-
4 Items Worth Noting from the Week of September 7th
Following are 4 news items worth noting from the week of Sept. 7th:
1. Hulu's boss says it needs to charge for content - Bloomberg ran a story this week quoting Chase Carey, deputy chairman of News Corp (Fox's owner, and therefore a part-owner of Hulu) as saying at a BofA investor conference, "Ad-supported only is going to be a tough place in a fractured world....You want a mix of pay and free."
VideoNuze readers know that while I've admired Hulu's user experience from the start, I've long been critical of its thin ad model, which falls well short of generating revenue/program/viewer parity with traditional on-air program delivery. That lack of parity has caused Hulu's owners to cordon off access to Hulu on TVs for most viewers. But the networks' fear of cannibalizing their own P&Ls only frustrates loyal Hulu users, who neither understand nor care about such legacy concerns. All of this and more led me months ago to conclude a subscription offering is inevitable from Hulu. The impending TV Everywhere launches, which further marginalize ad-only business models, and now Carey's public remarks, solidify my thinking. We'll soon see some type of Hulu subscription tier.
2. Move Networks notches a win with Cable and Wireless deal - Score one for Move Networks, which this week announced Cable and its first tier 1 telco customer. Move enables C&W to deliver an HD, linear multichannel video service, plus on-demand and broadband content to its broadband customers, all through existing DSL connections. Move's repositioning, which I wrote about recently, obviates telcos' need to invest billions in upgrading their networks to get into the IPTV business. Indeed, Roxanne Austin, Move's CEO told me yesterday that C&W has for years considered all the various options for getting into video, but has never pulled the trigger until now. The deal covers up to 7 million homes and interestingly, rather than getting a license fee, Move will be paid a share of subscriber revenue. Roxanne says another big deal will be announced shortly.
3. iPod Nano gets video, battle with Cisco's Flip escalates - As you likely know, Steve Jobs unveiled the new iPod Nano this week, which incorporates an SD video camera. Following the iPhone 3GS adding video recording capability, I think it's pretty clear that Apple has decided video is the next big thing for its devices. As I suggested recently, Apple's embrace is going to drive user-generated video - and YouTube, as the undisputed home for it - to a whole new level.
But one wonders what this all means for Cisco's recently-acquired Flip video camera, and others from Creative, Sony, Kodak, etc? Cisco in particular has a lot on the line since it just shelled out almost $600M for Flip's parent Pure Digital. Granted Apple's devices are still SD, while Flip now emphasizes HD, but still, getting video recording "for free" as Jobs put it at the launch is pretty compelling for consumers. Even if the Flip deal doesn't work out as planned, Cisco will still be selling a whole lot more routers to handle all of this newly-generated broadband video, so it's a winner either way.
4. AT&T Wireless adding 3G capacity - In last Friday's "4 Items" post, I noted a great story the NY Times ran showcasing the frustrations that AT&T Wireless customers are experiencing due to the millions of data-intensive iPhones clogging up the network. AT&T has been hearing complaints from all sides, and this week announced 3G network upgrades in 6 cities this year, with plans to cover 25 of the top 30 U.S. cities by the end of next year, and 90% of its current 3G footprint by the end of 2011. These upgrades can't come soon enough for iPhone users. Meanwhile the company's YouTube video, featuring "Seth the blogger guy" explaining how AT&T is addressing network issues itself came under attack, as AdAge reported. There's no pleasing everyone.
Enjoy the weekend!
Categories: Advertising, Aggregators, International, Mobile Video, Technology, Telcos
Topics: Apple, AT&T, Cable and Wireless, Cisco, Hulu, iPod Nano, Move Networks, News Corp.
-
4 Items Worth Noting from the Week of August 24th
Following are 4 news items worth noting from the week of August 24th:
1. Time Warner Cable, Verizon launch TV Everywhere trials - Little surprise that Time Warner Cable announced its own TV Everywhere trial yesterday, given that former sister company Time Warner has been one of its biggest proponents. More interesting was Verizon launching a TV Everywhere initiative, which I regard as a pretty strong indicator that most or all service providers will eventually get on board. (The Hollywood Reporter has a story that DirecTV is in talks too for online distribution of TBS and TNT to start).
I have to give credit to Time Warner CEO Jeff Bewkes, TV Everwhere's key champion, who's clearly generated a groundswell of support. While some critics see TV Everywhere as being at odds with the "open Internet" ethos, I continue to think of it as a big win for consumers eager to get online access to their favorite cable programs. Assuming authentication is proven in during the trials I expect a speedy rollout.
2. Conde Nast distributes through boxee - I was intrigued by news that Conde Nast Digital will begin distributing video from its Wired.com and Style.com sites through boxee. boxee and others who connect broadband to TVs are valuable for magazines and other content providers who have long been shut out of the cable/satellite/telco distribution ecosystem, thereby unable to reach viewers' TVs. Years ago special interest magazines missed big opportunities to get into cable programming, allowing upstart cable networks to grow into far larger businesses (consider ESPN vs. Sports Illustrated, Food Network vs. Gourmet or CNBC vs. Forbes). Broadband gives magazines, belatedly, an opportunity to get back into the game.
3. Amazon announces 5 finalists in UGC ad contest - Have you seen the 5 finalists' ads in Amazon's "Your Amazon Ad" contest, announced this week? They're quite clever, with some amazing special effects. The contest is another great example of how brands are tapping users' talents, posing new competition to ad agencies. I haven't written about this in a while, but I continue to be impressed with how different brands are pursuing this path. Doritos has been the most visible and successful with its user-generated Super Bowl ads.
4. Microprojectors open up mobile video sharing opportunities - Maybe I've been living under a rock because I just read about "microprojectors" for the first time this week (I have a decent excuse since as I non-iPhone owner I wouldn't have a use for one, yet). As the name suggests, these are pocket-size projectors that allow you to output the video from your iPhone to project onto a large surface like a wall or ceiling. According to this NY Times review the quality is quite respectable, and is no doubt only going to improve. The mind boggles at what this could imply for sharing mobile video. Imagine bringing a kit - consisting of an iPhone, portable speakers and microprojector - to your friend's house, then plugging in and projecting either a live stream or an on-demand program for all to see.
Enjoy your weekend!
Categories: Cable Networks, Cable TV Operators, Commerce, Devices, Magazines, Telcos, UGC
Topics: Amazon, Comcast, Conde Nast, Time Warner Cable, Verizon
-
A Deep Dive Into Why the iPhone is Going to Unleash Mobile Video Streaming
VideoNuze readers will recall that back in Dec '08, my 2nd prediction for 2009 was that mobile video was finally going to take off. Among the drivers I identified, the main one was clearly the massive, and growing, popularity of the iPhone. But despite all of its gee-whiz capabilities, the iPhone 3G, which was then the latest one on the market, and was running the iPhone OS 2.0, still wasn't really optimized for video.
Flash forward to June '09 and the release of the iPhone OS 3.0, which is downloadable to iPhone 3G, and pre-installed on the iPhone 3GS, and we can see that Apple now has the architecture in place to fuel a massive takeoff of mobile video streaming.
Following is a deep dive explanation of why that is, based on a detailed conversation I had John Bishop, SVP of Business Development & Strategy at Inlet Technologies, an encoding company that's involved with recent iPhone video apps, an excellent new white paper from Akamai, "HTTP Streaming for iPhone Best Practices" and other research I conducted. (For those that want to get further into the weeds, note also that Akamai, Inlet and Turner Sports have an upcoming webinar on this topic.) If you're a video provider looking to capitalize on mobile video distribution, and the iPhone in particular, all of this is crucial to understand.
