-
7 Quick Reactions to Hulu Plus
Hulu unveiled its much-rumored subscription service this afternoon, dubbed "Hulu Plus." I haven't used the new service, but based on the explanation and the teaser video, here are 7 quick reactions:
"Hulu Plus." I haven't used the new service, but based on the explanation and the teaser video, here are 7 quick reactions:
1. Is there consumer demand for Hulu Plus? - This looms as the fundamental question that will be answered as Hulu Plus rolls out. From CEO Jason Kilar's blog post, it appears that, at least initially, Hulu Plus is a bet on consumers having an appetite for a library of broadcast network programs since that's all that's been highlighted so far. Hulu identifies about 2,000 library episodes in addition to current seasons. Unless Hulu Plus really beefs up its catalog, it won't be long before the library holds few surprises for returning visitors.
2. Hulu Plus lacks many of Netflix's advantages - It's tempting to think of Hulu Plus competing directly with Netflix, and to an extent of course they're after the same general target consumer. But Netflix has several very significant advantages: a brand that's identified with subscriptions and 14 million+ currently paying subscribers, a deep DVD library of 100,000+ titles (which has every single episode Hulu Plus will be offering), a streaming library of 17,000+ titles (offered at no extra cost to subscribers) and integrations with all the same devices Hulu Plus is touting (except the iPhone, which is coming soon). Further, Netflix has far deeper resources; it is a public company with a $6 billion market cap that spends $250 million/year on marketing and has publicly-stated commitment to obtain more streaming rights from Hollywood. With Netflix on one side and cable on another, it's unclear how Hulu Plus will expand its menu. I don't see Hulu Plus diminishing Netflix's rapid growth.
3. Ads in Hulu Plus would be a big-time buzz-kill - I did a double-take when I first read this line in Jason's post: "Hulu Plus is a new revolutionary, ad-supported subscription product that is incremental and complementary to the existing Hulu service." Whoa - are there going to be ads in Hulu Plus? That will be a flat-out non-starter for many prospective subscribers. Yes, I know about ad-supported cable networks, but that's for first-run programming, not for library or catch-up fare. Hulu Plus must be an ad-free zone. Meanwhile, it's important that Hulu still prove the 100% ad-supported business model for its existing experience. With much in flux regarding ad loads there's new messaging Hulu will likely be rolling there too.
4. Why wasn't Android or Google TV mentioned? - Is it a little weird that there was no mention of Android or Google TV in today's unveiling? I think so. Android is fast-gaining on the iPhone (surpassed by some metrics) and Google TV is poised to make a big splash in the fall. Why no mention? Is there an anti-Google bias at work?
5. Hulu Plus adds more support for HTML5 - Hulu Plus is another boost for HTML5 and another small dent for Flash. By making Hulu Plus available on non-Flash supported Apple devices, the it seems the Hulu team has been willing to make the investment to diversify beyond Flash, which it has used since launch.
6. Comcast must already be considering how it exits the Hulu joint venture - When the Comcast-NBCU deal clears, Comcast will inherit NBCU's ownership stake in Hulu. With Hulu Plus it's hard to see why Comcast will want to retain that stake. There's no discernible benefit to Comcast owning a minority position in a new over-the-top subscription service that whets the appetite of potential cord-cutters. It's one thing for selective NBC programs to be freely available for catch-up on Hulu.com, but a deeper library in a paid subscription service? No way, especially not as Comcast is trying to build value in its own TV Everywhere service.
7. Hulu gets credit for a well-executed launch - Stepping back, the Hulu team deserves credit for keeping its subscription under tight wraps and executing a solid launch. There have been no shortage of rumors, but to my knowledge there haven't been any specifically identifiable leaks in the Hulu ship. That's a big accomplishment, especially when you consider how many people must have had knowledge of the plans. The launch includes a well-articulated CEO message, a nicely-done sizzle reel (that is in Flash, which makes it not viewable on the iPad or iPhone!), several device integrations and a roadmap of add-ons, and a slow-rollout plan that will generate excitement among early adopters.
There are still many unknowns about Hulu Plus, but for now this is plenty to chew on.
