, or alternatively will leave critical components unresolved as they've done with VOD. The answer could well determine whether TV Everywhere is a killer app (as I believe it has the potential to be) or if just becomes a half-baked nice-to-have for consumers and content providers alike. For Comcast at least, thePlatform and other technologies are important building blocks to success. As Ian pointed out, the key is being able to "quickly ascertain" the networks and programs that subscribers should have access to, a challenge that gets more complicated as content available through TV Everywhere-type offerings grows over time.
If cable doesn't get TV Everywhere quite right another implication is that certain gaps in consumers' experiences will persist - gaps that companies like Roku are seeking to fill with video they're bringing into the home solely over broadband connections. Today the $99 Roku device offers users the ability stream Netflix, Amazon and MLB video. It's tempting to see Roku as a potential cable competitor down the road, yet Chuck was quick to clarify that Roku sees itself as augmenting the cable experience, not supplanting it. In fact, he added that Roku is talking to cable operators about how it can partner with Roku to extend their viewer experiences.
Coming away from the session I'm reminded that while broadband is causing significant shifts in consumer behavior and expectations, fully capitalizing on them will take time as business requirements and technologies evolve.
What do you think? Post a comment now.
(Note: Steve Donohue contributed to this post.)
Categories: Cable Networks, Cable TV Operators, Devices
Topics: Comcast, Discovery, Hulu, Roku, TV Everywhere
-
In the Digital Era, Disney is Walking to the Beat of its Own Drummer
Yesterday's WSJ article about Disney's new DRM initiative, dubbed "Keychest" was another sign that in the digital era, Disney keeps walking to the beat of its own drummer. Combine Keychest with Disney CEO Bob
 Iger's repeated skepticism about TV Everywhere and the need for Disney to receive incremental payments for online distribution and it's not hard to conclude that Disney envisions retaining much more control over how its content is delivered and priced going forward. It's also not hard to conclude that Disney's largest individual shareholder Steve Jobs's influence is being felt in the company's decision-making.
Iger's repeated skepticism about TV Everywhere and the need for Disney to receive incremental payments for online distribution and it's not hard to conclude that Disney envisions retaining much more control over how its content is delivered and priced going forward. It's also not hard to conclude that Disney's largest individual shareholder Steve Jobs's influence is being felt in the company's decision-making. The Keychest DRM initiative in particular shows a real streak of separatism by Disney given the critical mass that DECE (the Digital Entertainment Content Ecosystem) has gained. DECE counts among its members multiple studios (Sony, Warner Bros., NBCU, Lionsgate, Fox), technology providers (Microsoft, Intel, Dolby, Philips, HP, Cisco, etc.) and delivery outlets (Comcast, Best Buy). Granted, DECE hasn't shown a whole lot of progress yet, but that's pretty much to be expected when you have this many big players at the table. Still, even getting all these companies to join forces is a hopeful sign of inter-industry collaboration.
And as the WSJ article underscores, the need to introduce some form of standardized DRM for movies in particular is growing more urgent. DVD sales, the industry's cash cow for years, are off by 25% at certain studios, yet movie downloads don't yet come close to filling the gap. Downloading is not only still a new experience for many, but it introduces key limitations (lack of portability, non-ubiquitous playback and confusing usage rights) that are significant inhibitors for future growth. Let's face it, not a lot of people are going to invest in building downloaded movie libraries when it's difficult or impossible to do something basic like play a movie on 2 different TV sets in their home. Downloading's issues need to be solved quickly if it is going to take off.
Meanwhile, Disney's posture on TV Everywhere has created real questions about what the company's goals are in online content distribution. VideoNuze readers know that I've been bullish on TV Everywhere because it's a win for the 3 main constituencies - incumbent video providers (cable operators and telcos), cable TV networks and consumers. By forcefully advocating a plan to offer TV Everywhere as a value-add to existing subscribers, with no incremental fees, video providers laid the logical foundation for cable networks not to expect incremental distribution fees ("We're not charging anything extra, so you shouldn't expect to either.").
From my point of view, rationale cable network executives should be excited with the prospect of TV Everywhere, as it provides them an on-ramp to online distribution (which they've been shut out of to date, given the absence of a sound online business model and fearing a backlash from paying distributors if they offered their content for free streaming) while preserving their incumbent dual revenue-stream approach and expanding their advertising potential.
Nonetheless, Disney seems unsatisfied. CEO Iger continues to float the idea of incremental payments for online access, even suggesting it will launch its own subscription services. That could mean consumers face the prospect of paying twice for the same content, which is unrealistic even for ESPN's vaunted sports coverage. Disney has seen success with ESPN 360, its premium online service, but it offers distinct content (supplementary pro-sports coverage and niche sports coverage) from its flagship channels. And it should be noted that broadband ISPs pay for 360, not consumers directly.
I tend to believe we're seeing Steve Jobs's influence behind the scenes with both Keychest and Disney's posture on TV Everywhere. That's pure speculation on my part I'll admit. But "Think Different" is more than a slogan for Jobs and Apple. The company's ability to succeed by pursuing a non-conformist, innovative path (e.g. iPods, iTunes, iPhones, Macs, etc.) in the face of market norms is beyond dispute. Emboldened by Apple's success and understanding the strength of Disney's franchises as an insider suggests Jobs would encourage Disney not to be constrained by nascent industry-wide initiatives. At a minimum Apple provides Disney with a pretty compelling case study of how to succeed by zigging when others are zagging.
No question, Disney has incredible brands, and is probably in the best position among major content providers to influence how things will unfold in the digital era. And its investment in Hulu shows it is willing (albeit belatedly), to align with joint industry initiatives. Still, its Keychest project and resistance to TV Everywhere raise the possibility that in pursuing its own path it could not only miss out on or delay benefiting from the efforts of others in the industry, but could also be over-reaching with the result being consumer confusion and discontent. Disney holds strong cards, but it needs to be careful how it plays them.
What do you think? Post a comment now.
Categories: Cable Networks, Cable TV Operators, DRM, Strategy
Topics: Apple, DECE, Disney, TV Everywhere
-
4 Items Worth Noting for the Oct 12th Week (Bell's TMN, BlackArrow-Comcast, Net neutrality opposition, hockey's wunderkind)
Following are 4 items worth noting from the week of Oct 12th week:
1. Bell Canada is first to offer "TV Everywhere" type service - While U.S. operators have been busy with their TV Everywhere trials, Bell Canada, which has 1.8 million linear video subscribers, has jumped into the lead, announcing this week the launch of "TMN Online." The service, available through the Bell TV Online portal, allows subscribers to The Movie Network premium channel to gain online access to about 130 hours of content.
I spoke briefly with Peter Wilcox, Bell TV's director of product strategy, who explained that ExtendMedia's OpenCASE is being used for content management, in conjunction with Microsoft's Silverlight and PlayReady DRM. Users login with their Bell user name and password and are authenticated against the billing database as valid TMN subs. Only 1 simultaneous log-in is allowed, and Bell is also geo-blocking, so for example, there's no accessing TMN Online from outside Canada. The launch is part of what Bell calls "TV Anywhere" - a broader context for eventual distribution to its mobile subscribers, and further content being added. The deployment is the first milestone in what promises to be a busy 2010 on the TV Everywhere news front.
