-
Google Content Network Has Lots of Potential, Implications
Many of you know that Google has recently begun distributing short animated videos from Seth MacFarlane (creator of TV's "Family Guy") to a wide network of sites that previously only received ads from Google, through their participation in AdSense. The company dubs this the "Google Content Network" (GCN for short), and from my vantage point, it has a lot of potential and implications for other players in the video distribution value chain. Yesterday, I spoke to Alexandra Levy, Google's Director of Branded Entertainment, and the point person for driving this initiative.
The first thing that resonates for me about GCN is that Google's vision for it harmonizes perfectly with my concept of the "Syndicated Video Economy." VideoNuze readers know that last March I introduced the SVE concept to capture a trend that I was noticing: an ecosystem was forming to distribute broadband video widely across the Internet, in contrast to the traditional, narrower distribution model.
Alex echoed the SVE, saying that in her many conversations with content producers, finding an audience is their top challenge. Great content, unwatched, is like the proverbial tree that falls in the forest when nobody is around to hear it.
So enter GCN, which Google rightly sees as a "media distribution platform." To understand its implications fully, you have to evaluate its potential to all relevant constituencies: Users get great updated content served to them at the sites they already visit. Those sites benefit from offering premium content, while also receiving a revenue share on the accompanying ads. The content provider benefits from leveraging Google's vast AdSense network to have video "pushed" to relevant audiences, increasing viewership and engagement. And advertisers' brands benefit from adjacency to premium content that is sought after and compelling.
Of course, last but not least, Google benefits from being the intermediary in this whole process. We all know from Google's massive success in web search that being the intermediary in a model where all constituent interests are neatly aligned creates near-infinite economic value. While Alex concedes the MacFarlane video (which is sponsored by Burger King and was brokered by Media Rights Capital) is still an "experiment," GCN sure does seem to bear a lot of resemblance to Google's traditional search model in the alignment of constituent interests.
Another twist here is that users who click for more video are driven back to MacFarlane's YouTube channel (already the 69th most subscribed channel, with almost 70K subscribers), which drives habituation, a key lever for ongoing video success as any network TV executive will admit. In this light, GCN gives Google a way of finally tying its powerful AdSense engine to YouTube. I'm not suggesting that Google is sweating the ROI on its $1.6 billion YouTube acquisition, but GCN surely looks like a way to move YouTube far beyond its roots as everyone's favorite UGC aggregator.
Alex is quick to point out that GCN does not budge Google from its often-stated position that it is not a content creator. Rather, it's using GCN to connect brands, content producers and users. If that connecting process drives audiences and generates revenues for content producers - and admittedly the proof is not yet in - that would give Google a lot of disruptive capital to help shape the video landscape. Just so nobody gets carried away, Google announced a similar experiment 2 years ago with MTV that fizzled out. So the company has yet to prove its experiment works and that it is fully committed to the GCN model.
Still, I continue to believe that video syndication - and the accompanying benefits to all - is a key, key driver of how the broadband video landscape is going to unfold. As a small teaser, there will be more interesting news on the syndication front early next week. Stay tuned.
(And note that the syndicated video economy will be one of the main topics of discussion at the Broadband Video Leadership Breakfast "How to Profit from Broadband Video's Disruptive Impact" with our A-list group of panelists, including Google's David Eun, on November 10th. Click here to learn more and register for special early bird rate.)
What do you think? Post a comment now.
Categories: Advertising, Aggregators, Indie Video, Syndicated Video Economy
Topics: Google, Google Content Network, Seth MacFarlane, YouTube
-
Google, Others Syndicating Video Into the Long Tail
The trend toward widespread video syndication to small-to-medium sized web sites continues to gain momentum.
Two recent initiatives - plus others I expect are still to come - point to the increasing likelihood that broadband video's eventual distribution model will look far different from traditional, tightly-controlled approaches. I'm becoming more convinced that "syndicated video economy" concept I sketched out in March is where the market is heading.
The first initiative, covered in a recent NYTimes article, "Google and Creator of 'Family Guy' Strike a Deal" suggests that Google may finally be ready to point its powerful AdSense engine toward video distribution.
 AdSense, as many of you likely know, essentially created a "long tail of advertisers" by dispersing targeted pay-for-performance keyword-based ads to tens of thousands of small-to-medium sized web sites. Including Google Ads has become a no-brainer for many sites seeking to easily pick up a few extra bucks by allocating some on-site real estate to AdSense.
AdSense, as many of you likely know, essentially created a "long tail of advertisers" by dispersing targeted pay-for-performance keyword-based ads to tens of thousands of small-to-medium sized web sites. Including Google Ads has become a no-brainer for many sites seeking to easily pick up a few extra bucks by allocating some on-site real estate to AdSense.Now instead of distributing ads, Google is looking to take the AdSense model a step further by distributing video content (along with ads) to myriad web sites hungry for video, and cash. First up are comedic webisodes from Seth MacFarlane (creator of Fox's "Family Guy"). Google's proposition to small, and even larger sites, makes sense: we'll give you free high-quality video content, all supported by pay-for-performance ads. You get great content and can make money at it. What's not to like? Not much in my opinion. It seems like such a compelling model that one wonders why Google hasn't done this earlier. In fact, they did. Back in August 2006, Google announced a test with MTV to do exactly the same thing (the ensuing YouTube-Viacom litigation no doubt scotched the test). Hopefully this time around Google will have more luck.
Meanwhile, hyper video syndication is not just for the mighty like Google. Consider Jambo Media, a two year-old company with 12 employees which has built out a syndication network now generating over 2 million video views per day. Web sites like BestCelebGossip.com, Epigee.org and MensTech.com may not be household names, but, as Jambo's CEO and co-founder Rob Manoff explained to me, they are representative of virtually unlimited long tail web publishers eager for video, but unable or unwilling to create it themselves.

Rob and his team of ex-affiliate marketing and advertising veterans have created the Jambo Video Network by licensing video from sources such AP, iVillage, Ivanhoe Broadcast News, and then packaging them into "channels" for distribution in a Jambo video player. Of course ads come along with the video content (though Jambo has a separate ad-free "JamboCast" white label solution in the works too).
Affiliate sites can login to their Jambo account to select which channels to receive while customizing the look and feel of the video player. Over 100 sites have affiliated, which Rob believes will grow to several hundred by the end of '08, driving a projected 5 million views/day. Rob said that sites earn $2-4 effective CPM with revenue per day ranging from $10-30 on the low end all the way up to $1,000/day on the high end.