What do you think? Post a comment now (no sign-in required).Categories: Aggregators, Broadcasters
Topics: ABC, Android, CBS, FOX, Google, Hulu, NBC
-
Here's What Fox, NBC and Hulu are Doing with Increased Online Ad Loads
Get ready to see more ads in TV programs viewed online. Following my exclusive 2 weeks ago about ABC doubling the number of ads in its iPad app, and soon on ABC.com, the same increased ad load is happening with Fox's and NBC's online programs, and in my opinion, likely with Hulu as well. Here's what I've learned:
Categories: Advertising, Broadcasters
Topics: ABC, CBS, FOX, Hulu, NBC
-
YouTube Surges to Almost 15 Billion Views in May
comScore has released its May online video rankings and at the top of the list, as usual, is YouTube. In May it racked up a record 14.6 billion video views, up 11.5% from April. YouTube's market share actually dipped slightly in May, to 43..1%, still its 3rd-highest monthly share since comScore began releasing this data in Jan '07. Total video views were also at a record high of 33.9 billion views in May.
The chart below shows how remarkable YouTube's growth has been since Jan '09. YouTube has more than doubled its monthly views from 6.3 billion. Meanwhile, YouTube's market share has hovered right around 40% each month, with its lowest level at 37.7% in Oct '09 and its highest of 43.5% in April '10. YouTube is generating more than 10 times the monthly views it was when Google acquired it.
Categories: Aggregators, Music
Topics: comScore, Hulu, VEVO, YouTube
-
Exclusive: ABC Has Doubled the Number of Ads in Its iPad App; ABC.com Will Be Next
Yesterday ABC began implementing a new ad policy for its popular iPad app, which up to doubles the number of ads included per episode. ABC intends to apply the new ad policy to programs viewed on ABC.com soon as well. Albert Cheng, EVP, Digital Media for Disney/ABC Television briefed me on the changes last week, adding that he believes the new ad policy will become common in the industry. ABC also shared with me that its iPad app has been downloaded over 800,000 times, with 4.2 million episodes started since the iPad's launch on April 3rd.
changes last week, adding that he believes the new ad policy will become common in the industry. ABC also shared with me that its iPad app has been downloaded over 800,000 times, with 4.2 million episodes started since the iPad's launch on April 3rd.
The changes are very significant as they signal a new push by broadcast networks to improve the profitability of their free online and mobile streams. For example, a typical ABC.com program has included 5-6 ads that are 30-seconds, totaling up to 2 1/2-3 minutes of ad time. This compares with around 20 minutes of ads shown in an hour-long program broadcast on-air.
Categories: Advertising, Broadcasters
-
Online Video Gains on Primetime, Led by Indie Content
The WSJ reported on Wednesday that online video viewing over the last year has begun shifting from the lunch time daypart to the coveted primetime daypart. Online primetime viewing rose 14% to an average of 62.4 million viewers over the last year according to Nielsen.
While network programming from Hulu certainly helped, the article credited the jump primarily to independent original web series and networks like blip.tv and Revision3. Revision3's CEO, Jim Louderback attributed its share to the 40% of its audience watching on connected devices like Roku while blip's CEO Mike Hudack argued it was the rise in quality and length of programming. The average length of blip's episodes is up to 14 minutes from 6 minutes a year ago.
Mike also posted yesterday on blip's blog further sharing his excitement that blip is also close to reaching 100 million views per month. This despite the fact that its web series are produced on a fraction of Hollywood's typical budgets (his estimate is blip's shows cost one-tenth of 1% of Hulu's). Mike's argument underscores the democratization of media underway. The Internet allows hardworking entrepreneurial content creators to work successfully far outside the world of Hollywood's ecosystem to create great content and gain sizable audiences.
Add in this week's NewFront and it's clear that independent original web video is uttering a battle cry for legitimacy. As devices and platforms that blur the line between online video and television continue to emerge, this trend will further accelerate, potentially positioning indie online content as a disruptor to traditional programming.
What do you think? Post a comment now (no sign in required).Categories: Indie Video
Topics: blip.TV, Hulu, NewFront, Revision3
-
Total Video Viewership Down Slightly in April; YouTube Share Jumps
comScore has released its new online video rankings for April '10 which show total videos viewed of 30.3 billion, down almost 3% from the prior month's 31.2 billion. As a result, YouTube, which was roughly flat in April at 13.1 billion videos, saw its market share increase to 43.5%, its highest level since July '08. It was also YouTube's second highest share since I started tracking the comScore numbers in Jan '07 (when YouTube had a relatively paltry 16.2% market).
billion videos, saw its market share increase to 43.5%, its highest level since July '08. It was also YouTube's second highest share since I started tracking the comScore numbers in Jan '07 (when YouTube had a relatively paltry 16.2% market).