2. BlackArrow launches ad insertion for Comcast video-on-demand - BlackArrow, the multiplatform ad technology provider, announced its first customer deployment this week, with Comcast's Jacksonville, FL operation. I talked to company CEO Dean Denhart and President Nick Troiano, who gave me an update on how the company dynamically inserts ads in long-form premium content across TV, broadband and mobile. As I wrote 2 years ago, BlackArrow has bitten off the hardest challenge first: working with cable operators to get its system into their headends/data centers. Dean and Nick believe that if the company can succeed in this goal then it will have created formidable differentiation that can be leveraged for the other two platforms.
The key risk is that cable operators are famous for grinding down promising technology startups with their endless testing and brutal negotiating tactics (I say this from personal experience with a promising technology startup earlier this decade, Narad Networks). Robust VOD ad insertion is plenty strategic for the industry, but years since cable operators launched free VOD, the fact that it still isn't widely deployed is a telling sign, particularly while ad insertion technology in broadband is now fully mature. Comcast's role as an investor in BlackArrow should help its odds of success. I'm rooting for BlackArrow; their holistic approach to multiplatform advertising is right on. Whether they have the juice to fully succeed remains the big question.
3. Political battle over net neutrality is heating up - This week brought fresh complaints from Republican Senators who are coalescing to fend off new FCC chairman Julius Genachowski's plan to introduce net neutrality regulations for both broadband ISPs and wireless carriers. B&C reported that 18 Republican senators wrote to Mr. Genachowski concerned that the FCC's process is "outcome driven" and unsupported by data.
I rarely find my views aligning with Republicans, but net neutrality is an exception. As I wrote last month in "Why the FCC's Net Neutrality Plans Should Go Nowhere," Mr. Genachowski's plan is deeply flawed and completely illogical. The core premise of the new regulations - that they're needed to ensure continued broadband investment and innovation - misses the reality that the market is already functioning well. As one example, investment in broadband-related technology is continuing apace. By my calculations, over $180 million was raised in Q3 '09 by video-related companies whose very viability depends on open broadband and wireless networks. The sector's potential is amplified by the fact that venture capital fundraising itself is at its lowest level since 2003, with new capital raised by the industry in 2009 down 58% from 2008. Despite the VC industry's troubles, it continues to bet big on video. Why do we need new Internet regulations to sustain innovation?
4. Have you seen the 9 year-old hockey player's trick goal? On a lighter note, you have to love the serendipity of online video sharing. For example, though I don't consider myself a hockey fan, when a friend sent me this video clip of a 9 year-old hockey player pulling off this incredible trick shot, I was reminded just how much fun online video is and promptly passed the clip on to my circle (it's also now all over YouTube). See for yourself, it's just amazing. And nothing fake about it either.
Enjoy the weekend!
Categories: Advertising, Broadband ISPs, Cable TV Operators, International, Regulation, Sports, Technology, Video Sharing
Topics: Bell Canada, BlackArrow, Comcast, ExtendMedia, FCC, Microsoft, Net Neutrality
-
Why the FCC's Net Neutrality Plan Should Go Nowhere
My hopes that the FCC, under its new chairman Julius Genachowski, would undergo a much-needed course correction with respect to net neutrality, were dashed yesterday. VideoNuze readers will remember that my 3rd prediction for 2009 was that net neutrality, under President Obama's pragmatic leadership, would likely remain dormant.
Mr. Genachowski's policy address, "Preserving a Free and Open Internet: A Platform for Innovation, Opportunity, and Prosperity" made clear that regrettably, he will be a forceful advocate for unprecedented Internet regulation. Mr. Genachowski has proposed codifying the FCC's four existing principles into Commission rules, and adding two new, additional principles. But read beyond the high-minded rhetoric about "preserving the openness and freedom of the Internet" and need for "fair rules of the road," and what you'll instead find is a jumble of illogical premises, inflammatory and threatening admonitions and pre-emptive, non fact-based conclusions.
I know my opposition to net neutrality regulations will bother many of you. So before I'm accused of being a cranky regulatory libertarian with nothing but distaste for government intervention, let me assure you I am anything but. In fact, I'm a strong believer that when market failures occur, the government should aggressively intervene. If you've had the experience of hearing my rants on the gross incompetence of our nation's financial regulators in contributing to our recent near catastrophic market meltdown, you will have no doubt about the sincerity of my beliefs.
That said, I'm also a fierce proponent of allowing market forces and competition to work in determining winners and losers, and that when this occurs, government influence, which is often distortive, should remain in check. If ever there was an example of a well-functioning market, it is the Internet, which since bursting into the public's consciousness 15 years ago has operated virtually regulation-free. This open and free Internet has spawned myriad innovative services that consumers enjoy today. And while the Internet has created billions of dollars of wealth for astute investors and entrepreneurs, it has also ruthlessly gobbled up many other billions of dollars ventured on ideas of illusory potential. In this respect, it could be argued that among the Internet's many marvels, it is likely the most efficient capital allocation mechanism we human beings have ever created.
By far the most sizable capital investment in the Internet landscape has been in the so-called "last mile" of broadband access. The 70 million American homes, thousands of educational institutions and countless businesses of every size that receive fast, affordable broadband Internet access is largely attributable to the hundreds of billions of dollars of investments that cable operators and telephone companies have made in upgrading their networks over the past 15 years - upgrades that continue to this day and are planned well into the future. Investments, it should be noted, that were made without a penny of government subsidies, tax breaks or bailout funds. These companies were driven by robust supply and demand forces, quantifiable business cases, vigorous competition, technological innovation and supportive lenders and shareholders. It is not an exaggeration to say that the broadband networks these companies built are the very foundation of our 21st century economy.
You might think that in a major policy speech premised on the importance of the Internet to our daily lives and commerce, the new FCC chairman might dwell for a few minutes on these contributions, if for no other reason than to demonstrate his understanding of what's truly at the core of today's Internet experience. But you would be wrong; instead the new FCC chairman used just over 50 words in a passing reference. You might also think that these companies' track records of being market driven might also influence the new chairman with regard to whether decisive regulatory action, particularly in the thorny area of network management, is now necessary. Here again you'd be wrong.
In fact, with yesterday's remarks, Mr. Genachowski has picked up where his predecessor, Kevin Martin left off: pre-emptively tagging the nation's cable and telco broadband ISPs as untrustworthy conspirators plotting to wall-off the Internet to all but their own favored services. Though professing to "ensure that the (FCC's) rulemaking process will be fair, transparent, fact-based and data-driven," by first proposing the rules be adopted, before evidence of their very need has been established, the chairman has only ensured that the rule-making process will be anything but what he says he wants it to be. Deciding that net neutrality regulations are essential, after being officially on the job for less than 90 days and absent supporting data to point to, does not inspire confidence about the likely fairness of the Genachowski-led Commission.
Mr. Genachowski further upped the ante by suggesting that if such regulatory action is not taken, perilous consequences to the Internet's openness await. His choice of words - that we could see "the Internet's doors shut to entrepreneurs," "the spirit of innovation stifled," "a full and free flow of information compromised" and that "if we wait too long to preserve a free and open Internet, it will be too late" - represent the kind of inflammatory, unjustified hyperbole that only serves to distract from the facts and data yet to be reported. Such comments virtually guarantee that the debate will be transformed quickly into an escalating war of opinionated arm-waving (as have prior FCC open sessions). Did we not just witness our crucially important health care debate devolve into just this sort of spectacle? And did candidate Obama not remind us, rightfully, that "words matter?"