The most important video-related elements Apple has released are support for HTTP streaming, a new protocol for adaptive bit rate (ABR) streaming and a new iPhone media player that can handle both. In
 addition, a significant increase in battery life (especially important to retain phone functionality) is enabled by a hardware-based video decoder. And the iPhone supports "HSDPA," an enhanced 3G protocol AT&T is rolling out, which provides up to 7.2 megabit per second delivery, guaranteeing outstanding video quality. All of these elements, when combined with the iPhone's open (well, relatively at least) App Store and web browsing, offer video providers a breakthrough mobile video environment.
addition, a significant increase in battery life (especially important to retain phone functionality) is enabled by a hardware-based video decoder. And the iPhone supports "HSDPA," an enhanced 3G protocol AT&T is rolling out, which provides up to 7.2 megabit per second delivery, guaranteeing outstanding video quality. All of these elements, when combined with the iPhone's open (well, relatively at least) App Store and web browsing, offer video providers a breakthrough mobile video environment.HTTP-based streaming is particularly key because CDNs already have massive deployments of HTTP (the web delivery standard) servers. That means they avoid significant capex to support proprietary video streaming protocols like RTSP and RTMP, and can instead focus just on hardening their HTTP infrastructure to scale video distribution.
Apple's new ABR streaming protocol means a far superior user experience that obviates disruptive buffering and users having to make confusing choices like "hi res" or "low res." ABR streaming was pioneered by Move Networks. Microsoft and Adobe now each have their own ABR streaming approaches.
Importantly, because the iPhone supports H.264, video providers can use existing encoding vendors like Inlet to simply create multiple iPhone-compatible video files encoded at different bit rates that are then delivered to their CDN for iPhone distribution. No intermediary "encapsulation" step needs to be taken to support Flash for example. As the iPhone's media player auto-detects available mobile bandwidth, it continuously re-selects the optimal video file to stream. Inlet makes a key contribution in this process by doing "key frame alignment" - essentially allowing the new file being streamed to start at the same frame where the old file left off. Pretty cool stuff.
From the content provider's standpoint, iPhone-directed video can either be embedded in a web page, or as part of an app, for distribution in the iPhone's gigantic app store. The open web approach of course means it's available for all to see. On the other hand, the app route means greater control of the brand, user experience and business model (e.g. free, paid, authenticated, etc.), though it will involve time and money is needed for development.
This whole paradigm is still so new that we've only begun seeing the first iPhone video apps come to market. Examples include the updated version of MLB.com's At Bat app, the live Aug. 7th concert from Underworld, the PGA Championship app from Turner Sports and the PGA, and yesterday, the launch of the HSN "shop app." I can relate to the value of the PGA app - I was in a car on my way back to Boston on Sunday afternoon, furiously - and unsuccessfully - trying to follow the Yang-Woods showdown shot-by-shot on my Blackberry (I'm a Verizon sub, so no iPhone for me, grrrr....). If I'd had an iPhone, would I have spontaneously paid $1.99 for the PGA app so I could watch the action? In a heartbeat.
Mobile video is an incredibly exciting extension of the broadband experience users have come to love, except with the additional benefit of being untethered. The iPhone is the first environment that brings all the necessary elements together and will, in my view, drive an explosion of mobile video streaming apps (though I concede to being uncertain what AT&T will think of all this). Think about video apps that are yet to come from folks like Hulu, Netflix, and others. No doubt we'll see Android, Palm and Blackberry further fuel the addressable market. Add it all up and there's a lot of growth ahead in the mobile video space.
What do you think? Post a comment now.
Categories: Devices, Mobile Video, Telcos
Topics: Akamai, Apple, HSN, Inlet Technologies, iPhone, MLB, PGA, Turner Sports
-
Interview with boxee Investors Bijan Sabet and Neil Sequeira
When boxee announced it raised a $6M second round last week it caught my attention for two reasons. First, it was further evidence that broadband video-related companies are continuing to raise money right through the current economic meltdown (industry companies raised at least $64M in Q2 '09, $75M in Q1 '09 and $78M in Q4 '08).
Second, and more noteworthy to me was how much industry experience and insight now backs boxee. The new lead investor in the round was Boston venture firm General Catalyst Partners (joining prior investors Spark Capital and Union Square Ventures), whose portfolio includes broadband video companies like Brightcove, DECA, EveryZing, Maven Networks (acquired by Yahoo), ScanScout, ViTrue and Visible Measures.
Spark also has many investments in the industry, including 5Min, Adap.tv, EQAL, KickApps, Next New Networks, thePlatform (acquired by Comcast) and Veoh. And Union Square is one of the most active firms in the online media/advertising industry with stakes in MeetUp, OddCast, Twitter (with Spark), Tacoda (acquired by AOL) and others.
Beyond the firms themselves are the individuals helping steer boxee. Joining its board from GC is Neil
 Sequeira, a veteran of the cable industry, who was most recently Managing Director, Technology of AOL Time Warner Ventures. Already on the board is Spark's Bijan Sabet who knows the cable/satellite ecosystem equally well, having done stints at Moxi, WebTV and Apple and Union Square's Fred Wilson, who is deeply immersed in online media and writes a hugely popular blog.
Sequeira, a veteran of the cable industry, who was most recently Managing Director, Technology of AOL Time Warner Ventures. Already on the board is Spark's Bijan Sabet who knows the cable/satellite ecosystem equally well, having done stints at Moxi, WebTV and Apple and Union Square's Fred Wilson, who is deeply immersed in online media and writes a hugely popular blog. I corralled Neil and Bijan (two old friends) for a phone interview late last week to explain boxee's future and where it fits into the current video ecosystem. Following is an edited transcript.
VideoNuze: What attracted you to invest in boxee?
Neil Sequeira: Three things. The boxee team, the market opportunity and our ability to be a great partner. We think boxee has the potential to be the next generation "Firefox for media," a widely- used consumer platform. That's incredibly exciting to us.
Bijan Sabet: We've been involved with boxee for a while now, and we're convinced the time is right for something like this. boxee has the right ingredients: it is open source and includes social media capabilities, an app store and a huge community of users/developers.
VideoNuze: boxee has gained a loyal following, but it doesn't have a business model yet. What do you see as boxee's business model and it what time frame must it develop it in order to succeed?
BS: boxee's still a very young company, but we have a number of ideas around business models. But the key is patience. The company has a very low burn rate, with around 16 people or so , most of whom are in Israel. The focus for now is building the product and the user base. And the company's been very successful doing that. Last year boxee had 10,000 users, now it has 600,000.
NS: It also has a very excited developer community. But I agree - patience is needed here. Too often companies can get themselves focused to early on a specific business model, which then constrains them. With the new funding, box has room to see how things evolve.
VideoNuze: Hulu recently told boxee to remove its content. What do you think boxee needs to do to win Hulu (and others) onto its platform?
NS: At a high level boxee we believe boxee is an incredible friend to content providers, and we want to work with everyone. We're big believers that consumers want access to everything and that's where the market will go over time.
 BS: All of us are Hulu fans and of course would love to have Hulu on boxee. But each content provider has its own business model, and has to decide what works best for them. boxee will continue to be a content provider-friendly platform, where different business models can be used and different technologies integrated. We think that's powerful.
BS: All of us are Hulu fans and of course would love to have Hulu on boxee. But each content provider has its own business model, and has to decide what works best for them. boxee will continue to be a content provider-friendly platform, where different business models can be used and different technologies integrated. We think that's powerful. VideoNuze: How should established video service providers (i.e. cable/satellite/telco) regard boxee - as friend, foe, or something else?
NS: We want boxee to be regarded as friend and we think boxee can add a lot of value to the ecosystem. Consider for example, the case of TiVo. Early on it looked like a foe. But now see how Comcast is integrating TiVo into its set-top boxes and driving incremental revenue. boxee brings great search, apps and context to the broadband viewing experience. All that will drive usage of broadband Internet connections, which in turn helps "fill the pipe" making cable and telco Internet access services that much more valuable to users - and to their providers.
BS: Agreed. We believe that in an IP world, these things aren't either/or, mutually exclusive. Again look at Comcast, which has great assets like Fancast, and is now working on entitlements with TV Everywhere. boxee can help drive more value from them. This is especially true for certain user segments, like new college grads, for whom the Internet is now far more important than is traditional TV. The point is traditional service providers need to figure out how to delight a variety of user segments. We believe boxee can help.
VideoNuze: You guys and your firms have deep relationships in the cable/satellite/telco industries. How are those folks reacting to boxee?
NS: People in the ecosystem are taking a "wait-and-see" approach. There's a certain amount of fascination, and though we don't see any impending deals, Avner (Ronen, boxee's founder/CEO) has multiple conversations ongoing with the industry.
VideoNuze: Who are boxee's primary competitors?