The 3% decrease in total videos from March '10 to April '10, compares with a 5% decrease from March '08 to April '08 and a 16% increase from March '09 to April '10. While it's hard to discern any trends around these 3 year numbers, one thing worth noting is that over the last 6 months, with the exception of blips up in Dec '09 and Jan '10, total video views have stayed relatively stable right around 30 billion. I'm not sure exactly what to conclude from that, but I'll certainly be watching the coming months to see if viewership is flat-lining or just taking a breather.
Categories: Aggregators
Topics: comScore, Hulu, VEVO, YouTube
-
With Leanback, YouTube Could be the First Big Beneficiary of Google TV
A couple of weeks ago at the Google I/O conference, YouTube provided a tantalizing glimpse of a new UI called "Leanback" which optimizes YouTube for viewing on TV.
With Leanback, YouTube videos can be navigated and consumed in more of a TV-like manner - more passively and for longer durations. Converting YouTube - the king of short online video clips - to a more conventional TV experience might seem like a surprising ambition for Google, but in the context of Google TV, it's actually quite strategic. Not only should it help Google TV gain acceptance, it could also position YouTube to be the first big beneficiary of Google TV.
Way back in March, 2008, in "YouTube: Over-the-Top's Best Friend," I argued that providing full, open Internet experiences was the best path for new OTT devices to succeed, and that YouTube would be their perfect partner. YouTube is so valuable for OTT devices like Google TV and others because it dominates the online video world, accounting for 40% of all video views every month for the past 2 years. For many users it is the only online video brand they know and by far the most heavily used.
Categories: Aggregators, Devices
Topics: Google, Google TV, Hulu, YouTube
-
Kylo TV Browser Can Now be Tweaked to Watch Hulu
Hillcrest Labs, maker of the Kylo browser, which lets users browse the Internet on their TVs, is announcing the Kylo 0.7 beta release this morning. The new release includes updates allowing advanced users to change the browser's user agent string in order to view Hulu. Just two months ago, when Kylo was introduced, Hulu very quickly blocked access, just as it had when boxee tried delivering Hulu to TVs. The new workaround represents another step in the cat-and-mouse game that Kylo is playing with Hulu.
browser's user agent string in order to view Hulu. Just two months ago, when Kylo was introduced, Hulu very quickly blocked access, just as it had when boxee tried delivering Hulu to TVs. The new workaround represents another step in the cat-and-mouse game that Kylo is playing with Hulu.
In the press release, Dan Simkins, Hillcrest's CEO and founder said, "It remains our position that Kylo is simply a Web browser based on open-source Mozilla code, like Firefox. We fully respect the rights of content owners and aggregators, and as such, we do no deep link, re-index, divert users past ads, or overlay different user interfaces on video players. However, we believe consumers should be able to use the Kylo browser to visit any site on the Web on the display screen of their choice. Our hope is that a respectful dialog with Hulu will encourage them to consider changing their policies."
To my knowledge Hulu hasn't ever publicly addressed this situation and I'm guessing it's won't this time either. It is extremely likely that Hulu will once again block Kylo, as it seeks to enforce its computer-only viewing model. As I wrote last week in "5 Reasons Google TV Looks Like a Winner," this insistence is really backing Hulu into a corner marginalizing the site for users who just want to watch whenever, wherever they'd like.
Aside from the Hulu tweak, Hillcrest is also announcing new features including a Windows Media Center plug-in, auto-hide control bar, improved zoom, keyboard hiding, multi-screen support for Mac, printing and updated links. Hillcrest is also putting its Loop pointer on half-price sale of $49 through June 11th. The Loop lets you easily navigate Kylo.