But worst of all is that despite the new chairman's lengthy service in the private sector, his remarks suggest a fundamental misunderstanding of how product innovation and the broadband market actually work. His view is that the government must pre-emptively step up to the plate to ensure that the Internet remains free and open, or innovation and investment will be curtailed, is just plain wrong.
The reality is that aside from random acts, no pattern of broadband ISP misconduct has ever been proven. Major industry players know this and their actions suggest they are utterly untroubled by the current state of laissez-faire Internet regulation. Consider recent deals predicated on the belief that the Internet will remain open and bandwidth plentiful: NBC, Fox and Providence Equity Partners (and later Disney) invested $100M in Hulu at a $1B pre-launch valuation; Cisco acquired Pure Digital, maker of the Flip video camera for $600M in a bid to further fuel user-generated video; and Marc Andreessen's investment firm is participating in a buyout of Skype valuing the firm at $2.75B. Then there's Apple, which has invested untold tens of millions of dollars upgrading the iPhone and iPod Nano to have video capabilities. And let's not forget Netflix, Intel, Sony, Microsoft and many others who are moving aggressively forward with bandwidth-heavy broadband video products and services. Looking ahead, as I suggested last week looms "TV Everywhere 2.0," portending massive over-the-top video competition.
But it's not just the giants that are investing. By my analysis, early and mid-stage broadband video-related companies raised almost $220M over the last 3 quarters, in the midst of the worst venture capital slump in memory. And as I'll report next week, Q3 '09 has been the highest fund-raising quarter of the last four. Deals are being done because history has repeatedly shown investors that in order to remain competitive and meet surging consumer demand, network operators are certain to continue to invest in upgrading their networks. When I helped start Continental Cablevision's high-speed Internet business 15 years ago, 1.5 mbps service was breakthrough; now 100 mbps or more is the state-of-art for wireline broadband.
Contrary to Mr. Genachowski's fear that the market will be immobilized absent FCC intervention, industry participants are moving briskly forward, confident that market and competitive forces will compel network operators to continue creating abundant, open bandwidth to support their new services.
This phenomenon appears to be true in the mobile space as well. AT&T's recent decision to accelerate its 3G wireless buildout is due mainly to high iPhone data traffic. And it should be noted that Apple's rejection of the Google Voice app (which continues a pattern of unfettered App Store selectivity by the company) raises the important question of who's the real gatekeeper when it comes to open wireless services - the network operator or the handset maker? How does Apple's newfound power figure into the FCC's regulatory paradigm?
Let's be clear: it is absolutely essential that the Internet remain open. But imposing new net neutrality and Internet regulation is not the way to ensure this. Instead, net neutrality remains a solution in search of a problem. With brushfires burning in every corner of the American economy, Washington's policy-makers would be wise to focus on real problems, not imaginary ones. The Internet has worked magnificently to date and there's every reason to believe it will continue to do so. The last thing we need are the unintended consequences that government intervention often brings. For now, FCC vigilance is required, but new regulations are not.
What do you think? Post a comment now.
Categories: Broadband ISPs, Cable TV Operators, Regulation, Telcos
Topics: FCC
-
VideoNuze Report Podcast #32 - September 18, 2009
Daisy Whitney and I are pleased to present the 32nd edition of the VideoNuze Report podcast, for September 18, 2009.
This week Daisy and I first discuss my post from earlier this week, "How TV Everywhere Could Turn Cable Operators and Telcos Into Over-the-Top's Biggest Players," which has become one of the most popular posts I've written in the past 2 years.
In the post I asserted that if certain cable operators and telcos were to unbundle their TV Everywhere ("TVE") offering from their video subscription requirement, they could offer a "TVE 2.0" service outside their current geographic areas. In effect they'd be going over the top of their industry counterparts, invading new service territories.
It would be a bold move, but one that I suggested might be irresistible. Between slowing growth in their existing markets and new competitors rolling out OTT services nationwide, big cable operators and telcos could face the prospect of being turned into marginalized, geographically-bound players. I've heard from lots of folks this week about the TVE 2.0 concept - some who think it's inevitable; some who think it's inconceivable. I explain more in the post and on the podcast. You decide.
Meanwhile, Daisy provides an update from this week's iMedia Brand Summit, where marketers and agencies spent a lot of time discussing the effectiveness of traditional TV advertising vs. online video advertising. Daisy shares some very interesting statistics she gathered at the conference concerning how some industries are overspending in TV and getting underperformance. As Daisy explains, the key to advertising is no longer reach, but targeting. Listen in to learn more.
Click here to listen to the podcast (15 minutes, 9 seconds)Click here for previous podcasts
The VideoNuze Report is available in iTunes...subscribe today!
Categories: Advertising, Cable TV Operators, Podcasts
-
How TV Everywhere Could Turn Cable Operators and Telcos Into Over-the-Top's Biggest Players
Though TV Everywhere ("TVE") is still in a nascent stage, with trials either underway or not even yet started, there has been no shortage of hype around it. I've been among those who have argued that if these trials work as intended and the rollouts ensue, TVE would be a big win for video service providers (cable, satellite, telco), content providers and consumers. But recently I've started to think there's another TVE angle that has not really been explored - the possibility that "TVE 2.0" could enable certain cable operators and telcos themselves to become the biggest players in "over-the-top" (OTT) video.
(For those not familiar with the term OTT, it refers to the idea of video being delivered to homes over a broadband network that isn't owned by the video provider itself. So for example, when you watch Hulu in your home over a Comcast broadband connection, Hulu is going "over-the-top" of Comcast. Hulu doesn't own the underlying network, it just rides on top of the one that's there, in effect competing with Comcast's own video service.)
To date TVE has been positioned by incumbent video service providers as an online adjunct solely available to their traditional, paying multichannel subscribers. While Comcast has been most emphatic on this point, no other operator that has announced TVE trials has deviated from this approach either.
But what if, at some point down the road, TVE was "unbundled," meaning that you could subscribe just to TVE, and not the traditional video service? Cable operators and telcos have little incentive to do this within their current service or "franchise" areas, but the lure to offer TVE 2.0 to households outside their franchises could prove irresistible. If pursued, this could actually turn cable and telcos into the biggest over-the-top players themselves, potentially dwarfing those typically thought of as key OTT competitors (e.g. CE companies like Sony or computing companies like Apple, or aggregators like Netflix or Hulu). In a TVE 2.0 world, the hunted could become the hunters.
The franchise concept is key to understanding how the cable and telco video distribution business work. In short, a cable or telco needs to win an agreement with the "franchising authority" - typically a municipal government - to offer video service in the municipality. Agreements are required because the video distributor needs legal access to rights-of-way to operate (to hang its wires on poles, dig up streets when necessary, etc.). Franchising may seem anachronistic in the digital age, but it remains the essential determinant of where cable companies or telcos operate (note that because satellite companies don't require rights-of-way, they operate nationally, outside the franchising domain).