Jambo is pursuing a space that syndicators like Roo, Voxant, ClipSyndicate, Newsmarket and others have been in for a while. All of these players, along with now Google, are doing what Rob articulates well: creating video ad inventory where none previously existed. Such is the power of syndication in the frictionless Internet environment. And why smart content providers - from startups to established TV networks - are recognizing that increasingly, syndication is where the broadband market is heading.
Note: if you want to learn more about syndication and how one big content provider is succeeding with it, please join me for a webinar entitled, "Profiting from the Syndicated Video Economy." The webinar is sponsored by Akamai and will feature a presentation from Greg Clayman, Executive VP, Digital Distribution and Business Development, MTV Networks and me. Registration is free.
Categories: Advertising, Indie Video, Syndicated Video Economy
Topics: ClipSyndicate, Google, Jambo Media, Newsmarket, ROO, Voxant
-
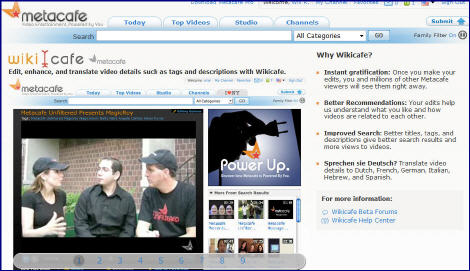
Metacafe's New Wikicafe Refines Metadata Process
Metacafe, the short-form video aggregator with 30 million monthly visitors, has unveiled a new feature called "Wikicafe" which addresses the daunting and ongoing problem of how to find exactly the video you're looking for and gain high-quality recommendations.
Now in beta and available to its registered users only, Wikicafe is philisophically similar to Wikipedia, which involves users in building the knowledge base around specific content. Similarly, Wikicafe's goal is to involve users in continually refining the metadata for specific videos. This in turn will yield improved search and discovery for subsequent users.
Wikicafe is an intriguing spin on video search which I have discussed a number of times. Last week I spoke to Eyal Hertzog, Metacafe's co-founder and now chief creative officer, who's leading the charge on Wikicafe. This was the first briefing Metacafe has given on the new Wikicafe feature.
Eyal notes that there are really two ways to tackle content navigation. One is through super-sophisticated algorithms and distributed hardware, an approach epitomized by Google. The other is community-based collaboration, an approach epitomized by Wikipedia. He is biased toward the latter because he believes that the likelihood that the original metadata assigned by the video's creator (and even subsequent metadata that may be produced by technology-based approaches) will never be as accurate as that which is produced by other humans with specific domain knowledge.
Thus the idea behind Wikicafe: if given the right tools, Metacafe's users will create and maintain the most accurate metadata for Metacafe's vast collection of videos. It's a classic "wisdom of crowds" approach. Of course, it also requires that users act appropriately or things could spin out of control very quickly.
Wikicafe is very straightforward to use. Once logged in, you simply click on "Editing Options" in the upper right corner of each video. Then you can start editing the video's title, tags, description and then save your changes. You can track your changes (and those that others add), be notified about subsequent changes and start a discussion about your changes. You can even translate your changes into other languages. As Eyal explains it, this "collaborative taxonomy" allows redirection between related terms ("PS3" and "Playstation3"), clarifies ambiguous words, resolves hierarchical terms and connects different languages.
In a sense, Wikicafe is a natural evolution for Metacafe, which has always emphasized community involvement in filtering which content gets added and promoted on the site. With a group of active, passionate users and Wikipedia as a model, it seems likely that Wikicafe will gain traction in the community.
What then becomes especially intriguing is the potential for carrying the Wikicafe approach outside of Metacafe's borders for the larger universe of broadband video. Could users eventually become an augment or even replacement to top-down driven video guides, the norm in today's cable and satellite offerings? It's an interesting vision to contemplate. First let's see how Wikicafe evolves in the Metacafe community.
What do you think? Post a comment now!
Categories: Aggregators, Technology, Video Search
Topics: Google, MetaCafe, Wikipedia
-
Viacom - Google/YouTube Litigation Moves Into Slippery Territory
If you were off the grid last week celebrating the July 4th holiday, there were some important fireworks in the ongoing Viacom - Google/YouTube litigation well worth paying attention to.
Judge Louis Stanton of the US District Court in New York, who is presiding over the litigation, handed down an opinion that granted and denied some of what each party was requesting. The opinion is here. I have read it and below is my synopsis (remember I'm not a lawyer):
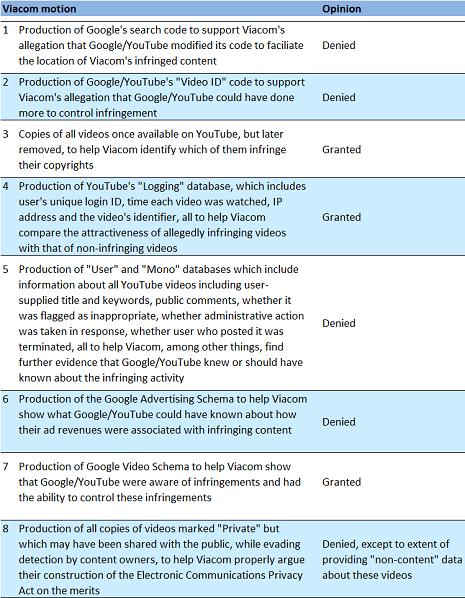
The fourth item is the one that has gained the most attention and controversy. Privacy advocates are ballistic that this is a violation of users' privacy rights. Specifically they have cited Judge Stanton's characterization of Google/YouTube's objection to this particular Viacom request on the basis of privacy concerns as "speculative." A cottage industry of ridicule has broken out across the blogosphere regarding whether the 80 year-old Judge Stanton is sufficiently tech literate to grasp online privacy concerns. Many believe Viacom will use the data to sue individual users for viewing pirated copies of Viacom's programs on YouTube.
Like everyone else, I'm concerned about privacy here as well and recognize that Judge Stanton has moved this case into some very slippery territory. Yet, at a higher level, I'm feeling some resentment toward Google and YouTube, especially given its famous "do no evil" mantra. There is no question that they knew pirated versions of key Viacom (and other) programs were showing up on YouTube, yet at the time months went by without them candidly addressing the issue and doing something sufficiently proactive about it. To many, including me, the standoff then was (and continues to be) a high-stakes battle between two multi-billion dollar companies jockeying for negotiating leverage.