BS: What Apple and Microsoft are doing is most competitive, though their approaches include both hardware and software. We think of boxee like Android (Google's mobile OS), sort of the "inside-out" version of Apple TV. And we believe convergence device/hardware providers want alternatives.
VideoNuze: How about Roku?
NS: We believe Roku should be partners with boxee. Hardware companies have core competencies and typically those don't include open source media platforms. So boxee can help devices like Roku be even better. We'll have a number of device deals to announce soon.
VideoNuze: A lot has been written about "over-the-top" services. Are they starting to succeed, and if so, what must happen for them to gain further success?
NS: Well, yes, when we look at what Netflix and others are doing already, we do believe over-the-top services are starting to succeed. And we think this isn't necessarily a bad thing for cable operators for example. That's because the video business has had margin compression due to rising programming costs, whereas broadband Internet service has been incredibly profitable for them.
Consider that that cable operators didn't offer DVR or voice services just 10-11 years ago, but now they are a significant driver of ARPU (average revenue per unit). There's a lot more that cable operators can derive from broadband services than they currently are, considering the IP connection is now - for many - the most important connection they have. Content providers know this and are looking for more, not fewer, ways to distribute their content.
BS: Agreed, look at an example like CNBC, whose ratings are down something like 30% year-over-year. What's causing this? Is there demo changing? Is the web providing alternatives? Some of both? The point is content providers need to figure out how to control their destiny. That doesn't mean they have to give their stuff away for free. But it does mean they need to figure out how to distribute as effectively as possible. We want to help them do that. You can't go backwards here. Broadband is too interesting and too important to too many people.
VideoNuze: Thanks guys.
Categories: Cable TV Operators, Deals & Financings, Devices, Satellite, Telcos
Topics: Boxee, General Catalyst, Spark Capital, Union Square Ventures
-
Hubris Cursed AOL But Broadband Crushed It
I highly recommend reading Saul Hansell's piece in last Friday's NY Times, recapping the ridiculously optimistic quotes senior executives at AOL and Time Warner have made over the years (and be sure to peruse readers' consistently vitriolic comments). For anyone who's watched AOL's rise and fall, the quotes are a stroll down memory lane. But while the picture that emerges is that hubris cursed AOL and contributed mightily to its downfall, in reality it was broadband, and AOL's colossal mismanagement in transitioning to it, that crushed the company.
The chart below shows that AOL's dial-up subscribers topped out in Q3 '02 at 26.7 million, and have been in a free-fall ever since, sitting at just 6.3 million at the end of Q1 '09, a drop-off of 20.4 million or 76%. Where did those 20.4 million dial-up subs go, along with tens of millions of other dial-up and new Internet users? To broadband Internet access, supplied by cable companies and telcos. These companies have grown their U.S. broadband subs from 15.2 million in Q3 '02 to 69.2 million in Q1 '09, an astonishing increase of 54 million subscribers in just 7 years.
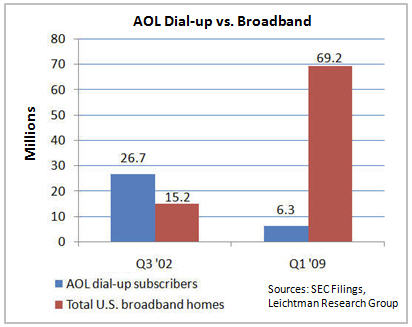
Cable and telco broadband providers have feasted on the carcasses of AOL and other dial-up services like MSN and Earthlink. But, here's what's both incredible and really sad: had AOL management been less arrogant and more strategic in its approach to broadband, it's quite possible that things could have turned out quite differently.
Back in the mid-to-late '90s, I had a front-row seat at AOL's initial reactions to broadband. In that period I was VP Business Development at Continental Cablevision, then the 3rd largest cable operator in the U.S. with over 5 million video subscribers. We were one of the pioneers in testing and rolling out "high-speed" Internet service. While we thought our speedy and always-on broadband connections were a better mousetrap vs. dial-up, we were very concerned about our lack of online content, video-centric branding and ability to effectively market this exciting new service.
In the pre-@Home days, I pushed to explore how we could partner with AOL to help us get our service off to a faster start. A deal with AOL would have had significant advantages to them as well. AOL at the time had a huge capex burden building out more modem banks to keep up with its swelling subscriber ranks. Even still, there was already plenty of AOL subscriber frustration with the slowness of the AOL network, and often you couldn't even get connected on your first or second tries. At least in our geographic footprint we could unburden them of their network build-out, offer better-quality connections and allow them to focus on content and brand-building. As the 3rd largest cable operator, we also offered them a valuable proof-point that they could use to build industry-wide relationships.
After much preparation and scheduling, we met with one of AOL's most senior executives. After articulating our broadband vision and opportunity to work together, he arrogantly dismissed us as if we were precocious children. To him the opportunity we were describing was far too small, and to illustrate his point he asserted that AOL would have 10 million subscribers before we had our first 100,000 (a prediction that was probably correct!).
Needless to say, no meaningful deal with us - or any other cable operator - every materialized. AOL went on to flounder around with various incarnations of AOL Broadband, none of which ever got any traction. AOL continued to grow its subscribers for a number of years and capitalized on its reach by extracting hundreds of millions of dollars from VC-backed startups eager for access to its massive captive audience (some of those deals would later come under scrutiny, as would AOL's accounting treatment for its subscriber business). AOL then bought Time Warner, and the rest as we know is history.
But what if things had gone differently? What if that AOL executive and others had seen the handwriting on the wall - that broadband would eventually render dial-up obsolete - and decided that AOL needed to figure out how to transition to it, instead of dismissing it? Had that happened, it could have forged partnerships throughout the cable and telco industries that would have let it focus on content and services in an open, broadband environment. In fact, I think it's quite possible that AOL could have pre-empted @Home and the RoadRunner venture that Continental eventually joined from getting traction (why start over when AOL, the 800 pound gorilla is in your corner?).
Instead AOL fell victim to its own arrogance and limited strategic vision. Broadband went on to become the single most powerful enabler of the Internet as we know it today (e.g. billions of spontaneous Google searches, Tweets, Amazon purchases, and more recently video views). AOL is now a crippled mish-mash of mostly second-rate properties, on its umpteenth management team, led by new CEO Tim Armstrong.
In retrospect, those fateful decisions AOL made about broadband 10-15 years ago set the stage for the company's eventual demise.
What do you think? Post a comment now.
Categories: Broadband ISPs, Cable TV Operators, Portals, Telcos
-
Unveiling Move Networks's New Strategy
Move Networks, the well-funded Internet television technology company which has been virtually silent for the last 60 days since acquiring Inuk Networks and bumping former CEO John Edwards to Executive Chairman, is pursuing a major repositioning. Earlier this week I met with Marcus Liassides, Inuk's former CEO and founder who joined Move's management team, who previewed the company's new strategy to be a wholesale provider of IPTV video services delivered over open broadband networks.
Broadband video industry participants know Move best for its proprietary adaptive bit rate (ABR) technology and player, which power super-high quality live and on-demand video streams for broadcasters
 like ABC and Fox. Move gained a lot of attention by raising over $67M, including a $46M Series C round in April '08 from blue chip investors.
like ABC and Fox. Move gained a lot of attention by raising over $67M, including a $46M Series C round in April '08 from blue chip investors.Despite all this, Marcus explained that coming into 2009 Move had at least 3 significant problems, symbolic of how fluid the broadband video market remains.
First, its core business of charging content providers in the range of $.30/GB of video delivered was being pressured by the fact that advertising-only business models couldn't support this pricing. Content providers loved Move's quality; they just couldn't afford it, particularly given the alternative of plunging CDN delivery rates.
Second, Move's pricing and business model were being challenged by both Microsoft and Adobe entering the market with ABR streaming features of their own (I wrote about this here). But because both were enabled on the server side (IIS and FMS respectively), the cost of ABR moved from content providers to CDNs, who might or might not choose to charge extra for these features. Either way, Move's direct cost looked comparatively more expensive, especially as the recession pounded ad spending.
Last, but not least, Marcus explained that Move's product development approach was undisciplined, leading to resources being spread too thin in too many directions. That was reflected by the market's ongoing difficulty in categorizing which business Move was really in.