Now put yourselves in the shoes of Comcast, for example. You've worked hard to wring every possible dollar out of subscribers who live in your franchise areas, by successfully introducing triple-play video/voice/Internet bundles, digital tiers, sports tiers, movie channels, HD, additional outlets, DVRs, etc. With all of these services, the average revenue per home serviced today is a multiple of what it was just 15 or 20 years ago.
But growth is slowing, and new competition from OTT providers looms. So where does the biggest new growth opportunity exist? Answer: outside traditional franchise areas. To get a sense of how big this opportunity is, even Comcast, the largest U.S. cable operator, serves only about 25% of the country, meaning almost three-quarters of American homes are currently out of its reach. To grow their addressable universes, Comcast and others traditionally bought other cable operators. In fact, fearful of the power any one cable company could gain, the FCC imposed a 30% ownership cap. Coincidentally that cap was just overturned by a U.S. Court of Appeals a few weeks ago.
In the traditional video distribution business, buying other operators was the only way to build an operator's footprint. But with TVE 2.0, a company like Comcast could use broadband so that, for the first time, it could operate everywhere. They key is being willing to unbundle TVE from core cable service so that a consumer can subscribe solely to TVE service.
Doing so would in effect pit Comcast, for example, against other cable operators, a major breach of cultural etiquette in the clubby cable industry. But faced with the choice of acquiring other operators for around $5,000 per sub, or just introducing a capital-efficient and high-quality linear/on-demand OTT service over broadband, powered by Move Networks (as one option) it wouldn't even be a close call. In fact, Comcast could cherry pick the incumbent's video customers, in turn driving that company's valuation down and thus opening up the option for it to eventually swoop in and acquire the incumbent operator for far less. Or it could decide not acquire, and instead just focus on rolling up OTT subs.
Will cable and telco go over the top? Who knows. They will surely have what it takes - TVE expertise, requisite technology, content relationships, private video delivery networks, customer care facilities and deep pockets. All that's really needed is the motivation to proceed. For now, operators are rightfully focused on getting TVE working right for their own subs. But I suspect the business cases for TVE 2.0 are already being run.
(Note - we'll explore this subject and others at both VideoSchmooze in NYC on Oct. 13th and at VideoNuze's CTAM Summit breakfast on Oct. 26th.)
What do you think? Post a comment now.
Categories: Cable TV Operators, Telcos
Topics: Comcast, FCC, TV Everywhere
-
4 Items Worth Noting from the Week of August 24th
Following are 4 news items worth noting from the week of August 24th:
1. Time Warner Cable, Verizon launch TV Everywhere trials - Little surprise that Time Warner Cable announced its own TV Everywhere trial yesterday, given that former sister company Time Warner has been one of its biggest proponents. More interesting was Verizon launching a TV Everywhere initiative, which I regard as a pretty strong indicator that most or all service providers will eventually get on board. (The Hollywood Reporter has a story that DirecTV is in talks too for online distribution of TBS and TNT to start).
I have to give credit to Time Warner CEO Jeff Bewkes, TV Everwhere's key champion, who's clearly generated a groundswell of support. While some critics see TV Everywhere as being at odds with the "open Internet" ethos, I continue to think of it as a big win for consumers eager to get online access to their favorite cable programs. Assuming authentication is proven in during the trials I expect a speedy rollout.
2. Conde Nast distributes through boxee - I was intrigued by news that Conde Nast Digital will begin distributing video from its Wired.com and Style.com sites through boxee. boxee and others who connect broadband to TVs are valuable for magazines and other content providers who have long been shut out of the cable/satellite/telco distribution ecosystem, thereby unable to reach viewers' TVs. Years ago special interest magazines missed big opportunities to get into cable programming, allowing upstart cable networks to grow into far larger businesses (consider ESPN vs. Sports Illustrated, Food Network vs. Gourmet or CNBC vs. Forbes). Broadband gives magazines, belatedly, an opportunity to get back into the game.
3. Amazon announces 5 finalists in UGC ad contest - Have you seen the 5 finalists' ads in Amazon's "Your Amazon Ad" contest, announced this week? They're quite clever, with some amazing special effects. The contest is another great example of how brands are tapping users' talents, posing new competition to ad agencies. I haven't written about this in a while, but I continue to be impressed with how different brands are pursuing this path. Doritos has been the most visible and successful with its user-generated Super Bowl ads.
4. Microprojectors open up mobile video sharing opportunities - Maybe I've been living under a rock because I just read about "microprojectors" for the first time this week (I have a decent excuse since as I non-iPhone owner I wouldn't have a use for one, yet). As the name suggests, these are pocket-size projectors that allow you to output the video from your iPhone to project onto a large surface like a wall or ceiling. According to this NY Times review the quality is quite respectable, and is no doubt only going to improve. The mind boggles at what this could imply for sharing mobile video. Imagine bringing a kit - consisting of an iPhone, portable speakers and microprojector - to your friend's house, then plugging in and projecting either a live stream or an on-demand program for all to see.
Enjoy your weekend!
Categories: Cable Networks, Cable TV Operators, Commerce, Devices, Magazines, Telcos, UGC
Topics: Amazon, Comcast, Conde Nast, Time Warner Cable, Verizon
-
4 Items Worth Noting from the Week of August 17th
Following are 4 news items worth noting from the week of August 17th:
CBS's Smith says authentication is a 5 year rollout - I had a number of people forward me the link to PaidContent's in-depth coverage of CBS Interactive CEO Quincy Smith's comments at the B&C/Multichannel News panel in which he asserted that TV Everywhere/authentication won't gain critical mass until 2014.
I was asked what I thought of that timeline, and my response is that I think Smith is probably in the right ballpark. However, these rollouts will happen on a company by company basis so timing will vary widely. Assuming Comcast's authentication trial works as planned, I think it's likely to expect that Comcast will have its "On Demand Online" version of TV Everywhere rolled out to its full sub base within 12 months or so. Time Warner Cable is likely to be the 2nd most aggressive in pursuing TV Everywhere. For other cable operators, telcos and satellite operators, it will almost certainly be a multi-year exercise.
NFL makes its own broadband moves - While MLB has been getting a lot of press for its recent broadband and mobile initiatives, I was intrigued by 2 NFL-related announcements this week that show the league deepening its interest in broadband distribution. First, as USA Today reported, DirecTV will offer broadband users standalone access to its popular "Sunday Ticket" NFL package. The caveat is that you have to live in an area where satellite coverage is unattainable. The offer, which is being positioned as a trial, runs $349 for the season. With convergence devices like Roku hooking up with MLB.TV, it has to be just a matter of time before the a la carte version of Sunday Ticket comes to TVs via broadband as well.
Following that, yesterday the NFL and NBC announced that for the 2nd season in a row, the full 17 game Sunday night schedule will be streamed live on NBCSports.com and NFL.com. Both will use an HD-quality video player and Microsoft's Silverlight. They will also use Microsoft's Smooth Streaming adaptive bit rate (ABR) technology. All of this should combine to deliver a very high-quality streaming experience. But with all these games available for free online, I have to wonder, are NBC and the NFL leaving money on the table here? It sure seems like there must have been some kind of premium they could have charged, but maybe I'm missing something.