What do you think? Post a comment now (no sign-in required).Categories: Aggregators, Technology
Topics: Hillcrest Labs, Hulu, Kylo
-
Online Video Viewing Rebounds in March According to comScore; Hulu Performance is Mixed
Online video viewing rebounded to 31.2 billion total streams in March '10 according to comScore's newly-released numbers. The March total marks an 11% increase in streams over February's 28.1 billion. As I wrote a couple of weeks ago, it also continues a leveling-dipping-rebounding pattern that has occurred in the Dec-Mar months for the last 2 years as shown in the chart below. If the pattern holds, we'll see strong growth for the next 6 months or so.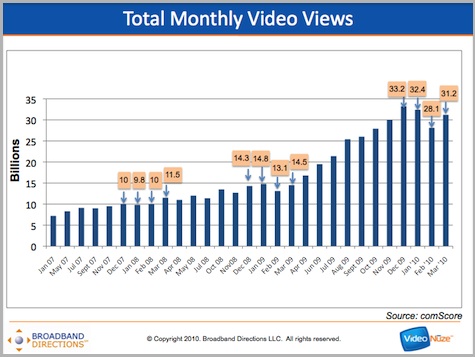
As always, YouTube was the top video site by a wide margin. In March it notched 13.1 billion views, up 10% vs. February's 11.9 billion. Its share was down just slightly to 41.8% from February's 42.5%. Still, it was the 21st consecutive month that YouTube's share has been plus or minus 2-3 percentage points of 40%, a remarkable run.
Hulu also bounced back strongly in March, recording its best month to date with 1.070 billion streams, up 7.5% vs. February's 912.5 million. But with Hulu viewers averaging 156 minutes, the minutes per viewer in March actually slipped to 5.84 from 6.18 in Feb. Hulu's average minutes has stayed stubbornly around 6 minutes for over a year now. In addition, total unique viewers came in at just over 40 million. As I've pointed out in the past, Hulu's viewership has been stuck around the 40 million mark now for a year. Absent a radical change, it seems that neither one of these metrics will break out of their respective range any time soon.
Lastly, on the ad network site, Tremor Media, which earlier this week announced a $40 million financing, saw its reach increase to 96 million viewers.
What do you think? Post a comment now (no sign-in required).Categories:
Topics: comScore, Hulu, YouTube
-
Hulu Missed Its Window for Subscription Success
Unless Hulu has something very unpredictable up its sleeve in the $9.95/mo subscription service it's rumored to begin testing in May, the bad news for the site is that it has already missed its window of opportunity for subscription success. In a one sense it's not Hulu's fault; as a startup 3 years ago, it had to choose what strategy to focus on and execute. Hulu chose the free, ad-supported route, with widespread distribution that has made it the 2nd most-used video site.
success. In a one sense it's not Hulu's fault; as a startup 3 years ago, it had to choose what strategy to focus on and execute. Hulu chose the free, ad-supported route, with widespread distribution that has made it the 2nd most-used video site.
The problem is that the world has changed significantly since Hulu was started 3 years ago, and launching a successful online subscription service now is far harder to do now than it would have been then. Here are some of the top reasons why:
Subscription competition - 3 years the online video subscription field was wide open, but now there's Netflix to contend with. As the company's blowout Q1 '10 results amply demonstrate, Netflix is firing on all cylinders. By providing unlimited streaming as a value add even for its $8.99/mo subs, Netflix has muddied the waters for any would-be online-only subscription competitor, which has to articulate a value prop to prospects of why they should pay the same or more for online-only access, for what will likely be a smaller catalog initially. Netflix also has the device partnerships, 28-day studio deals for more content, well-baked UI/recommendations and deep financial resources. 3 years ago it had none of this; back then it was still imposing confusing online usage caps and pursuing its own set-top box with LG Electronics.
TV Everywhere - 3 years ago cable operators were contemplating their navels when it came to online video delivery, now with TV Everywhere they have a game plan (though admittedly not a lot of actual success just yet). For most cable networks, preserving their relationships in the cable ecosystem is paramount. Taking a leap by licensing content for a Hulu subscription service isn't going to be very appealing. Absent cable content, Hulu will be pitching a monthly subscription to archived commercial free broadcast network programs; that's a pretty narrow value prop.
Comcast-NBCU deal - 3 years ago Comcast was still licking its wounds from its ill-considered bid for Disney; now it has a deal to acquire NBCU, one of Hulu's original partners and a top-tier cable network owner. While Comcast will say all the right things during the deal's review process, I've wondered how long Comcast would even retain its Hulu stake once the deal is completed. Hulu's free "ad-lite" model is antithetical to Comcast's belief in subscriptions and bottom line accountability. A Hulu subscription service is unlikely to help either. Why would Comcast want another competing subscription offer in the market, much less one that would tempt would-be "cord-cutters?"