Meanwhile, U.K.-based Inuk, which had been on its own funding and product development roller-coaster, was delivering its Freewire IPTV service to about 200K university students in the UK, Ireland and Canada. Because Inuk needed to serve these students when they were off campus, it had developed a "virtual set-top box" application that duplicates on the PC the IPTV service that had traditionally been delivered via an expensive IPTV set-top box. Inuk was using Move's ABR technology to power video delivery to the PC. Recognizing potential synergies and trying to address its other issues, Move acquired Inuk in April.
Move's new positioning as a provider of IPTV video services delivered over open broadband networks essentially replicates what Inuk has been doing, except that going forward services will be offered wholesale, not retail like with Freewire. Move's strategy starts from the proposition that to get cable TV networks online requires that they be paid consistent with the norms, rather than expecting them to free and ad-supported only. It also anticipates that consumers demand not just VOD offerings, but a full linear lineup as well (as an aside, that aligns with Sezmi's thinking too). While Move will continue supporting existing customers like ABC and others, its new wholesale model is a major shift in that it uses the company's core technology to support packaged multichannel video services, instead of a la carte web-based video.
Marcus explained that Move is targeting 3 verticals: (1) telcos which haven't traditionally offered video services (or have through direct satellite partnerships), (2) broadband ISPs looking to get into the video business, and (3) existing video service providers looking for a lightweight capex approach for extending their service either for remote access (a la "TV Everywhere") or in other rooms in the house (a model which has traditionally required another set-top box and truck roll for installation).
Marcus demo'd the Freewire service to me using his PC and a large monitor, and it looks great. There's instant channel changing, HD (when available), a great looking guide and auto-DVR of every program, all in the cloud. Freewire also offers targeted advertising, and HTML-based apps like Twitter integration, etc. My caveat is that I have no idea how well the service would scale to millions of homes.
Move's new positioning puts it in the middle of tectonic video industry shifts. For example, what's the appetite of 3rd parties like telcos and ISPs for new video solutions? Will other, well-suited consumer brands like Google, Netflix, Yahoo enter the multichannel video business, and if so how? What approach will cable operators like Comcast use for emerging, "TV Everywhere" services that would benefit from Move's lightweight capex model (note Comcast said it was using Move in its 5,000 subscriber technical trial yesterday)? How will major cable TV networks expect to get compensated in the broadband era where individuals, not homes, are the new unit of measurement? How will local ISPs, over whose networks remotely-accessed video will run, expect to be compensated? It's way too early to know the answers, but if Move's technology works as intended, and its costs are reasonable, it will likely find itself in the middle of a lot of very strategic industry discussions.
Another big change is that Marcus said the company's messaging will be focused more around business cases and services than its specific technologies. That seems smart given giants like Microsoft and Adobe are closely circling these waters with lots of their own technology, which could easily swamp Move. If all this wasn't enough, Move is also in the midst of hiring a new CEO and implementing a new management team, all of which will be announced imminently. One thing Move isn't doing for now is raising additional capital, which Marcus said is not needed.
What do you think? Post a comment now.
(Note: Move Networks is a current sponsor of VideoNuze)
Categories: Broadcasters, Cable Networks, Cable TV Operators, Deals & Financings, IPTV, Technology, Telcos
Topics: ABC, Adobe, FOX, Microsoft, Move Networks
-
Made-for-Broadband Video and VOD are Looking Like Peanut Butter and Chocolate
Remember "two great tastes that taste great together," the slogan from the classic Reese's ads featuring the mixing of peanut butter and chocolate? Recent developments suggest that independently produced/made-for-broadband video and Video-on-Demand could be another Reese's-like combination, bringing together two disparate worlds that have attracted loyal audiences in an offering that could have significant consumer appeal.
Consider, last week Multichannel News reported that Verizon plans to bring over 7 million broadband video clips from providers like blip.tv, Veoh and Dailymotion to its FiOS service, which users can browse with their set-top boxes. Also last week, AnySource Media, a software company that powers broadband-connected TVs, announced content deals with TheStreet.com, Break.com, Revision3 and Next New Networks, creating hundreds of "virtual VOD channels." And yesterday, Clearleap, a startup technology platform I recently profiled, announced its own deals with blip.tv, Revision3 and Next New Networks, providing content that cable operators can meld with their VOD offerings.
This push among made-for-broadband producers, technology companies and incumbent video service providers is not coincidental. While they each have their own motivations, their alignment could signal a winning proposition for viewers.
For the indie content producers, on-demand access on TVs augments their viewing experience and access to their programming. Given how difficult the environment has become for independents (Daisy had a good piece on this topic yesterday) on-demand access is a real differentiator. For cable operators and telcos, popular indie video gives them a targeted pitch to the tech-savvy, younger audiences who have become loyal fans of indie content. Down the road this group is probably most up-for-grabs for alternative "over-the-top" services, so focusing on defending them is smart. And for technology providers, a big market opportunity looms trying to connect the previously disparate worlds of broadband and VOD.
In fact, in a conversation I had last week with Braxton Jarratt, CEO/founder of Clearleap, he explained that cable operators get all this. They're looking for quality "mid-tail" video from broadband producers, including clips and short-form programs. The company's technology is currently feeding broadband video to a couple hundred thousand cable VOD homes, with a backlog of "double digit" markets pending deployment. Braxton has a lot of content deals on Clearleap's docket, creating a menu for its cable customers to pick and choose from to incorporate into their VOD offerings. Clearleap also offers an ad insertion platform, so indie video can be monetized, not just offered as a value add.
Meanwhile, VOD has long proven itself popular with viewers. Comcast recently announced it has delivered 11B views since it launched VOD. It has continued to augment its library and add more HD titles. While VOD hasn't really been a money-maker itself, it has become a strong part of the digital value proposition and a defensive move against other viewing alternatives. By incorporating popular broadband video into its VOD choices, its appeal is only strengthened.
While the tectonic plates of "convergence" continue to shift, examples of broadband video making its way to the TV continue to happen. TiVo has been at this for a while with its "TiVoCast" service, along with technology providers like ActiveVideo Networks and others. The likelihood for independently-produced broadband video and VOD to get together seems poised to increase.
What do you think? Post a comment now.
Categories: Cable TV Operators, Indie Video, Technology, Telcos
Topics: ActiveVideo Networks, AnySource Media, Clearleap, Comcast, TiVo, Verizon
-
Clearleap Bridges Broadband Video and Ads to TVs
Summary:
What: Clearleap has introduced a new technology platform for distributing broadband video content directly to TVs and an accompanying ad management system.
For whom: Incumbent service providers (cable/telco) and new over-the-top entrants (device makers, aggregators, etc.), content providers and advertisers
Benefits: For service providers, a flexible, cost-effective system for offering broadband content to their subscribers with minimal technology integration; for content providers a scalable system for distributing content across multiple providers and platforms; for advertisers a new method of targeting on-demand audiences.
More innovation is coming to the ongoing quest to bring broadband content to TVs as Clearleap, an Atlanta-based startup, pulled back the curtain yesterday on its ambitious technology platform. Last fall, CEO/founder Braxton Jarratt gave me a glimpse into what the company was working on and yesterday he explained it more fully.
Clearleap aims to do multiple things with its "clear|flow" and "clear|profit" products. For incumbent video service providers (cable and telco operators) and new "over-the-top" entrants (device makers, aggregators,
 etc.), Clearleap enables delivery of broadband and other video to the TV including integrating with existing Video-on-Demand infrastructure when present; for content providers, it improves the process of distributing of content across multiple providers and platforms; and for both service providers and content providers it offers an ad management solution that allows flexible ad insertion and business rules for ads running with Clearleap-delivered video.
etc.), Clearleap enables delivery of broadband and other video to the TV including integrating with existing Video-on-Demand infrastructure when present; for content providers, it improves the process of distributing of content across multiple providers and platforms; and for both service providers and content providers it offers an ad management solution that allows flexible ad insertion and business rules for ads running with Clearleap-delivered video. That's a mouthful, so to break it down a bit, here's my interpretation. First the delivery side. Obviously there's been a lot of discussion, particularly just since CES in January, of new entrants delivering broadband content to TVs, thereby presenting potential alternatives for consumers to "cut the cord" on existing cable and telco providers. One way for incumbent to combat this is for them to offer the best of the web (like TiVo has been doing with TiVoCast for a while now) in one seamless package delivered through the existing set-top box.