Metacafe grows to 12 million unique viewers in July - More evidence that independent video aggregators are hanging in there, as Metacafe announced uniques were up 67% year-over-year and 10% over June (according to comScore). I've been a Metacafe fan for a while, and their recent redesign around premium "entertainment hubs" has made the site cleaner and far easier to use. Metacafe's news follows last week's announcement by Babelgum that it grew to almost 1.7 million uniques in July since its April launch. Combined, these results show that while the big whales like YouTube and Hulu continue to capture a lot of the headlines, the minnows are still making swimming ahead.
Kodak introduces contest to (re)name its new Zi8 video camera - It's not every day (or any day for that matter) that I get to write how a story in a struggling metro newspaper had the mojo to influence a sexy new consumer electronic product being brought to market by an industrial-era goliath, so I couldn't resist seizing this opportunity.
It turns out that a review Boston Globe columnist Hiawatha Bray wrote, praising Kodak's new Zi8 pocket video camera, but panning its dreadful name, prompted Kodak Chief Marketing Officer Jeffrey Hayzlett to launch an online contest for consumers to submit ideas for a new name for the device, which it intends to be a Flip killer. Good for Hayzlett for his willingness to change course at the last minute, and also try to build some grass roots pre-launch enthusiasm for the product. And good for the Globe for showing it's still relevant. Of course, a new name will not guarantee Kodak success, but it's certainly a good start.
Enjoy your weekend!
Categories: Aggregators, Broadcasters, Cable TV Operators, Devices, Indie Video, Sports
Topics: Babelgum, Boston Globe, CBS, Comcast, Kodak, MetaCafe, MLB, NFL, Roku, Time Warner Cable
-
Interview with boxee Investors Bijan Sabet and Neil Sequeira
When boxee announced it raised a $6M second round last week it caught my attention for two reasons. First, it was further evidence that broadband video-related companies are continuing to raise money right through the current economic meltdown (industry companies raised at least $64M in Q2 '09, $75M in Q1 '09 and $78M in Q4 '08).
Second, and more noteworthy to me was how much industry experience and insight now backs boxee. The new lead investor in the round was Boston venture firm General Catalyst Partners (joining prior investors Spark Capital and Union Square Ventures), whose portfolio includes broadband video companies like Brightcove, DECA, EveryZing, Maven Networks (acquired by Yahoo), ScanScout, ViTrue and Visible Measures.
Spark also has many investments in the industry, including 5Min, Adap.tv, EQAL, KickApps, Next New Networks, thePlatform (acquired by Comcast) and Veoh. And Union Square is one of the most active firms in the online media/advertising industry with stakes in MeetUp, OddCast, Twitter (with Spark), Tacoda (acquired by AOL) and others.
Beyond the firms themselves are the individuals helping steer boxee. Joining its board from GC is Neil
 Sequeira, a veteran of the cable industry, who was most recently Managing Director, Technology of AOL Time Warner Ventures. Already on the board is Spark's Bijan Sabet who knows the cable/satellite ecosystem equally well, having done stints at Moxi, WebTV and Apple and Union Square's Fred Wilson, who is deeply immersed in online media and writes a hugely popular blog.
Sequeira, a veteran of the cable industry, who was most recently Managing Director, Technology of AOL Time Warner Ventures. Already on the board is Spark's Bijan Sabet who knows the cable/satellite ecosystem equally well, having done stints at Moxi, WebTV and Apple and Union Square's Fred Wilson, who is deeply immersed in online media and writes a hugely popular blog. I corralled Neil and Bijan (two old friends) for a phone interview late last week to explain boxee's future and where it fits into the current video ecosystem. Following is an edited transcript.
VideoNuze: What attracted you to invest in boxee?
Neil Sequeira: Three things. The boxee team, the market opportunity and our ability to be a great partner. We think boxee has the potential to be the next generation "Firefox for media," a widely- used consumer platform. That's incredibly exciting to us.
Bijan Sabet: We've been involved with boxee for a while now, and we're convinced the time is right for something like this. boxee has the right ingredients: it is open source and includes social media capabilities, an app store and a huge community of users/developers.
VideoNuze: boxee has gained a loyal following, but it doesn't have a business model yet. What do you see as boxee's business model and it what time frame must it develop it in order to succeed?
BS: boxee's still a very young company, but we have a number of ideas around business models. But the key is patience. The company has a very low burn rate, with around 16 people or so , most of whom are in Israel. The focus for now is building the product and the user base. And the company's been very successful doing that. Last year boxee had 10,000 users, now it has 600,000.
NS: It also has a very excited developer community. But I agree - patience is needed here. Too often companies can get themselves focused to early on a specific business model, which then constrains them. With the new funding, box has room to see how things evolve.
VideoNuze: Hulu recently told boxee to remove its content. What do you think boxee needs to do to win Hulu (and others) onto its platform?
NS: At a high level boxee we believe boxee is an incredible friend to content providers, and we want to work with everyone. We're big believers that consumers want access to everything and that's where the market will go over time.
 BS: All of us are Hulu fans and of course would love to have Hulu on boxee. But each content provider has its own business model, and has to decide what works best for them. boxee will continue to be a content provider-friendly platform, where different business models can be used and different technologies integrated. We think that's powerful.
BS: All of us are Hulu fans and of course would love to have Hulu on boxee. But each content provider has its own business model, and has to decide what works best for them. boxee will continue to be a content provider-friendly platform, where different business models can be used and different technologies integrated. We think that's powerful. VideoNuze: How should established video service providers (i.e. cable/satellite/telco) regard boxee - as friend, foe, or something else?
NS: We want boxee to be regarded as friend and we think boxee can add a lot of value to the ecosystem. Consider for example, the case of TiVo. Early on it looked like a foe. But now see how Comcast is integrating TiVo into its set-top boxes and driving incremental revenue. boxee brings great search, apps and context to the broadband viewing experience. All that will drive usage of broadband Internet connections, which in turn helps "fill the pipe" making cable and telco Internet access services that much more valuable to users - and to their providers.
BS: Agreed. We believe that in an IP world, these things aren't either/or, mutually exclusive. Again look at Comcast, which has great assets like Fancast, and is now working on entitlements with TV Everywhere. boxee can help drive more value from them. This is especially true for certain user segments, like new college grads, for whom the Internet is now far more important than is traditional TV. The point is traditional service providers need to figure out how to delight a variety of user segments. We believe boxee can help.
VideoNuze: You guys and your firms have deep relationships in the cable/satellite/telco industries. How are those folks reacting to boxee?
NS: People in the ecosystem are taking a "wait-and-see" approach. There's a certain amount of fascination, and though we don't see any impending deals, Avner (Ronen, boxee's founder/CEO) has multiple conversations ongoing with the industry.
VideoNuze: Who are boxee's primary competitors?
BS: What Apple and Microsoft are doing is most competitive, though their approaches include both hardware and software. We think of boxee like Android (Google's mobile OS), sort of the "inside-out" version of Apple TV. And we believe convergence device/hardware providers want alternatives.
VideoNuze: How about Roku?
NS: We believe Roku should be partners with boxee. Hardware companies have core competencies and typically those don't include open source media platforms. So boxee can help devices like Roku be even better. We'll have a number of device deals to announce soon.