Lack of ownership will - 3 years ago, NBCU and News Corp were full of platitudes about their new online video baby. But in addition to NBCU's changed status, News Corp has become the most vocal content provider for the paid online content model. MySpace's travails are rumored to have soured Rupert Murdoch's appetite for chasing fickle online users. Meanwhile, Disney, the last partner to the Hulu venture, is plenty interested in subscriptions, but it wants to offer them directly. Then there's Hulu's key financial partner, Providence Equity Partners. I've never quite understood their investment decision given Hulu's limited exit opportunities, but one thing's for sure - they're unlikely to be motivated to help fund the considerable development and marketing expenses Hulu must undertake to make subscriptions succeed.
Retransmission consent - 3 years ago, the idea of broadcasters getting paid for their content still seemed like a stretch. But broadcasters are winning their chosen high-stakes battles, and given their success, are far more inclined to pursue a wholesale model (i.e. getting distributors to pay them monthly) than back a retail, subscription model. Plus, a Hulu subscription model departs from the message of free broadcast service that the broadcast lobby is using with the FCC and Congress to justify why it should retain its excess spectrum, rather than yielding it to mobile data providers under the National Broadband Plan's reclamation program.
User expectations - As if these weren't enough to contend with, the single biggest impediment Hulu faces is likely itself. Having invested its brand heavily in the free ad-supported positioning (and computer-based viewing only) Hulu lacks what experts would call "brand permission" to now pursue subscriptions. Companies are frequently chastened to find out what their customers really think when stretching for new products or business models. Moving customers from free to paid is one of the hardest things any company can do (just ask YouTube which is attempting to do the same); trying to pull it off from a cold start is nearly impossible in my mind. Hindsight is 20-20, but what Hulu probably should have done 3 years ago is offered a "freemium" model that would have immediately conditioned its users to thinking Hulu stands for both free and paid.
I've learned to never say never in this business, but to succeed, Hulu has to surmount the above challenges and more. If it can do so, it will be a significant win for the company. If it can't it will be yet another reminder of how treacherous things are even for well-funded startups trying to navigate a quickly-shifting competitive landscape.
What do you think? Post a comment now (no sign-in required).Categories: Aggregators
Topics: Comcast, Disney, FCC, FOX, Hulu, NBC
-
comScore's February 2010 Numbers Show Further Online Video Usage Declines
comScore released its Feb '10 online video rankings yesterday, which showed the 2nd straight month of usage declines in aggregate and for many of the top 10 sites. Total video views came in at 28.1 billion, vs. 32.4 billion in January and 33.2 billion in December '09. As I pointed out in my analysis of comScore's Jan numbers last month, and as the chart below shows, in each of the last 3 years, the period from December to February has seen flat to slightly declining viewership.
It's still too early in online video's evolution to form hard and fast conclusions about the impact of seasonality, but judging from the past 3 years it seems as though we're beginning to see the pattern. February is also a shorter month than either Dec or Jan, so this too plays a role in explaining the downward trend in viewership.
As usual, YouTube was the most-used video site, generating 11.9 billion views, down from 12.8 billion in Jan and 13.2 billion in Dec. YouTube's share jumped up to 40% in Jan, marking almost 2 years that the site's share of the overall video market has been plus or minus 3 percentage points of 40% share, a remarkable achievement given the growth of other video sites.
Hulu is one of those sites that achieved growth in Feb, increasing its video views to 912.5 million from January's 903 million, though both are down from the site's December record of just over a billion views. In Feb Hulu averaged 6.18 minutes viewed per video, the first time the site has been back up over 6 minutes since Sept '09. Hulu's audience came in at 39.2 million uniques, continuing to be stubbornly stuck around the 40 million mark for a full year. I've commented before that Hulu appears to be encountering a challenge broadening its user base. The deletion of the Jon Stewart and Stephen Colbert programs will only make this challenge harder.
As the chart above also shows, in the past 2 years March has been a month when viewership rebounded, setting the stage for growth over the following 9 months. We'll see whether the same pattern starts to play out next month.
What do you think? Post a comment now (no sign-in required).
Categories:
Topics: comScore, Hulu, YouTube
-
VideoNuze Report Podcast #55 - April 2, 2010
Daisy Whitney and I are pleased to present the 55th edition of the VideoNuze Report podcast, for April 2, 2010.