To date incumbents haven't pursued this strategy much though. Braxton attributes this intransigence to lack of adequate technology, than to lack of interest. Braxton says Clearleap has a couple of small deployments active and other announcements pending. The key to success is allowing the incumbents to control the process of what content they acquire and to present it in context with other VOD offerings. clear|flow ingests video from content partners into Clearleap's data centers, transcodes it and properly formats it for target devices, adds metadata and business rules and then enables service providers to subscribe to whatever content they want. The video is either served from Clearleap's data centers or pushed to an incumbent's own hosting facility.
On the other side of the coin, another goal of clear|flow is to become the glue that allows content providers who want to distribute across all these emerging platforms to do so with minimal work. Just upload your content, specify business rules and the service providers take it from there. Of course, there's a "chicken and egg" challenge here that content providers will only take an interest when there's sufficient distribution. Braxton recognizes this issue as well and said they've been encouraged by the willingness of certain "friendlies" to get involved, which he hopes will provide validation for others to come on board soon.
Last, but not least, clear|profit allows ad avails to be created and properly divided between the content providers and service providers according to specified rules. Ad management and insertion has of course been the Achilles heel for existing VOD systems, rendering today's VOD a largely revenue-free pursuit for most service providers. Cost-effectively solving the ad insertion process for VOD alone would be a major win.
Clearleap has an ambitious vision and ordinarily I'd say it feels like a lot for any startup to bite off. But Clearleap has a veteran executive team from N2 Broadband, which was a successful VOD software provider prior to its acquisition by Tandberg Television. The Clearleap team knows its way around cable data centers, has strong industry relationships and is benefitting from pressure incumbents feel to broaden their offerings - all no doubt key factors in helping the company raise money.
Still, there's going to be plenty of competition. Others circling this space in one way or another include ActiveVideo Networks, AnySource Media, GridNetworks, Sezmi, TiVo and lots of others who all have their own approaches and systems for connecting content providers with incumbent and new service providers to bring broadband video to TVs. It's going to be an interesting space to watch as there is no shortage of energy aimed at merging broadband with the TV and vice versa.
What do you think? Post a comment now.
Categories: Cable TV Operators, Startups, Telcos
Topics: ActiveVideo Networks, AnySource Media, Clearleap, GridNetworks, SezMi, TiVo
-
Comcast: A Company Transformed
Three numbers in last week's third quarter Comcast earnings release underscored something I've believed for a while: Comcast is a company transformed, now reliant on business drivers that barely existed just ten short years ago. Comcast's transformation from a traditional, plain vanilla cable TV operator to a digital TV and broadband Internet access powerhouse is profound proof of how consumer behaviors' are changing and value is going to be created in the future.
The three numbers that caught my attention were the net additions of 382,000 broadband Internet subscribers and 417,000 digital subscribers, with the simultaneous net loss of 147,000 basic subscribers. The latter number is the largest basic sub loss the company has sustained and, based on the company's own earnings releases, the sixth straight quarter of basic sub contraction. In the pre-digital, pre-broadband days, when a key measure of cable operators' health was ever-expanding basic subscribers, this trend would have caused a DEFCON 1 situation at the company. (see graph below for 2 year performance of these three services)
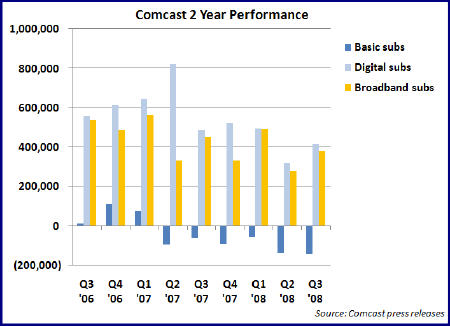
That it doesn't any longer owes to the company's ability to bolster video services revenue and cash flow through ever-higher penetration of digital services into its remaining sub base (at the end of Q3 it stood at 69% or 16.8 million subs). Years after Comcast and other cable operators introduced "digital tiers," stocked with ever-more specialized channels that consumers resisted adopting, the industry has hit upon a winning formula for driving digital boxes into Americans' homes: layering on advanced services like HD, VOD and DVR that are only accessible with digital set top boxes and then bundling them with voice and broadband Internet service into "triple play" packages. Comcast has in effect gone "up-market," targeting consumers willing and able to afford a $100-$200/month bundle in order to enjoy the modern digital lifestyle.
Still, in a sense the new advanced video services represent just the latest in a continuum of improved video services. Far more impressive to me is the broadband growth that both Comcast and other cable operators have experienced. Comcast's approximately 15 million YE '08 broadband subscribers will generate almost $8 billion in annual revenue for Comcast, up dramatically from its modest days as part of @Home 10 years ago. (It's also worth noting the company now also provides phone service to over 6 million homes today vs. zero 10 years ago)
The cable industry as a whole will end 2008 with approximately 37 million broadband subs, again up from single digit millions 10 years ago. And note that the 387,000 net new broadband subs Comcast added in Q3 '08 compares with just 277,000 net broadband subs that the two largest telcos, AT&T and Verizon added in quarter, combined. As someone who was involved in the initial trials of broadband service at Continental Cablevision less than 15 years ago, observing this growth is nothing short of astounding.
While broadband's financial contribution to Comcast is unmistakable, its real impact on the company is more
 keenly felt in its newfound importance in its customers' lives. Broadband Internet access has become a true utility for many, as essential in many homes as heat, water and electricity. A senior cable equipment executive told me recently that research done by cable companies themselves has shown that in broadband households, broadband service would be considered the last service to get cut back in these tough economic times. In these homes cable TV itself - long thought to be recession-resistant - would get cut ahead of broadband.
keenly felt in its newfound importance in its customers' lives. Broadband Internet access has become a true utility for many, as essential in many homes as heat, water and electricity. A senior cable equipment executive told me recently that research done by cable companies themselves has shown that in broadband households, broadband service would be considered the last service to get cut back in these tough economic times. In these homes cable TV itself - long thought to be recession-resistant - would get cut ahead of broadband.But Comcast and other cable operators must not rest on their laurels. Their next big challenge is to figure out how to take this massive base of broadband subs and start delivering profitable video services to it. If Comcast allows its broadband service to be turned into a dumb pipe, with "over the top," on demand video offerings from the likes of Hulu, YouTube, Neflix, Apple and others to ascend to dominance, that would be criminal. Not only would it devalue the broadband business, it would dampen interest in the company's advanced video services (VOD in particular) while making the company as a whole vulnerable in the coming era of alternative, high-quality wireless delivery.
Comcast is indeed a company transformed from what it was just 10 years ago. Technology, changing consumer behaviors and a little bit of "being in the right place at the right time" dumb luck have combined to allow Comcast to remake itself. Comcast itself must fully recognize these changes and aggressively build out Fancast and other initiatives to fully capitalize on its newfound opportunities.
What do you think? Post a comment now.
Categories: Aggregators, Broadband ISPs, Cable TV Operators, Telcos
Topics: Apple, AT&T, Comcast, Netflix, Verizon, Verizon, YouTube
-
Cutting the Cord on Cable: For Most of Us It's Not Happening Any Time Soon
Two questions I like to ask when I speak to industry groups are, "Raise your hand if you'd be interested in 'cutting the cord' on your cable TV/satellite/telco video service and instead get your TV via broadband only?" and then, "Do you intend to actually cut your cord any time soon?" Invariably, lots of hands go up to the first question and virtually none to the second. (As an experiment, ask yourself these two questions.)
I thought of these questions over the weekend when I was catching up on some news items recently posted to VideoNuze. One, from the WSJ, "Turn On, Tune Out, Click Here" from Oct 3rd, offered a couple examples of individuals who have indeed cut the cord on cable and how their TV viewing has changed. My guess is that it wasn't easy to find actual cord-cutters to be profiled.