When we use various web sites (whether for broadband or other uses), there is an implicit and explicit understanding that our privacy will not be trifled with. Sites have a right to defend their business practices based on their interpretation of the existing laws, but they need to be balanced by what impact their actions may ultimately have for their users. Each of us has our own interpretation of whether Google/YouTube should have done more to protect Viacom's and others' copyrights, but as Judge Stanton's decision shows, to what extent YouTube's users' privacy is protected is now entirely up to his interpretation.
What do you think? Post a comment and let everyone know!
Categories: Cable Networks, Video Sharing
Topics: Google, Viacom, YouTube
-
YouTube: "Over-the-Top's" Best Friend
The announcement a couple of weeks ago that YouTube was partnering with TiVo got me to thinking that YouTube is probably the best friend that so called "over-the-top" or "cable bypass" aspirants could have.
As a quick refresher, "over-the-top" and "cable bypass" refer to the emerging category of devices and service providers seeking to bring broadband video to the consumer's TV, but without the involvement of existing video providers such as cable and satellite. Some of these efforts (Apple TV, Vudu and Internet-enabled TVs) are positioned as augmenting incumbent providers, while some (Building B, others) are meant to compete directly.
Today's players share the common trait of being closed, "walled gardens," offering only certain content that they select. This contrasts with the open Internet/broadband model, where users are able to access any content they choose. Many of you know that I have been a strong proponent that open is the winning competitive path for aspiring over-the-top players.
If the over-the-top crowd adopts the open approach, YouTube is their perfect ally; it is the best-known brand name in broadband video, has the largest library of both user-generated and increasingly premium
 video and has huge loyalty. Positioned properly it could be a killer value proposition for over-the-top players. I've previously argued that Apple missed the boat by not adopting this positioning for Apple TV.
video and has huge loyalty. Positioned properly it could be a killer value proposition for over-the-top players. I've previously argued that Apple missed the boat by not adopting this positioning for Apple TV.I talked last week with David Eun, VP of content partnerships at Google and Chris Maxcy, head of biz dev for YouTube, and they both made clear that the goal is to morph YouTube from a consumer destination site to a full-fledged video platform distributing video everywhere - devices, mobile, web sites, others. To this end, YouTube recently published an expanded set of APIs to allow 3rd parties to gain easier access to YouTube's content. This of course is great news for over-the-top devices, who should have considerable flexibility for how to incorporate YouTube into their offering. For now TiVo is leading the way in offering YouTube, albeit to a very small audience.
If you were wondering whether YouTube or Google itself will enter the device business, that seems unlikely. David and Chris were clear in saying that devices are not their core competency, and they'll leave it to others to decide how to implement the YouTube APIs and create and test various user experiences. Meanwhile with more premium content flowing into YouTube, its value as an over-the-top partner only increases.
What do you think? Post a comment!
Categories: Aggregators, Devices
Topics: Apple, Apple TV, Google, TiVo, VUDU, YouTube
-
Welcome to the "Syndicated Video Economy"
I am ever mindful of the old adage about "missing the forest for the trees" as I try daily to understand the often minor feature differences between competing vendors or the nuances of startups' market positioning. As we all know, when you get too close to something, it's quite easy to lose the larger perspective. So periodically I think it's essential to take a huge step back to try to identify the larger patterns or trends that crystallize from the daily frenzy of deals and announcements.
As a result, I've come to believe that recent industry activity points to an emerging and significant trend: the early formation of what I would term the "syndicated video economy." By this I mean to suggest that I'm
 seeing more and more industry participants' strategies - in both media and technology - start from the proposition that the broadband video industry will only succeed if video assets are widely dispersed and revenue creatively apportioned.
seeing more and more industry participants' strategies - in both media and technology - start from the proposition that the broadband video industry will only succeed if video assets are widely dispersed and revenue creatively apportioned. For content providers the notion of widespread video syndication big change in their business approach. In the past year I think we've observed content providers of all stripes transition from "aggregating eyeballs", to "accessing eyeballs," wherever they may live now or in the future: portals, social networks, portable devices, game consoles, etc. Underlying this shift is the realization that advertising-based revenues are going to fuel the broadband video industry for the foreseeable future. The ad model requires scale and syndication is the best way to deliver it.
This shift by content providers has been accompanied by a loosening of traditional tightly-controlled, scarcity-driven distribution strategies, an acknowledgement that fighting newly-empowered consumers is a futile exercise. The evidence of this shift abounds. Consider the broadcasters like CBS, NBC and Fox, which through their affiliates (Hulu, CBS Audience Network) are syndicating programming to many portals/aggregators (e.g. Yahoo, MSN, AOL, YouTube), social networks (e.g. Facebook, MySpace, Bebo) and others. And Disney's Stage 9 digital studio, which premiered with YouTube and explicitly plans to tap into broadband video hubs. And cable networks like MTV Networks, which is pursuing a plethora of distribution deals. And traditional news-gatherers like local TV stations, newspapers and news services (e.g. Reuters, AP) which have stepped up their activity to scatter their video clips to the Internet's nooks and crannies. And the list goes on and on.
Taking their cue from the media companies' strategy shift, technology entrepreneurs and investors have ramped up their focus on this market opportunity. The prospect of the syndicated video economy blossoming drives news/information distributors such as Voxant, ClipSyndicate, Mochilla, TheNewsMarket and RedLasso, an ad manager such as FreeWheel, and a content accelerator such as Signiant, plus many others. Then there are more established companies guiding areas of their product development process by the prospect of the syndicated video economy's growth: Google, WorldNow, Akamai, thePlatform, Anystream, Maven Networks, Brightcove, PermissionTV and plenty of others (apologies to those I've left out!)
All of this suggests that the eventual "value chain" of the broadband video industry will look quite different than the traditional one (for more on this, I've posted some my slides from late '07 here.) As with all economies, in the nascent syndicated video economy there is vast interdependence among the various players, not to mention shifting market positions and degrees of pricing power and negotiating leverage. It is far too early to gauge who will emerge as the syndicated video economy's winners and losers. But make no mistake, lots of energy and investment will be expended trying to nurture its growth and exploit its opportunities.
Do you see the syndicated video economy forming as well? Post a comment and let us all know!