This week Daisy and I first discuss my post from this past Monday, "New comScore Research Available; More Ads Tolerable in Online TV Programs" (the post also includes a link for a complimentary download of the research presentation). Among other things the research concludes is that viewers of online-delivered TV programs could tolerate 6-7 minutes of ads which is approximately double the typical current ad load.
I have argued for some time that the ad load in online programs is way too light and that it was jeopardizing the broadcast networks' P&Ls, particularly as convergence devices allow online video viewing directly on TVs. Coincidentally, this week the CW Network announced that it would double its ad load next TV season. And Hulu, though announcing this week that it has been profitable for the past 2 quarters, is under continued pressure by its content partners to increase its ad load to generate more revenue (recall that Hulu recently blocked the new Kylo browser, which I asserted was due to concern about cannibalizing audience and ad dollars from on-air).
Daisy then tells us more about "hot-spotting," which is the ability to click on an item in an online video and learn more about it and possibly purchase. Hot-spotting has become very hot (no pun), with multiple companies now offering technology that appears to be yielding significant results. Daisy reports that ConciseClick, ClickThrough and VideoClix are among the leaders and she provides some interesting stats on their performance. Listen in to learn more.
Click here to listen to the podcast (14 minutes, 45 seconds)
Click here for previous podcasts
The VideoNuze Report is available in iTunes...subscribe today!Categories: Advertising, Podcasts
Topics: ClickThrough, comScore, ConciseClick, CW, Hulu, VideoClix
-
New comScore Research Available: More Ads Tolerable in Online TV Programs
An article I read last week in Mediaweek about new comScore research which concluded more ads are tolerable in online-delivered TV programs really intrigued me. The research was presented by Tania Yuki, comScore's director of cross media and video products at an Advertising Research Foundation meeting. I called Tania to follow up and learn more about the data. Today I'm pleased to share her presentation with the research findings as a complimentary PDF download. Outside of the ARF meeting, this is the first time this data has been made available.
Click here to download the research presentation
As VideoNuze readers know, I've been a proponent of increasing the number of ads in online TV shows, in order to improve their economics. Note, I'm not advocating a jump to 18-20 minutes of ads typically found in on-air distribution that would likely turn users off. But I do believe that the current model of 3-4 minutes of ads in premium network programs is way too light, and that viewers will tolerate more without any drop-off in usage, particularly if the ads are well-targeted and engaging. ABC has told me in the past that research it conducted when it experimented with doubling its ad load corroborated this point, just as the comScore research now does as well. Just last week the CW announced it would double the number of ads in its online-delivered programs.
model of 3-4 minutes of ads in premium network programs is way too light, and that viewers will tolerate more without any drop-off in usage, particularly if the ads are well-targeted and engaging. ABC has told me in the past that research it conducted when it experimented with doubling its ad load corroborated this point, just as the comScore research now does as well. Just last week the CW announced it would double the number of ads in its online-delivered programs.
Increasing the number of ads - and thereby strengthening the economic model for online-delivered TV - is critical for the industry to succeed long-term. The current lack of economic parity between online and on-air is gaining urgency; just last week when Hulu blocked access to its content via the new Kylo browser (meant for on-TV browsing), we were reminded of the absurd lengths to which the popular site will go to prevent its viewership from migrating to TVs. This is because Hulu was conceived as an online-only augment. Given its lack of economic parity with on-air (or with DVR viewing, as ABC.com is now achieving), Hulu on TV would undermine its owners' P&Ls.
The new comScore research concludes that viewers will tolerate 6-7 minutes of "total advertising time" during online-delivered TV programs. And note that this response reflects expectations of conventional advertising. I think it's quite possible that if respondents had been shown the kinds of targeted, entertaining and interactive video ads that blip.TV and others are now offering, they would have said their tolerance would be even higher. Providing further comfort that more ads are reasonable, when asked about the most important reasons for watching TV online, the answers were first, "Missed an episode on TV" (71%) and second, "Convenience" (57%). A distant third was "Less ads" (38%). Ad avoidance is important to online viewers, but it isn't their sole motivator.
The comScore research further underscores the growing importance of online, particularly in terms of raising programs' visibility and sampling. For example, for people who watch both on TV and online, an "online video site" (28%) is already the third most-cited way of discovering new TV shows, following "TV advertising" (59%) and "Friend/family member recommendation" (44%). Related, 28% said that they believed that if they hadn't been made aware of their favorite program online first, they probably wouldn't have discovered it on TV, and therefore would have missed the show entirely. Across all respondents, 20% of shows watched regularly had been watched first online.