There are 2 key reasons for this. First it's very difficult to watch broadband video on your TV. There are special purpose boxes (e.g. AppleTV, Vudu, Roku, etc.), but these mainly give access to walled gardens of pre-selected content, that is always for pay. Other devices like Internet-enabled TVs, Xbox 360s and others offer more selection, but are not really mass adoption solutions. Some day most of us will have broadband to the TV; there are just too many companies, with far too much incentive, working on this. But in the short term, this number will remain small.
The second reason is programming availability. Potential cord-cutters must explicitly know that if they cut their cord they'll still be able to easily access their favorite programs. Broadcasters have wholeheartedly embraced online distribution, giving online access to nearly all their prime-time programs. While that's a positive step, the real issue is that cord-cutters would get only a smattering of their favorite cable programs. Since cable viewing is now at least 50% of all TV viewing (and becoming higher quality all the time, as evidenced by cable's recent Emmy success), this is a real problem.
To be sure, many of the biggest ad-supported cable networks (MTV, USA, Lifetime, Discovery) are now making full episodes of some of their programs available on their own web sites. But these sites are often a hodgepodge of programming, and there's no explanation offered for why some programs are available while others are not. For example, if you cut the cord and could no longer get Discovery Channel via cable/satellite/telco, you'd only find one program, "Smash Lab" available at Discovery.com. Not an appealing prospect for Discovery fans.
Then there's the problem of navigation and ease of access. Cutting the cord doesn't mean viewers don't want some type of aggregator to bring their favorite programming together in an easy-to-use experience. Yet full streaming episodes are almost never licensed to today's broadband aggregators. Cable networks are rightfully being cautious about offering full episodes online to aggregators not willing to pay standard carriage fees.
For example, even at Hulu, arguably the best aggregator of premium programming around, you can find Comedy Central's "The Daily Show" and "Colbert Report." But aside from a few current episodes from FX, SciFi and Fuel plus a couple delayed episodes from USA like "Monk" and "Psych," there's no top cable programming to be found.
As another data point, I checked the last few weeks of Nielsen's 20 top-rated cable programs and little of this programming is available online either. A key gap for cord-cutters would be sports. At a minimum, they'd be saying goodbye to the baseball playoffs (on TBS) and Monday Night football (on ESPN). In reality, sports is the strongest long-term firewall against broadband-only viewing as the economics of big league coverage all but mandate carriage fees from today's distributors to make sense.
Add it all up and while many may think it's attractive to go broadband only, I see this as a viable option for only a small percentage of mainstream viewers. Only when open broadband to the TV happens big time and if/when cable networks offer more selection will this change.
What do you think? Post a comment now.
Categories: Aggregators, Broadcasters, Cable Networks, Cable TV Operators, Devices, Telcos
Topics: AppleTV, Comedy Central, Discovery, ESPN, FX, Hulu, Lifetime, Roku, SciFi, TBS, USA, VUDU, Xbox360
-
Inside the Netflix-Starz Play Licensing Deal
This past Wednesday, Starz, the Liberty Media-owned premium cable network, licensed its "Starz Play" broadband service to Netflix. The three year deal makes all of Starz's 2,500 movies, TV shows and concerts available to Netflix subscribers using its Watch Instantly streaming video feature. Very coincidentally I happened to be at Starz yesterday for an unrelated Liberty meeting, and had a chance to speak to Starz CEO Bob Clasen, who I've known for a while, to learn more.
On the surface the deal is an eye-opener as it gives a non-cable/telco/satellite operator access to Starz's
 trove of prime content. As I've written in the past, cable channels, which rely on their traditional distributors for monthly service fees, have been super-sensitive to not antagonizing their best customers when trying to take advantage of new distribution platforms. This deal, which uses broadband-only distribution to reach into the home, no doubt triggers "over-the-top" or "cable bypass" alarm bells with incumbent distributors.
trove of prime content. As I've written in the past, cable channels, which rely on their traditional distributors for monthly service fees, have been super-sensitive to not antagonizing their best customers when trying to take advantage of new distribution platforms. This deal, which uses broadband-only distribution to reach into the home, no doubt triggers "over-the-top" or "cable bypass" alarm bells with incumbent distributors. Then there is the value-add/no extra cost nature of Netflix's Watch Instantly feature. That there is no extra charge to subscribers for Starz's premium content (as there typically is when subscribing to Starz through cable for example) raises the question of whether Starz might have given better pricing to Netflix to get this deal done than it has to its other distributors.
But Bob is quick to point out that in reality, the Netflix deal is a continuation of Starz's ongoing push into broadband delivery begun several years ago with its original RealNetworks deal and continued recently with Vongo. To Starz, Netflix is another "affiliate" or distributor, which, given its tiny current online footprint does not pose meaningful competition to incumbent distributors. With only about 17 million out of a total 100 million+ U.S. homes subscribing to Starz, broadband partnerships are seen as a sizable growth opportunity by the company.
Further, Starz has been aggressively pitching online deals to cable operators and telcos for a while now, though only the latter has bit so far (Verizon's FiOS is an announced customer). Cable operators seem interested in the online rights, but have been reluctant to pay extra for them as Starz requires.
Bob also noted that Starz's wholesale pricing was protected in its Netflix deal, and that for obvious reasons of not hurting its own profitability, Starz has strong incentives to preserve incumbent deal terms in all of its new platform deals.
To me, all of this adds up to at least a few things. First is that Netflix must be paying up in a big way to
 license Starz Play. I assume this is an obvious recognition by Netflix that it needed more content to make Watch Instantly more compelling (see also Netflix's recent Disney Channel and CBS deals). Since it's not charging subscribers extra, Netflix is making a bet that over time - and aided by its Roku and other broadband-to-the-TV devices - Watch Instantly will succeed and as a result, will drive down its costs by reducing the number of DVDs the company needs to buy and ship. That seems like a smart long-term bet as the broadband era unfolds.
license Starz Play. I assume this is an obvious recognition by Netflix that it needed more content to make Watch Instantly more compelling (see also Netflix's recent Disney Channel and CBS deals). Since it's not charging subscribers extra, Netflix is making a bet that over time - and aided by its Roku and other broadband-to-the-TV devices - Watch Instantly will succeed and as a result, will drive down its costs by reducing the number of DVDs the company needs to buy and ship. That seems like a smart long-term bet as the broadband era unfolds.And while I agree that Starz Play on Netflix doesn't represent real competition to cable, telco and satellite outlets today, it's hard not to see it as a signal that traditional distributors are losing their hegemony in premium video distribution. (for another example of this, see Comedy Central's licensing of Daily Show and Colbert to Hulu). As I've said for a while, over the long term, the inevitability of broadband all the way to the TV portends significant disruption to current distribution models. I see Netflix at the forefront of this disruptive process.
What do you think? Post a comment now.
Categories: Aggregators, Cable Networks, Cable TV Operators, Devices, Telcos
Topics: CBS, Comedy Central, Disney, Liberty Media, Netflix, Starz, Verizon
-
Akimbo, Vongo Expose Risks for Broadband Pioneers
The last few days' news about Akimbo and Starz's Vongo service, two of the earliest players in broadband video delivery, shows how risky the broadband video market can be for pioneers.
Akimbo - which has closed its doors after raising approximately $50 million since 2003 - demonstrates that
 misjudging the key characteristics of an early market can be devastating. Akimbo's faulty assumptions included:
misjudging the key characteristics of an early market can be devastating. Akimbo's faulty assumptions included:- Anticipating that consumers would be willing to buy a broadband-only set-top box, despite overwhelming research to the contrary.
- Expecting that consumers would be willing to pay yet another monthly subscription fee, although broadband's value proposition was still in its infancy and consumers were already complaining about the high cost of cable/satellite subscription services.
- Building its initial content strategy using a pure "Long Tail" approach of aggregating lots of niche programmers, not grasping that Long Tail models only succeed when "head" content - in this case from broadcasters and cable networks - is also included.
As these misjudgments became obvious, the box was dropped, select cable programming was added to the content lineup, pricing was changed and management was overhauled. Ultimately in February '08, the whole company strategy was blown up, as Akimbo unsuccessfully tried to get a toehold in the already over-crowded white-label content management/publishing business. But once a startup is in a deep hole, it's almost impossible to climb out.