Categories: Advertising, Aggregators, Broadcasters, Cable Networks, Newspapers, Portals, Startups, Syndicated Video Economy
Topics: Akamai, Anystream, ClipSyndicate, FreeWheel, Google, Mochilla, RedLasso, Signiant, TheNewsMarket, thePlatform, Voxant, WorldNow
-
Three Broadband Video Themes from February `08
At the end of each month I plan to step back and recap a few key themes from recent VideoNuze posts. Here are three from February '08:
Brand marketers embrace broadband video
One clear theme from the past 4 weeks has been brand marketers' accelerating moves into the broadband video space. This was on full display by select Super Bowl and Oscar advertisers. We are witnessing an unprecedented commitment by brands to create their own entertainment/information video content and also to induce consumers to create brand-related video through user-generated contests. As I detailed in yesterday's webinar, examples in the former category include Kraft/Tassimo, J&J, CIT Financial and GoDaddy.com, while examples in the latter category include TideToGo/MyTalkingStain.com, Heinz/Top This, Dove Cream Oil Body Wash and T-Mobile/Current TV.
Through VideoNuze I track all brands' broadband video initiatives, and it is clear that their involvement in this new medium is intensifying. Faced with splintering audiences, ad-skipping DVRs and changing media consumption habits - particularly by younger demos - brands have no choice but to get into broadband video. This results in an entirely different awareness/engagement paradigm than we're accustomed to from the world of interruptive TV advertising. Brands today increasingly recognize that a key way to create loyalty (and generate sales!) is by engaging the audience on its terms, using broadband and other technologies to accomplish this.
Monetization is the #1 challenge
Another key theme of the past month was the ongoing quest for broadband video monetization. As I also mentioned in yesterday's webinar, this is the number 1 business challenge for all broadband video industry participants - both content and technology providers. Two companies I wrote about this month, EveryZing and Veveo, are focused on improving content discovery, which leads to more consumption and revenue-generating opportunities. I also wrote about Jake Sasseville, a young entertainer who is pioneering multi-platform initiatives to forge a new revenue model.
Innovation is key in this space. Next week I'll be writing about Freewheel, an innovative startup that's just surfaced, which is providing a new approach to managing broadband video advertising. And yesterday, Magnify.net, one of my favorite early-stage companies, which focuses on enabling video content distribution, announced that it has raised an additional $1 of financing.
In addition, the big dogs of the technology and media landscape are in hot pursuit of improved video monetization as well. This month alone brought news of Yahoo's acquisition of Maven Networks, an ad-centric video platform, Google's beta rollout of AdSense for video, and the hostile bid by Microsoft for Yahoo, a deal that has vast longer-term implications for online and broadband video advertising. In short, monetization is a key focus for all large and small industry participants - cracking this nut is crucial to the long-term health of the industry.
Net neutrality re-surfaces
Lastly, this month also brought a lot of news on the regulatory front. Twice I wrote about "net neutrality," a regulatory concept its proponents believe will keep the Internet free from discrimination by broadband ISPs. While I don't agree with their viewpoint, what is clearly true is that net neutrality is being spurred by the massive adoption of broadband video, which places an unprecedented load on broadband ISPs' networks.
So that's it for this leap year month. Three themes you'll be hearing much more about going forward: brand marketers' broadband video initiatives, video monetization and net neutrality. See you on Monday for the start of a new month!
Categories: Advertising, Brand Marketing, Broadband ISPs, Regulation
Topics: EveryZing, FreeWheel, Google, Magnify.net, Maven Networks, Microsoft, Net Neutrality, Veveo, Yahoo
-
Making Sense of Google's AdSense for Video
For me, Google and its initiatives in broadband video advertising and distribution have conjured a comparison to the lion of the jungle. Like the lion, Google often seems to be slumbering in this hot space, yet every once in a while it wakes up, raises its head and roars to the market with a new video advertising announcement. These roars serve as a reminder to others that it is, of course, the king of the online jungle.
But then, rather than following up these periodic roars with steady follow-on news of accomplishments,
 financial success and new features, Google inexplicably seems to go back to its slumber, thus returning the jungle to the startup antelopes and established elephants to do the spade work of building the broadband video ad market.
financial success and new features, Google inexplicably seems to go back to its slumber, thus returning the jungle to the startup antelopes and established elephants to do the spade work of building the broadband video ad market. Yesterday, Google roared again, this time announcing the "beta" release of its AdSense for Video product and the launch of its destination "Video Advertising Solutions" center, which explains all of Google's video ad opportunities and offers very well produced explanatory videos.
Video ads have been previously announced by Google, and AdSense for video builds on these by allowing a broad range of content providers to tap into AdSense for graphical or text overlay ads on their video streams. Google announced a large network of content and platform partners, augmenting the massive inventory already available on YouTube.
By tying AdSense for Video to its AdWords capability, advertisers have a one-stop shop for text and video ads contextually placed across web pages and video streams. Since participating publishers can expose a percentage of their streams to AdSense, they enhance their overall monetization opportunities.
I spoke with a number of people in the advertising/technology/content communities yesterday and there was a consensus that Google's actions help validate the broadband video advertising market opportunity and overlays in particular (note Google doesn't support pre-rolls). I agree with those who said that with the overall market growing fast, Google isn't terribly competitive with other contextual ad firms; there's clearly room for more than just one player.
On the content provider side, of course any initiative to better monetize video streams, particularly by an established player like Google, will always be welcomed. This feeling is offset somewhat by the underlying anxiety that all content providers have vis-a-vis Google - it is part competitor on the content side, and also part competitor on the ad sales side. This is particularly true of YouTube, which offers significant distribution benefits to content providers, but while also competing for eyeballs.
For content providers' advertising revenues, while AdSense promises improved monetization, it might also lead to channel conflict as advertisers may try to pay less for targeted ad inventory available through Google rather than from the provider itself. This has been less a concern in traditional web publishing, because Google hasn't sold display ads. The risk is that over time AdSense for video could lead to a "hollowing out" of content providers' crucial ad sales capabilities. This dynamic reinforces why it's so important that those who work with AdSense for video set business rules and then adhere to them, rather than be too tempted to grab the easy, short-term money Google can provide.
With the beta of AdSense for video, Google has again reminded the market that its unparalleled technology, content, monetization and financial strength makes it the lion of the online jungle. It is well-positioned to also become the lion of the broadband video ad jungle. Let's see if Google keeps on roaring, or if it appears to lapse back into slumber.