VideoNuze: A lot has been written about "over-the-top" services. Are they starting to succeed, and if so, what must happen for them to gain further success?
NS: Well, yes, when we look at what Netflix and others are doing already, we do believe over-the-top services are starting to succeed. And we think this isn't necessarily a bad thing for cable operators for example. That's because the video business has had margin compression due to rising programming costs, whereas broadband Internet service has been incredibly profitable for them.
Consider that that cable operators didn't offer DVR or voice services just 10-11 years ago, but now they are a significant driver of ARPU (average revenue per unit). There's a lot more that cable operators can derive from broadband services than they currently are, considering the IP connection is now - for many - the most important connection they have. Content providers know this and are looking for more, not fewer, ways to distribute their content.
BS: Agreed, look at an example like CNBC, whose ratings are down something like 30% year-over-year. What's causing this? Is there demo changing? Is the web providing alternatives? Some of both? The point is content providers need to figure out how to control their destiny. That doesn't mean they have to give their stuff away for free. But it does mean they need to figure out how to distribute as effectively as possible. We want to help them do that. You can't go backwards here. Broadband is too interesting and too important to too many people.
VideoNuze: Thanks guys.
Categories: Cable TV Operators, Deals & Financings, Devices, Satellite, Telcos
Topics: Boxee, General Catalyst, Spark Capital, Union Square Ventures
-
4 Items Worth Noting from the Week of August 10th
Following are 4 news items worth noting from the week of August 10th:
Discovery Channel signs onto Comcast On Demand Online trial - Comcast added yet another cable programmer this week to the roster of those participating in its TV Everywhere trial. Discovery will make available episodes of "Man vs. Wild," "Swords," "Stormchasers" and "Verminators" though with some delayed windows that take a little edge off their appeal. Comcast has made a ton of progress corralling networks for its trial, but 4 of the big 5 cable network owners - Disney, Fox, NBCU and Viacom - remain holdouts. No coincidence that the first 3 are Hulu's owners.
Swarmcast powers MLB.TV on Roku, introduces "Autobahn Live for CE" - Following on Roku's announcement this week that it is offering MLB.TV, Swarmcast announced it was powering the service through a new offering called "Autobahn Live for CE." Swarmcast's COO Chad Tippin explained to me that integrating with CE devices that drive broadband/TV convergence is a key company goal. Chad is confident that Swarmcast's high-quality, scalable HTTP streaming service will work on these various CE devices, and that as the number of them deployed swells, a new "long tail of live sports" will flourish. Live sports and events (e.g. concerts) could be a significant contributor to device adoption. For example, picture getting a coupon for $50 off the purchase of a Roku when you buy a pay-per-view of a streaming blockbuster concert.
Babelgum grows to nearly 1.7 million unique visitors in July, 2009 - I heard from Michael Rosen, EVP and Chief Revenue Officer at Babelgum this week, with news that the site has grown to nearly 1.7 million unique visitors in July (comScore), following its U.S. launch in April. I profiled Babelgum back in April and was cautiously optimistic about its approach to curate high-quality, independently-produced video into 5 channels (music, film, comedy, Our Earth and Metropolis). The site is fully ad-supported. Babelgum's growth comes on top of a slew of made-for-broadband video initiatives I detailed recently. The NY Times also had a great story this week on how independent filmmakers are taking distribution into their own hands. Despite the recession, this corner of the broadband market seems to be hanging in there.
Zune HD coming Sept 15th - Microsoft at last announced this week that the Zune HD digital media player will be in retail on Sept 15th, with pre-orders now being accepted. Zune HD introduces a touch-screen interface, 720p video playback, HD radio and other goodies. It is sure to raise the visibility of high-quality portable video another notch. But I find myself wondering: as the iPhone and other smartphones incorporate video playback (and recording) into one device, how large is the market for standalone high-end media players like Zune? Related, the iPhone's risk of cannibalizing the iPod has become a hot topic recently. Things to ponder: will users want to carry 2 devices? Or might they appreciate the ability to drain their battery watching video without risking the loss of their cell phone? Lots of different things in play.
Categories: Aggregators, Cable Networks, Cable TV Operators, Devices, Indie Video, Sports, Technology
Topics: Apple, Babelgum, Comcast, Discovery, iPhone, iPod, Microsoft, MLB.TV, Roku, Swarmcast, Zune
-
Netflix's ABC Deal Shows Streaming Progress and Importance of Broadcast TV Networks
Yesterday's announcement by Netflix that it will be adding to its Watch Instantly library past seasons ABC's "Lost," "Desperate Housewives," "Grey's Anatomy" and "Legend of the Seeker" is another step forward for Netflix in strengthening its online competitiveness.
At a broader level though, I think it's also further evidence that the near-term success of Watch Instantly and other "over-the-top" broadband video services is going to be tied largely to deals with broadcast TV networks, rather than film studios, cable TV networks or independently-produced video sources.
Key fault lines are beginning to develop in how premium programming will be distributed in the broadband era. Content providers who have traditionally been paid by consumers or distributors in one way or another are redoubling their determination to preserve these models. Examples abound: the TV Everywhere initiative Comcast/Time Warner are espousing that now has 20+ other networks involved; Epix, the new premium movie service backed by Viacom, Lionsgate and MGM; new distribution deals by the premium online service ESPN360.com, bringing its reach to 41 million homes; MLB's MLB.TV and At Bat subscription offerings; and Disney's planned subscription services. As I wrote last week in "Subscription Overload is On the Horizon," I expect these trends will only accelerate (though whether they'll succeed is another question).
On the other hand, broadcast TV networks, who have traditionally relied on advertising, continue mainly to do so in the broadband world, whether through aggregators like Hulu, or through their own web sites. However, ABC's deal with Netflix, coming on top of its prior deals with CBS and NBC, shows that broadcast networks are both motivated and flexible to mine new opportunites with those willing to pay.
That's a good thing, because as Netflix tries to build out its Watch Instantly library beyond the current 12,000 titles, it is bumping up against two powerful forces. First, in the film business, well-defined "windows"
 significantly curtail distribution of new films to outlets trying to elbow their way in. And second, in the cable business, well-entrenched business relationships exist that disincent cable networks from offering programs outside the traditional linear channel affiliate model to new players like Netflix. These disincentives are poised to strengthen with the advent of TV Everywhere.
significantly curtail distribution of new films to outlets trying to elbow their way in. And second, in the cable business, well-entrenched business relationships exist that disincent cable networks from offering programs outside the traditional linear channel affiliate model to new players like Netflix. These disincentives are poised to strengthen with the advent of TV Everywhere.In this context, broadcast networks represent Netflix's best opportunity to grow and differentiate Watch Instantly. Last November in "Netflix Should be Aggressively Pursuing Broadcast Networks for Watch Instantly Service," I outlined all the reasons why. The ABC deal announced yesterday gives Netflix a library of past seasons' episodes, which is great. But it doesn't address where Netflix could create the most value for itself: as commercial-free subscription option for next-day (or even "next-hour") viewing of all prime-time broadcast programs. That is the end-state Netflix should be striving for.