Meanwhile, Starz's announcement yesterday with Verizon, of its first "wholesale deal" for broadband delivery of its programming, shows additional risks for early players. Yesterday I caught up with Bob Greene, EVP of Advanced Services at Starz, for whom I did some consulting work several years ago on Vongo's predecessor service, Starz Ticket.
 Starz launched Vongo in early '06 as a broadband-only subscription and download-to-own service, featuring programming it had under contract, plus other categories it later added. Vongo went to market direct-to-consumer and through device partners like HP, Samsung, Toshiba, Creative and Archos, but Vongo's growth has been modest as the broadband subscription category has yet to really take off.
Starz launched Vongo in early '06 as a broadband-only subscription and download-to-own service, featuring programming it had under contract, plus other categories it later added. Vongo went to market direct-to-consumer and through device partners like HP, Samsung, Toshiba, Creative and Archos, but Vongo's growth has been modest as the broadband subscription category has yet to really take off.Vongo's larger goal was getting deals done with existing service providers like cable, telco, and broadband ISPs. But this aspiration ran into the buzzsaw of incumbents' intransigence, illustrating that reliance on ecosystem partners, who often have divergent motivations, can be very risky. In this case, Vongo's would be distributors perceived Vongo as less as an opportunity to grow the market and tap new consumer behaviors, and more as a potential long-term end-run, with immediate threats to profit margins and cash flow contribution.
Cable operators have been saying "no thanks" to distributing Vongo, concluding it had more downside risk to existing Starz linear subscriptions and Video on Demand than it had upside broadband potential. The Verizon deal may reverse things; Bob says more deals are in the offing. Time will tell. In the meantime, with Vongo's direct marketing efforts set to be further de-emphasized, Starz's broadband fate is falling squarely into the hands of reluctant incumbent service providers.
Akimbo and Starz show that to succeed, it's essential to make correct fundamental assumptions about a market's early growth have a keen understanding of ecosystem partners' motivations and concerns. Missteps on any of these can have disastrous implications.
What do you think the lessons are from Akimbo and Starz's Vongo? Post a comment!
Categories: Cable Networks, Cable TV Operators, Devices, Startups, Telcos
Topics: Akimbo, Starz, Verizon
-
Comcast Announces Moves at CES; Still Missing Key Strategic Piece
In his CES keynote today, Comcast CEO Brian Roberts will outline several Comcast's initiatives (under the umbrella "Project Infinity") to stay competitive in the fast-changing video arena.

These include:
"Wideband"- New "wideband" broadband technology which allows much faster downloads (this is impressive, though was previously displayed at '07 National Cable Show). Wideband is aimed at blunting criticism that telcos' fiber networks have more capacity and faster speeds.
HD expansion - Plans for a 10-fold increase in the number of HD movies available in its VOD library to 3,000, with at least 6,000 total titles, including SD programming, eventually available. This is all meant to offset the widely held view that satellite and telco have surpassed cable in current HD offerings, a key value prop to millions of Americans now bringing home shiny new HD TV sets.
Fancast - Comcast's video portal will include 3,000 hours of streaming TV content, from NBC, Fox, CBS and others. These moves will help bring Fancast to parity with other syndicated partners of the networks which are themselves trying to proliferate their programs everywhere. Fancast will also allows remote scheduling of DVRs (both Comcast's and TiVo's), a feature that has been widely available at sites like TiVo.com and Yahoo for years now.
All of these actions are intended to help restore Comcast's reputation as the leading provider of entertainment programming, amid the swirl of changes that have enveloped the company. Despite its formidable size, Comcast is fighting competitive fires on virtually every front: fierce multichannel competition from satellite and telcos, rising expectations of HD content, consumer behavior shifts to broadband video consumption (premium and UGC) and place-shifting/time-shifting/device-shifting. The list goes on. Amid these changes, and with a slowing of the American economy, Wall Street has punished Comcast's stock price, cutting it in half in the last year.
While I applaud today's announcements, there is still one big strategic piece missing which Comcast has yet to comprehensively address: what are its plans to allow subscribers using its digital set-top boxes to seamlessly watch broadband video content as they do broadcast and cable programs?
As many of you know, I have been on a "broadband-to-the-TV" jag recently (see here, here and here) analyzing different options and their potential, or lack thereof. I continue to maintain that incumbents with boxes already in the home - mainly cable, satellite, telcos - are best-positioned to bridge the current divide between broadband and TV.
A breakthrough value proposition for Comcast would be allowing its subscribers to gain easy access on their TVs to YouTube, Break.com, Metacafe, NYTimes.com and all the others broadband sites that have surged in popularity. In theory, Comcast and other cable operators have always been about providing more video choices to subscribers. But the caveat has been those choices are only offered when Comcast makes a deal to carry these new channels. With broadband it's a wide open world. Any video provider - deal or no deal would gain access. This "openness" is a fundamental paradigm change for Comcast and other "walled garden" loyalists.
Surmounting this change to its business and cultural model are in fact Comcast's #1 strategic challenge. How to effectively respond to customers' broadband desires, while maintaining a robust economic and competitive model? When Brian Roberts, and others in the cable industry are finally ready to address the question of how they'll integrate broadband into their TV-based user experience, that will be a keynote well worth watching.
Categories: Broadcasters, Cable Networks, HD, Portals, Telcos
Topics: Comcast
-
Broadband Video vs. IPTV, The Differences Do Matter
It's funny how often I'll be talking to someone and they will casually start interchanging the terms "IPTV" and "broadband video/online video/Internet TV".
The fact that many people, including some that are actually well-informed, continue doing so is a reminder of how nascent these delivery platforms still are, and how common terms of use and understandings have yet to be established.
Yet it's important to clarify that there are differences and they do matter. While some of the backend IP transport technology is common between IPTV and broadband video, the front end technology, business models and content approaches are quite different.
In presentations I do, I distinguish that, to me at least, "IPTV" refers to the video rollouts now being pursued by large telcos (AT&T, etc.) here in the U.S. and internationally. These use IPTV-enabled set-top boxes which deliver video as IP packets right to the box, where they are converted to analog video to be visible to the viewer. IPTV set tops have more capabilities and features than traditional MPEG set-tops, and telcos are trying this as a point of differentiation.
However, at a fundamental level, receiving IPTV-based video service is akin to subscribing to traditional cable TV - there are still multi-channel tiers the consumer subscribes to. And IPTV is a closed "walled garden" paradigm - video only gets onto the box if a "carriage" deal has been signed with the service provider (AT&T, etc.). IPTV can be viewed as an evolutionary, next-gen technology upgrade to existing video distribution business models.
On the other hand, broadband video/online video/Internet TV (whatever term you prefer) is more of a revolutionary approach because it is an "open" model, just like the Internet itself. In the broadband world, there's no set-top box "control point" governing what's accessible by consumers. As with the Internet, anyone can post video, define a URL and quickly have video available to anyone with a broadband connection.
The catch is that today, displaying broadband-delivered video on a TV set is not straightforward, because most TVs are not connected to a broadband network. There are many solutions trying to solve this problem such as AppleTV, Microsoft Media Extender, Xbox, Internet-enabled TVs from Sony and others, networked TiVo boxes, etc. Each has its pros and cons, and while I believe eventually watching broadband video on your TV will be easy, that day is still some time off.
Many people ask, "Which approach will win?" My standard reply is there won't be a "winner take all" ending. Some people will always prefer the traditional multichannel subscription approach (IPTV or otherwise), while others will enjoy the flexibility and features broadband's model offers. However, for those in the traditional video world, it's important to recognize that over time broadband is certainly going to encroach on their successful models. Signs of change are all around us, and many content companies are now seizing on broadband as the next great medium.UPDATE: Mark Ellison, who is the SVP of Business Affaris and General Counsel at the NRTC (National Rural Telecommunications Cooperative, an organization which delivers telecom solutions to rural utilities) emailed to clarify that it's not just LARGE telcos that are pursuing IPTV, but many SMALLER ones as well. Point well taken Mark, it was an oversight to suggest that IPTV is solely the province of large telcos like AT&T.Categories: Cable TV Operators, IPTV, Technology, Telcos
Topics: Apple, AppleTV, Media Extender, Microsoft, Sony, TiVo, XBox
-
Telcos Embrace Video at NXTcomm

I made a quick trip to NXTcomm earlier this week to moderate a panel, have some meetings and walk the show floor. For those of you not familiar, NXTcomm is the joint event of the Telecommunications Industry Association (the association for telecom technology vendors) and the U.S. Telecom Association (the association of telecom service providers). This show, which drew about 20,000 people, grew out of Supercomm and GlobalComm conferences, is now the telco industry's main confab.