Categories: Advertising
-
CES 2008 Broadband Video-Related News Wrap-up
CES 2008 broadband video-related news wrap-up:
Panasonic and Comcast Announce Products With tru2way™ Technology
Panasonic And Comcast Debut AnyPlay™ Portable DVR
NETGEAR® Joins BitTorrent™ Device PartnersD-Link Joins BitTorrent™ Device Partners
Vudu Expand High Definition Content Available Through On-Demand Service
Sling Media Unveils Top-of-Line Slingbox PRO-HD
Open Internet Television: A Letter to the Consumer Electronics Industry
Paid downloads a thing of the past
Samsung, Vongo Partner To Offer Movie Downloads For P2 Portable Player
Comcast Interactive Media Launches Fancast.com
New Year Brings Hot New Shows and Longtime Favorites to FLO TV
P2Ps and ISPs team to tame file-sharing traffic
ClipBlast Releases OpenSocial API
Categories: Advertising, Aggregators, Broadband ISPs, Broadcasters, Cable Networks, Cable TV Operators, Devices, Downloads, FIlms, Games, HD, Mobile Video, P2P, Partnerships, Sports, Technology, UGC, Video Search, Video Sharing
Topics: ABC, BitTorrent, BT, Comcast, D-Link, Disney, Google, HP, Microsoft, NBC, Netgear, Panasonic, Samsung, Sony, TiVo, XBox, YouTube
-
Highlighting 3 Partnerships Announced at CES
Among the many partnership announcements at CES this week, there are a number worth highlighting. Today I focus on the following three:
Viacom syndication - Viacom announced syndication deals for MTV Networks' stable of content with five leading broadband video sites: Dailymotion, GoFish, Imeem, MeeVee and Veoh. As those of you who have been following my previous posts know, I believe syndication is a critical engine in driving the advertising business model, which itself is the key to broadband video succeeding. As a result, I follow these syndication deals closely.

I've previously been critical of MTVN which appeared reluctant about syndicating its content when it launched its DailyShow.com destination site. However, with its recent deal with AOL, and now these five deals, it appears that MTVN does in fact believe syndication is the way to go. As one of the biggest cable network groups, MTVN is a key barometer for other networks' moves, so I view this as a real positive for the market.
Panasonic/Google - In this deal, Google and Matsushita announced that YouTube videos and Picasa photos would be directly accessible on new model Panasonic HDTVs launching in Q2 '08. Ordinarily I wouldn't be
 too excited about a deal like this, a permutation of which we've seen with other TV makers such as Sony.
too excited about a deal like this, a permutation of which we've seen with other TV makers such as Sony. Yet this one rises in potential importance because YouTube is not just the most popular video site - with 40% of all video traffic - but because Google is determined to turn YouTube into a platform for legitimate content distribution. This was underscored by the Sony mini-sode deal also announced this week, and the
 many partnerships YouTube has already struck with premium content providers. If successful (and there are many if's to be sure), YouTube would be far more than a scraggly collection of UGC. So, marry a broad-based premium video aggregator to HDTVs and you could see a new device/content model emerge.
many partnerships YouTube has already struck with premium content providers. If successful (and there are many if's to be sure), YouTube would be far more than a scraggly collection of UGC. So, marry a broad-based premium video aggregator to HDTVs and you could see a new device/content model emerge.BitTorrent device deals Netgear and D-Link - In a less publicized move, BitTorrent announced expanded deals with Netgear and D-Link covering a range of home networking products, with an emphasis on HD distribution. BitTorrent, which has been steadily legitimizing itself from its P2P file-sharing roots, has launched an aggressive SDK program called BitTorrent Device Partners, intended to permeate the market with its client software. BitTorrent also integrates easy access to its digital download store with these partners as well.

While I'm not very bullish about the market potential of bridge devices from companies like Netgear and D-Link, I do believe that P2P distribution has a real role to play in content distribution, especially for heavy HD files. I continue to see P2P as more of a "peer assist" play. To the extent that BitTorrent can continue getting its software into multiple devices, it gains validation and strengthens its potential to be a meaningful partner in the larger content distribution ecosystem.
Share your thoughts on these deals, and suggest others you think are noteworthy from CES!
Categories: Cable Networks, Devices, HD, Indie Video, P2P, Partnerships, UGC
Topics: BitTorrent, D-Link, DailyMotion, GoFish, Google, Imeem, MeeVee, MTVN, Netgear, Panasonic, Veoh, YouTube
-
MTV Networks Dips Toe Into Syndication Waters
I was very happy to see news today of MTVN striking a big video syndication deal for its multiple networks' content with AOL Video.

Recently I praised Comedy Central's launch of TheDailyShow.com, but I took it to task for what appeared to be a destination-centric strategy, which was further supported by some executives' remarks. In this age of syndication, I thought that was a wrong-headed approach. Coupled with Viacom's misguided lawsuit against Google/YouTube, it felt like further evidence that MTVN was falling out of step with key broadband opportunities.
Today's news shows renewed hope that this may not be the case. I know these deals don't get done in a day, but I'd really like to see more syndication momentum from MTVN (and other content providers for that matter) to spread its content far and wide. Broadband Internet users don't expect to have to go to destination sites to get their favorite videos, they want them accessible where they already frequently visit. Hulu and CBS, to name two content providers that are solidly focused on syndication understand this, as do many others.
Categories: Cable Networks, Partnerships, Portals
Topics: AOL, CBS, Google, Hulu, MTVN, TheDailyShow.com, Viacom, YouTube
-
ClipBlast 3.0 Beta Released; Further Video Search Improvements
Next week ClipBlast, a player in video search space, will announce that is has launched a beta of its 3.0 product. It's actually now live and I've had a chance to play around with it for the last couple of days. I also got a briefing and demo when I met up with Gary Baker, ClipBlast's CEO, at Digital Hollywood a few weeks ago.
Video search has been a murky, yet fast-evolving area. You have to get way down into the weeds to fully understand the nuances, but here is the gist. First, video isn't nearly as searchable as text is. Video search primarily relies on metadata, which describes what's inside the video itself. This metadata can be created by the content provider or by the video search engine itself using techniques like speech-to-text processing. A key challenge for video search engines has been returning results in which the context matches what the user was intending. This is no easy feat, as the same word can obviously be used in many different contexts, yielding lots of useless results.
ClipBlast's 3.0 beta is crawling 10,000 different video providers now and they've continued to make many enhancements to their metadata processing. They've also done a lot of work to improve user navigation so that browsing is a viable complement to search. (This gets to how users actually interact with video search engines, which is yet another issue in the video search world). ClipBlast now places all videos into 70 different categories, which have easy scrolling thumbnails, showcases featured clips and featured partners and today's most popular searches.

ClipBlast has also introduced more personalization features such as saving providers, categories, searches and results. You can also configure your own personal home page and set email alerts for when new video matching your search criteria. Perhaps most fun is a new widget feature, allowing ClipBlast widgets to be embedded on your desktop and blog with customized video. Gary demo'd this for me and it's quite cool. It's only available for Macs right now with a PC release coming soon.