I'm not suggesting for a moment that this will be easy to accomplish. But if it could, Netflix would really enhance the competitiveness of Watch Instantly and its underlying subscription services. It would obviate the need for Netflix subscribers to record broadcast programs, making their lives simpler and freeing up room on their DVRs. It would be jab at both traditional VOD services and new "network DVR" service from Cablevision. It would also be a strong competitor to sites like Hulu, where comparable broadcast programs are available, but only with commercial interruptions. And Hulu still has limited options for viewing on TVs, whereas Netflix's Watch Instantly options for viewing on TVs includes Roku, Xbox, Blu-ray players, etc. Last but not least, it would also be a powerful marketing hook for Netflix to use to bulk up its underlying subscription base that it intends to transition to online-only in the future.
Beyond next-day or next-hour availability, Netflix could also offer things like higher-quality full HD delivery or download options for offline consumption. Broadcasters, who continue to be pinched on the ad side, should be plenty open to all of the above, assuming Netflix is willing to pay.
I continue to believe Netflix is one of the strongest positions to create a compelling over-the-top service offering. But with numerous barriers in its way to gain online distribution rights to films and cable programs, broadcast networks remain its key source of premium content. So keep an eye for more deals like the one announced with ABC yesterday, hopefully including fast availability of current, in-season episodes.
What do you think? Post a comment now.
Categories: Aggregators, Broadcasters, Cable Networks, Cable TV Operators, FIlms
Topics: ABC, Cablevision, CBS, Comcast, EPIX, ESPN360, MLB, NBC, Netflix, Time Warner
-
Hubris Cursed AOL But Broadband Crushed It
I highly recommend reading Saul Hansell's piece in last Friday's NY Times, recapping the ridiculously optimistic quotes senior executives at AOL and Time Warner have made over the years (and be sure to peruse readers' consistently vitriolic comments). For anyone who's watched AOL's rise and fall, the quotes are a stroll down memory lane. But while the picture that emerges is that hubris cursed AOL and contributed mightily to its downfall, in reality it was broadband, and AOL's colossal mismanagement in transitioning to it, that crushed the company.
The chart below shows that AOL's dial-up subscribers topped out in Q3 '02 at 26.7 million, and have been in a free-fall ever since, sitting at just 6.3 million at the end of Q1 '09, a drop-off of 20.4 million or 76%. Where did those 20.4 million dial-up subs go, along with tens of millions of other dial-up and new Internet users? To broadband Internet access, supplied by cable companies and telcos. These companies have grown their U.S. broadband subs from 15.2 million in Q3 '02 to 69.2 million in Q1 '09, an astonishing increase of 54 million subscribers in just 7 years.
Cable and telco broadband providers have feasted on the carcasses of AOL and other dial-up services like MSN and Earthlink. But, here's what's both incredible and really sad: had AOL management been less arrogant and more strategic in its approach to broadband, it's quite possible that things could have turned out quite differently.
Back in the mid-to-late '90s, I had a front-row seat at AOL's initial reactions to broadband. In that period I was VP Business Development at Continental Cablevision, then the 3rd largest cable operator in the U.S. with over 5 million video subscribers. We were one of the pioneers in testing and rolling out "high-speed" Internet service. While we thought our speedy and always-on broadband connections were a better mousetrap vs. dial-up, we were very concerned about our lack of online content, video-centric branding and ability to effectively market this exciting new service.
In the pre-@Home days, I pushed to explore how we could partner with AOL to help us get our service off to a faster start. A deal with AOL would have had significant advantages to them as well. AOL at the time had a huge capex burden building out more modem banks to keep up with its swelling subscriber ranks. Even still, there was already plenty of AOL subscriber frustration with the slowness of the AOL network, and often you couldn't even get connected on your first or second tries. At least in our geographic footprint we could unburden them of their network build-out, offer better-quality connections and allow them to focus on content and brand-building. As the 3rd largest cable operator, we also offered them a valuable proof-point that they could use to build industry-wide relationships.
After much preparation and scheduling, we met with one of AOL's most senior executives. After articulating our broadband vision and opportunity to work together, he arrogantly dismissed us as if we were precocious children. To him the opportunity we were describing was far too small, and to illustrate his point he asserted that AOL would have 10 million subscribers before we had our first 100,000 (a prediction that was probably correct!).
Needless to say, no meaningful deal with us - or any other cable operator - every materialized. AOL went on to flounder around with various incarnations of AOL Broadband, none of which ever got any traction. AOL continued to grow its subscribers for a number of years and capitalized on its reach by extracting hundreds of millions of dollars from VC-backed startups eager for access to its massive captive audience (some of those deals would later come under scrutiny, as would AOL's accounting treatment for its subscriber business). AOL then bought Time Warner, and the rest as we know is history.
But what if things had gone differently? What if that AOL executive and others had seen the handwriting on the wall - that broadband would eventually render dial-up obsolete - and decided that AOL needed to figure out how to transition to it, instead of dismissing it? Had that happened, it could have forged partnerships throughout the cable and telco industries that would have let it focus on content and services in an open, broadband environment. In fact, I think it's quite possible that AOL could have pre-empted @Home and the RoadRunner venture that Continental eventually joined from getting traction (why start over when AOL, the 800 pound gorilla is in your corner?).
Instead AOL fell victim to its own arrogance and limited strategic vision. Broadband went on to become the single most powerful enabler of the Internet as we know it today (e.g. billions of spontaneous Google searches, Tweets, Amazon purchases, and more recently video views). AOL is now a crippled mish-mash of mostly second-rate properties, on its umpteenth management team, led by new CEO Tim Armstrong.
In retrospect, those fateful decisions AOL made about broadband 10-15 years ago set the stage for the company's eventual demise.
What do you think? Post a comment now.
Categories: Broadband ISPs, Cable TV Operators, Portals, Telcos
-
4 News Items Worth Noting from the Week of July 20th
Following are 4 news items worth noting from the week of July 20th:
Apple reports blowout iPhone sales in Q2, continuing to drive market - It was another record quarter, as Apple reported selling 5.2 million iPhones, bringing to 21.4 the total sold to date. This despite acknowledging temporary shortages during the quarter. The iPhone continues to revolutionize the mobile market, and from my standpoint is the key catalyst for both recording and consumption of mobile video. This market is poised for significant growth as new smartphones hit the market along with fixed monthly data plans. Apps like MLB.com At Bat 2009, which offers live streams of games, are certain to be hits and emulated widely.
8 minute video of Amazon's Jeff Bezos discussing lessons learned and Zappos acquisition - You couldn't miss news this week of Amazon acquiring Zappos for around $900M, its largest deal ever. Interestingly, Amazon posted a video on YouTube of Bezos discussing the deal, but not until he walked through several maxims of Amazon's success (obsess over customers, think long term, etc.). The video is extremely informal, with Bezos flipping hand-scrawled notes on an easel and improvising funny anecdotes. It has a slightly random feel (until he gets to the Zappos part, you start to wonder, what's the point of all this?), but I give Amazon and Bezos lots of credit for using video in a totally new way to communicate with stakeholders. I'd love to see more CEOs do the same.