As Tania reminded me, TV is still by far the dominant platform for viewing TV programs and that it's important to remember that online-only viewing is nascent. ComScore's research found that only 6% of respondents tune-in online only, though another 29% view both online and on-air. The key for me is looking toward the future. When the 6% of online-only viewers is broken down by age groups, about 75% are between 18-34. And if my 8 and 10-year old kids are any example, no doubt that those under 18 are only going to be even more avid online video viewers. In order for the TV industry to succeed in the future, it is essential that the business models to sustain online viewing be figured out pronto.
For this research, comScore which surveyed 1,825 people from its U.S.-only panel, weighted to match the total online population in age, income and gender. The research was conducted between Dec. 30, 2009 and Jan. 22, 2010. It was not sponsored by any third-party.
A reminder that if you're keen on this topic, join us for the complimentary April 8th webinar, "Demystifying Free vs. Paid Online Video" and then at the April 26th VideoSchmooze in NYC, where our panel topic is "Money Talks: Is Online Video Shifting toe the Paid Model?" (early bird tickets now available).
What do you think? Post a comment now (no sign-in required).
Categories: Advertising, Broadcasters
-
Is Hulu Now Blocking Access for Kylo Users? Yes, It Is.
No sooner did I post "With New Kylo Browser Convergence is Another Step Closer" this morning, than I've come to understand that Hulu programs are now not accessible through the Kylo browser. Hulu worked completely fine for me yesterday, but now when I go to watch a program on Hulu, I'm getting the text message, "Unfortunately this video is not available on your platform. We apologize for any inconvenience." Huh, what's going on here? Is Hulu blocking Kylo users' access to its programs? I've asked Hulu for a comment.
If Hulu is indeed doing this, it's a PR fiasco in the making for the site. Blocking access to its content would mean that Hulu is putting itself on the wrong side of convergence and risking turning off its users (not to mention censoring as if this were China). The episode recalls February, 2009, when Hulu demanded that boxee turn off access to Hulu at the request of its content partners. That tempest highlighted the artificially made quagmire that Hulu's owners find themselves in - eager to have Hulu boost their programs' viewership, so long as it remains on the computer and not on the TV.
With Kylo, Hulu will once again be called upon to justify how it's making decisions. For example, if I'm using Kylo on my computer, how is watching Hulu content any different than if I were using IE, Firefox, Safari, etc? And if I choose to connect my computer to a TV screen, how is that any different than if I connected it to a large monitor? In short, this is a hairball for Hulu.
Update: Hillcrest Labs, the company behind the new Kylo browser, has confirmed that Hulu is indeed preventing its content from being shown. The statement from Hillcrest's CEO Dan Simpkins:
"We have confirmed with Hulu that they are preventing the Kylo browser from playing Hulu videos. Prior to our formal launch, Hulu videos would play within the Kylo browser. Like Internet Explorer, Firefox or Safari, the Kylo browser is simply a Web browser that enables consumers to visit any site on the Web. We have tremendous respect for Hulu, and we hope that a continued dialog might influence their thinking."
Meanwhile Hulu seems to be in a bunker. I haven't heard back from them, nor has anyone else it appears. I have confirmed from ABC (one of Hulu's owners) that it found out about Hulu's action when everyone else did, which means that ABC is not the instigator here. Much more on this story as it unfolds.
Update 2: Now Tuesday morning and still no word back from Hulu. Nobody else seems to have heard from them either. It looks like their PR strategy is avoidance. That's a bad move because going mum just means that story continues to live (just ask Tiger).
Hulu's decision to block Kylo users is all about preventing Hulu viewership from migrating to TVs, which would undermine broadcast network economics. That's because Hulu, with its light ad load, still hasn't been able to prove its business model. The problem for Hulu - and the networks - is bigger than Kylo though as the push toward convergence between online video delivery and TV is going to be relentless (lots more on this tomorrow). Hulu is facing an escalating "Whac-a-mole" problem which will only lead to huge user frustration and increasingly tortured justifications.