I'm planning a deeper dive into video search in December and will have more detailed analysis on the category then. In the mean time I suggest the best way to get into it and evaluate which video search engine is best for you is to run the same search across some of the more popular video search engines. A good list would include: Truveo (now owned by AOL), Google (still officially in "beta"), blinkx, SearchForVideo, EveryZing, Dabble, Pixsy, Fooooo and others I'm sure I'm missing.
I'm interested in what you find, so please post a comment or email me.
Categories: Video Search
Topics: AOL, Blinkx, Dabble, EveryZing, Fooooo, Google, Pixsy, SearchForVideo, Truveo
-
Google's Android: Striving for Broadband's Openness
Google's announcement on Monday of its "Android" mobile operating platform is another example of open platforms' appeal and underscores why broadband video has grown so quickly and is so compelling.

For those who missed the news, on Monday Google announced its Android mobile platform and the Open Handset Alliance, with 33 other companies, aiming to accelerate innovation and application development for mobile devices. In essence the goal is to develop a widely-deployed open platform,
 comparable to the Internet itself. Mobile video would certainly be a key beneficiary if Android succeeds.
comparable to the Internet itself. Mobile video would certainly be a key beneficiary if Android succeeds.This push to openness in mobile can be seen as an attempt to emulate what's unfolded in the broadband video industry over the last 5 years. The result of broadband's openness has been nothing short of staggering, Whether it's video found at YouTube, iTunes, Hulu, NYTimes.com, MLB.com, Cosmopolitan.com or countless others, the torrent of video that's been unleashed, the shift in consumer behavior that's ensued and the capital that's been invested in this sector are all the direct result of broadband's open pipe.
In fact, as I have said innumerable times, the reason why broadband video delivery is the single most disruptive influence on the traditional video industry is precisely BECAUSE it offers an open platform for producers to send video directly to their target audiences. As such, it eliminates the requirement for video producers to land a deal with a traditional gatekeeper to the home such as a broadcast or cable TV network, or a cable TV, satellite or telco service provider.
In short, the ability for producers to connect directly with their audiences strikes at the heart of the traditional video distribution value chain, threatening a permanent re-ordering of the economics of the video business. It enables all kinds of players who have been shut out of the video game to now jump in.
And while broadband video is admittedly still in its embryonic stage from a revenue standpoint, its long-term appeal portends vulnerability for those who cling too long to the traditional closed, walled-garden model. The Internet has shown us all the power of open over closed models, of interoperability over proprietary approaches, and of often chaotic, but user-centric growth over top-down control.
Broadband's ecosystem is experiencing a rapid "layer-cake" effect where new technologies and applications are being built on top of preceding ones. The result is a vibrant, entrepreneurial culture in the broadband sector. If Android succeeds the same will be true in the mobile video sector as well.
Categories: Mobile Video, Partnerships
Topics: Android, Cosmopolitan, Google, Hulu, iTunes, MLB.com, NYTimes.com, Open Handset Alliance, YouTube
-
Dailyshow.com: Third-Party Distribution Isn't an Either/Or Decision
 First things first, congrats to the folks at MTVN, Comedy Central and The Daily Show. The newly unveiled Dailyshow.com is fabulous. It is the best TV program-centric web site I have yet seen. As a long-time Jon Stewart fan, being able to see all the old clips is nirvana, and will no doubt send fans over the moon.
First things first, congrats to the folks at MTVN, Comedy Central and The Daily Show. The newly unveiled Dailyshow.com is fabulous. It is the best TV program-centric web site I have yet seen. As a long-time Jon Stewart fan, being able to see all the old clips is nirvana, and will no doubt send fans over the moon.However, a bigger picture question that Dailyshow.com's launch raises is how these direct-to-consumer initiatives work vis-a-vis third-party distribution deals. With media companies newly empowered to engage directly with their audiences using the Internet and broadband, many analysts have predicted the result will be diminishing relevance of third-party aggregators, including everyone from Comcast to Yahoo to Joost to you name 'em.
It's pretty apparent that MTVN/Comedy Central is coming down on the side of heavily emphasizing direct-to-consumer as its broadband video strategy when you combine Viacom's ongoing lawsuit against Google/YouTube, MTVN EVP Erik Flannigan's comment ("People should be reacting to 'The Daily Show' on its own site...God bless them for doing it everywhere else, but this should be the epicenter of it") and a company spokesman's comment ("that a few selected clips could become available on sites through syndication deals").
Count me among those who think this is both the wrong approach and one that will ultimately under-optimize the value of the Daily Show and other franchises in the broadband era. Quite simply, building out a strong direct-to-consumer presence like Dailyshow.com is NOT an either/or decision relative to also developing strong third-party distribution relationships.
In fact, the reality is that strong third-party distribution is essential in the Internet era, because Internet usage is both highly distributed among millions of web sites and also concentrated at a few large portals. Media companies' goal should be to proliferate their content (under the right deals of course) into all the nooks and crannies of the Internet while also striking deals with big portals to maximize exposure, usage and ad revenue.
But don't think distributors get a free ride in the Internet era. They need to prove they can leverage their audience devotion and traffic to drive value for content providers. Those that do will succeed. Proof of this is already emerging. One senior broadband executive recently told me that over 80% of his traffic comes from YouTube and other distribution partners, with his own site's traffic in the minority.
Not aggressively pursuing third-party distribution, as it appears is MTVN's plan, in essence requires that users reorient their behavior to come solely to one uber destination site like Dailyshow.com. To me this smacks of classic traditional media thinking where consumer convenience or preference gets short shrift in the name of what's supposedly "best" for the brand. My guess is if you asked Jon Stewart off the record what his preference is, he'd likely say, "make my stuff available everywhere!"
So kudos to the folks behind Dailyshow.com. But don't let your good works end now. Go out and find the best third-party distributors you can and let them help you extend the Daily Show franchise even further.
Categories: Cable Networks, Portals
Topics: Comedy Central, Daily Show, Google, Jon Stewart, MTVN, Viacom, YouTube
-
YouTube Gets Serious About Copyright Protection with New Video ID Service
At long last YouTube has launched "Video Identification" in beta, its answer to copyright owners who feel
 YouTube has built its business on the back of their copyrighted content.
YouTube has built its business on the back of their copyrighted content. Having not seen the system in actual use, it's impossible for me to judge how well it works. But having read how YouTube describes its approach in developing the system, considering how it allocates responsibilities for copyright protection with the rights-holders themselves and thinking about the bigger picture challenges all media companies face in the broadband era, my initial reaction is that Video ID is a pretty good first step.