Is Disney CEO Bob Iger serious about creating a subscription site for its online video? This week at Fortune's Brainstorm conference, Iger floated the idea that Disney will offer movies, TV shows and games for paying subscribers. The timing seems more than coincidental as Comcast gears up for its On Demand Online trial. Is Iger serious about this, or is it a head fake from Disney so it can try to negotiate incremental payments from Comcast and others seeking to distribute Disney content online? It's hard to tell, but I'd be curious to see what Disney has in mind for its possible subscription service. Consumers hate the idea of paying twice for anything (even paying once is not so popular), so if Disney is somehow going to create another window where they charge for access to content that's still on, or was recently on cable, that would be an awkward model.
"Mad Men" coming to Comcast's On Demand Online trial - Speaking of the Comcast trial, I was thrilled to hear from David Evans, SVP of Broadband at Rainbow Media (owners of AMC, the network behind Mad Men) at yesterday's CTAM Teleseminar that the show will be included in Comcast's trial and presumably in rollout. David is very bullish on online distribution and the larger TV Everywhere concept, though cautioned that there are many rights-related issues still hanging out there. I'm a huge Mad Men fan (whose new season starts on Aug 16th) and the idea that I don't have to worry about recording each episode or managing space on my DVR, and that I can watch remotely when I'm on the road, all underscore TV Everywhere's value.
Categories: Cable Networks, Cable TV Operators
Topics: Amazon, AMC, Apple, Comcast, Disney, iPhone, MLB, Rainbow Media, YouTube, Zappos
-
Cable's Emmy Nominations Illustrate Cord-Cutting's Challenge
Last week when the primetime Emmy award nominees were announced, cable programs turned in another strong performance, garnering 272 of the 487 nominations. The Emmys and other awards illustrate one of the key challenges for would-be cord-cutters: outside of per-program download options (e.g. iTunes) that will persist, in the coming TV Everywhere world, virtually none of cable's award-winning programming will be accessible online unless you subscribe to a cable/satellite/telco service provider. This is a critical fact in understanding how the broadband video world is going to unfold.
One of the reasons TV Everywhere is so compelling is that it offers cable networks an on-ramp to online distribution while preserving their existing - and increasingly valuable - dual revenue (monthly affiliate fees and advertising) business model. As more content executives are concluding that advertising alone will not be sufficient for profitable long-form program distribution online, the payments cable networks receive from cable/satellite/telco providers is more valuable than ever. TV Everywhere's online access will inevitably lead to heavier viewership and enhanced loyalty.
The Emmy nominations show the expanding breadth of cable's quality. As the below chart depicts, this year 26 different cable networks' programs were nominated, with HBO, the perennial leader picking up 99 nominations (it should be noted that last week HBO signed on to Comcast's On Demand Online technical trial, further entrenching HBO in the cable world, therefore dimming the notion that HBO will ever be available outside the traditional premium subscription model).
Cable's strength is even better understood by looking at the major Emmy award categories. For example, in the outstanding drama series category, cable got 5 of 7 nominations (AMC-2, FX, HBO, Showtime). In the outstanding children's program category, cable got all 3 nominations (Disney Channel-2 and Nickelodeon). In the outstanding reality program series category, cable got 5 of 6 nominations (A&E, Bravo, Discovery-2, NGC). Even in outstanding comedy series, cable got 3 of 7 nominations (HBO-2, Showtime).
When TV Everywhere gets fully rolled out, cable networks will have little-to-no incentive to make much of their programming available to non-paying video subscribers. That means that the Hulus of the world will have to content themselves with a catalog of broadcast programs, older movies and made-for-broadband series. As broadcast's Emmy nominations show, that still means there's plenty of popular content to drive online audience. But until Hulu figures out a subscription model, it (and its content suppliers) will be economically disadvantaged to cable both on-air and online. This is no small issue given each TV program episode now costs $2-3 million to produce.
Meanwhile, consumers will make their own video choices. If they choose to cut the cord they won't have subscription-based online access to programs like Entourage, Weeds, MythBusters, Hannah Montana, Mad Men or Dexter, not to mention top-shelf sports from ESPN, TNT and others. For some people eager to cut the cord, that will be just fine. But I'm betting that for the majority of viewers that would be unacceptable and they'll continue to choose to subscribe. TV Everywhere can use cable programs' popularity to blunt cord-cutting before it ever takes off and cement cable's appeal in the broadband era.
What do you think? Post a comment now.
Categories: Broadcasters, Cable Networks, Cable TV Operators
Topics: Comcast, HBO, TV Everywhere
-
4 News Items Worth Noting from the Week of July 13th
Following are 4 news items worth noting from the week of July 13th:TV Everywhere survey should have cable industry clicking their heels - I wasn't at all surprised to read results of a new Solutions Research Group survey fielded to 500 Comcast and Time Warner Cable subscribers giving the concept of TV Everywhere positive reviews. As Multichannel News reported, in the overall survey 28% of respondents said the idea was "excellent" and 45% said it was "good." Digging in further though, among those 18-49 the "excellent" score surged to 80%, while 87% of Hulu and Fancast users approved of the idea. Unprompted, respondents cited benefits like convenience, remote viewing, getting better value from their cable subscriptions, watching on PCs in rooms without TVs and catching up on missed programs. My take: consumers "get" what TV Everywhere is all about and already have positive initial reactions, meaning there's very significant upside for the cable industry.Paid video forecast to surpass free - A Strategy Analytics forecast that got attention this week says that the global paid online video market will be worth $3.8B in 2009, exceeding the global free online video segment which will total $3.5B. I haven't seen the details of the forecast, but I'm very curious what's being included in each of these numbers as both seem way too high to me. The firm forecasts the two segments to grow at comparable rates (37% and 39%), suggesting that their size will remain relatively even. I suspect we're going to be seeing a lot of other research suggesting the paid market is going to be far larger than the ad-supported market as sentiment seems to be shifting toward subscriptions and paid downloads.
Consumer generated video contests remain popular - VideoNuze readers know I've been intrigued for a while now about contests that brands are regularly running which incent consumers to create and submit their own videos. Just this week I read about two more brands jumping on the bandwagon: Levi's and Daffy's retail stores. NewTeeVee had a good write-up on the subject, citing new research from Forrester which reviewed 102 different contests and found the average prize valued at $4,505. I see no end in sight for these campaigns as the YouTube generation realizes it's more lucrative to pour their time into these contests than training their cats to skateboard. Brands too are recognizing the wealth of amateur (read cheap!) talent out there and are moving to harness it.
MySpace has lots of work ahead to become a meaningful entertainment portal - The WSJ ran a piece on Monday based on an interview with Rupert Murdoch in which he was quoted as saying MySpace will be refocused "as an entertainment portal." That may be the winning ticket for MySpace, but I'm not totally convinced. MySpace has been in a downward spiral lately, with a 5% decline in audience over the past year, a 30% headcount reduction and an executive suite housecleaning. While always strong in music, according to comScore, its 48 million video viewers in April '09 were less than half YouTube's 108 million, while its 387 million video views were about 5% of YouTube's 6.8 billion. Clearly MySpace has a very long way to go to give YouTube serious competition. It will be interesting to see if the new management team Murdoch has installed at MySpace can pull off this transition.
Categories: Aggregators, Brand Marketing, Cable Networks, Cable TV Operators, UGC
Topics: Comcast, Forrester, MySpace, Strategy Analytics, Time Warner