What struck me the most was how much the show focused on video and entertainment. I was at Supercomm years ago and remember it being a bunch of telco engineers inspecting the latest gear for routing phone calls. No more. As new NXTcomm executive director Wayne Crawford explained in an interview with Telephony magazine, "NXTcomm has a much broader conference program in terms of different types of technologies represented a and much more of its emphasis is placed on technology as it relates to the entertainment industry.
Boy, was this emphasis was evident on the show floor. All the big vendors, Microsoft, Intel, NEC, Nortel, Tandberg and others had major booth visibility around video. The telco industry is coming after the IPTV and broadband markets hard, and all of these vendors are providing the enabling gear. Having attended the Cable Show last month, NXTcomm doesn't yet have the glitzy booths of a Viacom or NBCU, but it wouldn't surprise me if they did by next year or the year after. Video is a major priority of the telco industry. Very exciting to see.
Categories: Telcos
Topics: Intel, Microsoft, NEC, Nortel, NXTcomm, Tandberg
-
Prognosticating P2P's Possibilities and Pitfalls - May E-Newsletter
With Joost's launch upon us, BitTorrent going mainstream, Akamai buying Red Swoosh and a raft of other peer-to-peer (P2P) initiatives underway, it's time to consider legitimate P2P's possibilities and pitfalls.First a disclaimer: I don't pretend to know all of the technical ins-and-outs of P2P, but I think I know enough to be dangerous. Here's my current take: P2P has a ton of potential as a legitimate distribution platform, but has to navigate some significant challenges if it is to succeed.A P2P PrimerFor those of you new to the P2P game, in essence, P2P's big advantage is that it allows users themselves to become servers of content to other users. In doing so, the load for delivering content is shifted from central servers to the "nodes" or users on the P2P network. Until relatively recently, P2P was popularly associated with the illegal "file sharing" networks (Napster, KaZaa, etc.), most of which were (and still are) used by users to swap audio or video files without permission of the copyright holder. Users could look up where certain content resided and then download it accordingly.What's new about P2P is that many (e.g. Joost, BitTorrent, others) see it as an important, if not essential, way for video to be legitimately distributed. P2P companies argue that the Internet's current architecture cannot effectively scale to deliver large quantities of video (especially live streams) in an economic manner. Since P2P gives users the ability to directly share with other users, P2P also has a potentially disruptive effect on the overall value chain and how video aggregators continue to establish value for themselves. P2P requires users to install client software on their computers. These clients are then available on the P2P network, sending files to subsequent users requesting content that they have already stored. In the case of video or audio, files can be delivered for either download or streaming.All of this is intended to happen invisibly to the average broadband video user. Of course, to nobody's surprise, the average user couldn't care less how video actually gets to his or her computer, as long as it gets there quickly and in reasonably good shape.Potential AboundsP2P is a potentially big deal for the biggest broadband video content providers. That's because delivering large volumes of video in the traditional client-server paradigm is still pretty expensive, notwithstanding the significant declines in content delivery networks' (CDN) pricing. With everyone forecasting huge increases in broadband video consumption, together with larger video files (due to better encoding, High Definition, etc.), getting a handle on delivery costs is a key challenge for content providers.Compounding matters is that broadband video business models remain relatively immature, so expense containment is all the more important. P2P allows these content providers to shift all or some of the responsibility for video distribution to the users themselves, while establishing direct connections with users (i.e. no 3rd party distribution costs). The users' computers are leveraged for both storage and delivery, while the bandwidth is essentially free, since users upload content using the local broadband ISP's network, not the content provider's CDN service. If P2P succeeds, its potential to cut content providers' delivery costs, while delivering high-quality video, is obviously very significant.Important Challenges Lie AheadOf course, potential is one thing, reality is another. From my vantage point, consumers' willingness to become P2P nodes and ISPs' restraint in blocking P2P traffic represent the biggest obstacles to P2P's future success. First the consumer acceptance challenge. Getting the P2P client on millions of users' computers or into their living rooms is not trivial. In this era of spyware, malware, viruses and other technical nuisances, mainstream Internet users are becoming more reluctant than ever about loading anything onto their machines that doesn't come from a recognized and trusted brand. Since P2P's whole promise relies on files being propagated to many users, anything that limits this from happening is obviously very detrimental to P2P's success.Then there is the even thornier issue of how broadband ISPs are going to react to users clogging up precious upstream bandwidth by serving as nodes. Virtually all American broadband ISPs offer "asymmetric" Internet access, meaning that the amount of bandwidth offered in the upstream path is usually only a fraction of that provisioned for the downstream path (this is due to some fundamental limitations related to the way that ISPs' networks are allocated). Re-architecting these networks for potentially burgeoning upstream traffic flows would be cost-prohibitive and a non-starter.To date, broadband ISPs have used "traffic shaping" technology to identify and limit P2P traffic. They have also kicked customers off their networks who have used too much bandwidth (a little secret in the industry). All of this has been sort of OK to do when most P2P use was for illegitimate file sharing. But what happens when it's for legitimate use, such as Joost or the newly legitimate BitTorrent? Limiting users' access to their full broadband service is going to evoke howls of protest.And of course, remember that the net neutrality proponents are waiting to pounce on any sign of broadband ISPs de-prioritizing or worse, blocking, certain types of traffic. Net, net, a big wildcard in P2P's success is how ISPs are going to react.Planning for P2P SuccessP2P proponents need a game plan to overcome these looming issues. Here's what I think makes sense: Well-established branded content players will need to take on the primary role for P2P client distribution. Of course, this approach has been used for previous media players' distribution (i.e. Real, WMP, Flash, etc.) and for updates. We've all had the experience of being asked to download player software or an updated version of previously installed software. P2P client distribution could be no different.But what will incent major content providers to assume this responsibility on a mass scale? They'll have to see real (not theoretical) business cases for delivery cost reductions and quality improvement. Of course, getting paid to become P2P client distributors (either in cash, or as part of distribution deal discounts, or some hybrid of the two) would also clear the way. Companies like Joost and BitTorrent need to remember that while their brand awareness among the Internet's cognoscenti is high, among more mainstream users it is still low. So leveraging their content partners' brands to turbo- charge distribution is key.BitTorrent, for one, is already doing this with their BitTorrent DNA technology. Another opportunity for P2P client distribution is embedding it in various consumer devices. For example, BitTorrent also offers a software development kit (SDK) that consumer electronics and chip makers can use to embed the P2P client in devices. This removes P2P download complexities for users, and is intended to make P2P usage completely invisible. The ISP solution seems more complex.Some believe that ISPs should look at P2P as a business opportunity to deliver a quality-of-service (QOS)-guaranteed platform to the P2P application providers such as Joost and BitTorrent. This would be accomplished by installing caching servers in broadband ISPs' facilities. These would essentially allow ISPs to serve content locally, mainly relying on the P2P protocols to deliver from the caches when appropriate, instead of from the nodes. This approach would preserve upstream bandwidth and limit ISPs' need to increase their peering capabilities to handle video coming in from the Internet backbone, while also leveraging P2P's scalability.This "peer-assisted" approach may be the optimal migration path to P2P adoption from an ISP perspective. Though the economics still need to be fully fleshed out, I've heard a pretty persuasive argument for this model from a company named PeerApp (disclaimer, they're a client), which is worth understanding further if P2P affects your business. One way or another, ISPs need to be brought into the P2P fold. Simply ignoring them or relying on their reluctance to tempt the net neutrality gods is not a sound business approach.Wrapping UpP2P offers very exciting potential to enhance users' broadband video experiences. For content providers, it holds the promise of profitably scaling up their broadband video activities. It will be very interesting to see how key P2P players navigate impending challenges to their success.Categories: Broadband ISPs, Cable TV Operators, P2P, Telcos
Topics: BitTorrent, Joost, Net Neutrality, PeerApp
Posts for 'Telcos'
Previous |