YouTube's approach - As the Video ID page says, YouTube was guided by 3 motivations in creating the system: accurate identification, choice for copyright holders and a great user experience. While there will be plenty of debate about how much emphasis each of these should have received relative to the others, my guess is that the DMCA's requirements and the health of YouTube's business drove the final balance. While YouTube has an image problem with major media which it would like to improve, nobody can expect that the company's SOLE motivation in developing a copyright protection scheme should be the concerns of copyright holders. Whenever I read a copyright holder complaining about YouTube or other piracy issues, I wonder, would these people only be happy if we returned to the pre-Internet age? Since that's not going to happen, less complaining and more adjusting is what's required of media companies now.
Allocating responsibilities - The most controversial part of Video ID will likely be the requirement that copyright holders provide their videos so YouTube can build its database against which to judge alleged pirated copies. The predictable reactions will be "it's too much work", "we don't trust that YouTube won't misuse it and "why should we?". There will be much second guessing whether other technical approaches not requiring submitting full video files would have been as effective. Of course nobody knows for certain, so at the end of the day either you trust that Google, with its pantheon of computer science experts, vetted the options well and selected the best choice, or you don't. It's ludicrous for lawyers and media executives who have never written a line of code in their life to suggest that Alternative A or Alternative B would have been better. I suggest that for now media companies give YouTube the benefit of the doubt. It is incumbent on YouTube to show it will be responsible with these video files and that having them really does make the Video ID system work well.
Bigger picture challenges - YouTube isn't going away, nor are the other video sharing sites. Broadband isn't going away either. And lastly, consumer behavior isn't going to change back what it was in the pre-Internet era. Media companies need to accept that the world is what it is, and learn to adapt themselves to it to succeed. My sense is that Video ID gives media companies all the options they should desire or expect: having the offending content removed, having it continue to run as promotional fodder, or making money off it through a revenue split (though these percentages are TBD). These tools, if they actually work, will give media companies lots of new flexibility to exploit their content with by far the largest audience of broadband video users. If media companies choose not to participate, shame on them for sticking their heads in the sand and wishing the world would return to a simpler time. YouTube has demonstrated for all of us what I believe and have said many times: that broadband is the single most disruptive influence on the traditional video industry. Companies that don't recognize this and don't work with the YouTubes of the world to adapt themselves will ultimately be rendered irrelevant or worse.
Categories: UGC, Video Search
-
Google's "Video Units": Turbocharging Video Syndication
 Google/YouTube's formal announcement of its "Video Units" content syndication this morning is a welcome development following previous moves in this direction that did not seem to materialize (there was a test with MTV and also comments about doing same with partners Sony BMG and Warner Music Group). What Google'sAdSense has already done in distributing ads to the "Long Tail" of publishers, Google is now going to try replicating with video. It's a very smart move.
Google/YouTube's formal announcement of its "Video Units" content syndication this morning is a welcome development following previous moves in this direction that did not seem to materialize (there was a test with MTV and also comments about doing same with partners Sony BMG and Warner Music Group). What Google'sAdSense has already done in distributing ads to the "Long Tail" of publishers, Google is now going to try replicating with video. It's a very smart move.As I have written repeatedly, robust syndication is a crucial piece of the broadband video economy. That's because advertising is going to be the main business model for a long time to come. And the only way to make the ad business work is through massive traffic increases, and of course improved ad monetization methods.
There's no better way to scale up traffic than through turnkey syndication. Google's ability to harness AdSense as a combination video syndication engine and monetization platform for content providers (by eventually marrying video units to AdWords) is unmatchable by anyone else.
As Google expands this initiative, it will be simultaneously alluring and threatening to others. Trying to capture the same benefits without the same underlying technology infrastructure and far-reaching distribution network is going to be very challenging to replicate.
Take for example, Hulu, the News Corp/NBCU JV, meant to regain control over their broadcast TV programs. Hulu has been striking its own distribution deals and will no doubt monetize its traffic with a "feet-on-the-street" ad sales approach. While there are benefits to this approach to aggregate the biggest sites as partners, Google's one-stop syndication/monetization capability provides the turnkey, hands-off approach needed to gather up the all the rest of the market (i.e. the Long Tail).
Depending how Google chooses to split the revenues between AdSense partners and content providers, Google/YouTube could well become a dominant part of the broadband-centric video value chain that is now taking shape.
Categories: Advertising, Broadcasters, Video Sharing
-
MGM's "Lions for Lambs" Google/YouTube Promotion Continues Studios' UGC Efforts
MGM is the latest studio to reach out to fans to help promote one of its films, the upcoming "Lions for Lambs". In a deal with Google/YouTube, the studio is sponsoring a contest in which users can submit a 90 second video on a topic they're passionate about. Entries are being accepted until Oct. 17th and the winner, who will have $25,000 donated to a charity of his/her choice, will be selected on Nov 9th.
This promotion follows the mashup competition Metacafe and Universal conducted this past summer around the studio's "Bourne Ultimatum" release. At the time, I noted that broadband is introducing a whole new element into the film marketing equation, opening up huge opportunities for creativity and fan involvement. As the tools continue to improve I expect we're going to see a lot more of these "UGC-assisted" campaigns.
Studios (and others) are going to continue to experiment with just how much fans are willing to be a part of the marketing machinery. Of course nobody knows, but my guess is that if the incentives are right, the promotions are fun and the stars are compelling, it's going to be a pretty rich vein for film marketers to tap into.
Categories: Brand Marketing, FIlms, Partnerships, UGC
Topics: Google, Lions for Lambs, MGM, YouTube
-
Broadband Video Isn't Competition for Cable Says My CTAM Panel
Today I moderated a spirited discussion panel at CTAM NY’s annual Blue Ribbon Breakfast at Gotham Hall in NYC. The title was "Over the Top TV....Can Broadband Video Be Cable's Newest Opportunity?" We had an amazing group of panelists (click here to see list and listen to podcast) and with 450+ attendees a packed house as well.
A key question we dug into was whether and to what extent cable’s traditional (and highly successful) paid subscription model will be impaired by the rise of broadband video usage. Try as I did to see if any of the panelists believe that it will, none would admit to it. The reasons given included, "some form of a paid model will always exist but will never succumb entirely to a free, ad-supported model" to "cable networks won’t push broadband video distribution of their programs so hard as to upset the current model of receiving affiliate fees from cable operators", to "the low probability that inexpensive PC-to-TV bridge devices will proliferate any time soon" to "viewers have shown that they want a selection of channels to browse."
While I think each of these answers is quite legitimate, my point of view is that we are in the early days of an fundamental transformation in the video (and indeed the media more generally) business that will eventually (though of course who knows when and to what eventual degree) see most, if not all programming get unbundled into a fully on-demand paradigm.
I believe the ultimate answer to how cannibalistic broadband is toward cable ultimately turns on whether consumers believe it’s a "zero sum" game, meaning they choose between EITHER accessing programs via a VOD or DVR offering only available if they’ve bought into a monthly multi-channel video subscription (that’s to say the way the world works today) OR if they opt out of that subscription offering and INSTEAD choose to buy these programs a la carte, or receive them free, courtesy of a highly targeted ad model. The opt out option would of course be available through open broadband video distribution.
All trends point to the latter ultimately prevailing. While cable operators are well-positioned to shift their models to exploit this behavior if they act aggressively, they are also vulnerable to it if they don’t. The most important driver of the "opt out" scenario is that for an increasingly larger portion of our society, their behavior and expectations are formed by the Internet. And the ‘net is a completely personalizable and on demand medium. Especially for most online media, it is also mainly free, or paid on a fully a la carte basis (e.g. iTunes). Users’ expectations are through the roof and only getting higher. As broadband proliferates they will bring these same expectations to their decision-making.
Is it really realistic to believe that in 5 years when today’s MySpace/Facebook/YouTube/iTunes crazed 16 year old kid goes to set up his/her first apartment, s/he is going to embrace the notion of subscribing to a hundred channel package just so s/he can watch a handful of programs on demand? And of course, the ‘net’s behavior change isn’t confined to kids, it’s pervasive across all age groups.
Cable operators have an outstanding opportunity to capitalize on these macro behavioral trends. But doing so will require cable operators to make a significant and risky departure from their traditional subscription-based business models. It’s a classic incumbent’s dilemma. It will be interesting to see if they can do so.
Categories: Aggregators, Cable Networks, Cable TV Operators, Events, Indie Video
Topics: Comcast, Cox, CTAM NY, Discovery, Google, Next New Networks
-
CTAM NY Blue Ribbon Breakfast is On Tap
 I'm really looking forward to moderating the CTAM NY chapter's annual Blue Ribbon Breakfast on Wednesday morning at Gotham Hall. The session is entitled, Over the Top TV....Can Broadband Video Be Cable's Newest Opportunity?"
I'm really looking forward to moderating the CTAM NY chapter's annual Blue Ribbon Breakfast on Wednesday morning at Gotham Hall. The session is entitled, Over the Top TV....Can Broadband Video Be Cable's Newest Opportunity?"We have a world-class group of panelists:
- Bruce Campbell, President, Digital Media and Business Development, Discovery Communications
- Dallas Clement, Senior Vice President, Strategy & Development, Cox Communications
- David Eun, Vice President, Content Partnerships, Google
- Herb Scannell, CEO & Co-Founder, Next New Networks
- Matt Strauss, Senior Vice President, New Media, Comcast
The event has been sold out for 2 weeks and CTAM just figured out a way to shoehorn in another 25 people from the waitlist, bringing the overall attendance to 460+.
It's going to be an amazing event. The cable industry – both operators and programmers – are right in the middle of the whole broadband video revolution. Their actions will have a big impact on the course and pace of the industry's future.
CTAM is recording the event to podcast it, and I'll be sharing my observations in this space as well.
Categories: Events
Topics: Comcast, Cox, CTAM NY, Discovery, Events, Google, Next New Networks
-
Good Riddance to Google Video Store

On Friday, AP carried the news that Google intends to stop offering paid downloads at Google Video and that it will discontinue support for any downloads made since its launch. Thus ends one of the most anachronistic initiatives I've observed in the broadband video industry.
I was at CES in January 2006 when Google co-founder Larry Page delivered a keynote in which he launched Google Video Store. The press release is here. My recollection of the event is still quite vivid. First, it was such a mob scene that just finding a place to watch the speech was an exercise unto itself. I ended up watching it in a courtesy tent packed cheek-to-jowl with hundreds of others.
As Larry introduced Google Video Store, I kept thinking to myself, "How is that a company with Google's IQ could have made such a startlingly bad product decision?"
Go back to that time for a moment, and imagine that you are Google. You are the foremost company in the world at monetizing content through advertising. You have the ability to meet with the CEO of every major media company in the world -- companies whose video is disproportionately supported by advertising. You have the opportunity to suggest trials, experiments and potentially longer-term deals to bring these companies' video online in an ad-supported manner. You can tantalize them with online riches beyond what they currently collect on-air. And you can be their trusted partner, with the Internet's leading technology, to help figure it all out.
(By the way, at the time, Google's official word was that their choice of the paid model was the only way they could get their hands on full length programs. Yet, just 3 months later, Disney/ABC announced online distribution of ad-supported full length programs. So this was clearly already in the works before January, 2006).
Instead of doing all of this though, you decide to launch using a commerce model, thus completely turning your back on all of the company's massive online advertising horsepower. In doing so, you choose to compete with Apple's iTunes, which has dominant market share and is seamlessly married to the wildly popular iPod. And in an act of arrogance and silliness, you decide to launch your own player, thus rendering all of the premium video incompatible with WMP, Flash, Real and other devices.
And yet, all of this is exactly what Google did. Somehow it managed to persuade premium content providers like Sony BMG, the NBA and Charlie Rose to partner. And it even managed to get Les Moonves, CBS's CEO to come on stage with Larry and make a fawning speech about how excited he was to be a part of all this action.
Now in August, 2007, 20 months later, Google Video Store is dead. Hallelujah. What a ridiculous distraction it has been. I have written over and over that I believe Google is one of the best-positioned companies to exploit broadband video. And yet, like Yahoo most prominently, I still view Google (outside of its YouTube acquisition) as all thumbs in this important new market.
For example - whatever happened to Google's deal with MTV to syndicate its content through the AdSense network? Did anything important come out of that, which might be used for other partners? What's going on with "click-to-play" video ads? And, any updates on Google for TV ads announced in April with EchoStar? Then there's the overhang of the Viacom lawsuit and the introduction of ‘fingerprinting' technology from Google to deter copyright violators. Recently it's looked like its introduction is imminent, and yet no firm timetables have been established.
I'm still expecting big things out of Google in the broadband video area, and I was encouraged to see Gabriel Stricker say in the AP piece that "The current change is a reaffirmation of our commitment to building out our ad-supported...models for video." I hope Google means it.
Categories: Advertising, Downloads, Portals
Topics: Google