What do you think? Post a comment now (no sign-in required).Categories: Aggregators, Technology
-
Interpreting comScore's January 2010 Online Video Usage Decline
comScore released its Jan '10 online video rankings yesterday, and while the numbers were still very strong, they did show declines from Dec '09. For example, in Jan, total monthly views were 32.4 billion, compared with 33.2 billion in Dec '09, a decline of 2.4%. To try to put this blip downward in a little more context see the chart below. I've called out the Dec-Feb period for the past 3 years. In prior years there have been slight to moderate decreases somewhere in this period. This might suggest some seasonality, based on limited historical data.

It's also worth noting that over the course of the last 3 years there have been 7 monthly sequential declines in the total monthly video views. Obviously nothing grows uninterrupted forever, and nobody should expect this from the online video market. Still, when you look at the overall growth curve, there can't be too many other Internet activities that have grown as consistently, with the exceptions maybe of social media (e.g. Twitter, Facebook, etc.).
Elsewhere in the comScore stats, YouTube remained the undisputed 800 pound gorilla for another month, once again maintaining its approximate 40% market share (39.4% in Jan to be exact). According to comScore, YouTube's market share hasn't been below 35% since May '08, when total video views were 12 billion. In other words, even as total views have almost tripled, YouTube has consistently held onto its market share. Pretty amazing.
Hulu also had another strong month, notching 903 million views (its 3rd best month) from 38.4 million unique visitors. Still, the unique visitor count tumbled by 13% from 44.2 million in Dec '09 to 38.4 million in Jan (by comparison YouTube increased from 135.8 million unique visitors in Dec to 136.5 million in Jan). As I mentioned recently, I'm looking for evidence that Hulu can expand its U.S. user base beyond the 35-45 million range it's been in for over a year.
One other point worth noting from the Jan data is that Vevo, the music video aggregation site just launched in Dec '09 broke into the top 10 with 32.3 million unique viewers and 226.1 videos viewed. Vevo's rapid growth is further testament to the popularity of music videos online and the continued importance of short-form.
What do you think? Post a comment now (no sign-in required).
Categories:
Topics: comScore, Hulu, VEVO, YouTube
-
Comedy Central Pulls Out of Hulu - Was This Really a Surprise?
This week brought news that Comedy Central was pulling its programs, including its hits "The Daily Show with Jon Stewart" and "The Colbert Report," from Hulu on March 9th. Both had been available on Hulu since the summer of 2008 in what Comedy Central had initially positioned as a test. Both will still be freely available at ComedyCentral.com.
The Daily Show in particular had been enormously popular on Hulu since launch, so in this respect losing it is a setback for Hulu. Still, Comedy Central's decision should come as a surprise to nobody. As I've been saying since I wrote "The Cable Industry Closes Ranks" in November '08, a bright line is being drawn in the broadband world between programs that consumers currently pay for and those that they don't. The industry is determined make sure the former stay that way and don't leak out onto the free Internet (in this sense, it's actually amazing to me that the Comedy programs are still available for free on its own site, but that's another story).
Central's decision should come as a surprise to nobody. As I've been saying since I wrote "The Cable Industry Closes Ranks" in November '08, a bright line is being drawn in the broadband world between programs that consumers currently pay for and those that they don't. The industry is determined make sure the former stay that way and don't leak out onto the free Internet (in this sense, it's actually amazing to me that the Comedy programs are still available for free on its own site, but that's another story).
The free ad-only Hulu model is bumping up against the industry's big TV Everywhere push (another effort to maintain the subscription model) and so it was inevitable that Comedy's programs would get pulled. Hulu could make itself more attractive to networks - and open up new opportunities for itself - if it offered a subscription model. This is something I've suggested for some time, however I'm somewhat skeptical that anything will happen on this front until the Comcast-NBCU deal closes. Comcast would then become an approximately 20% owner of Hulu and will surely want to influence its strategic direction.
What do you think? Post a comment now (no sign-in required).Categories: Aggregators, Cable Networks
Topics: Comedy Central, Hulu
-
ABC.com is Now Achieving "DVR Economics" for Its Programs
Last week while I was in LA I had a chance to sit down for an extended chat with Albert Cheng, EVP of Digital Media for Disney-ABC Television. Aside from general catch-up, I wanted to dig into a comment I'd heard Albert make at the recent NATPE conference - that full-length programs on ABC.com are now achieving "DVR economics."
The comment caught my attention because, as I've written a number of times, I've been concerned that the broadcast networks' streaming initiatives (and Hulu specifically) could be undermining their traditional business models. The main reason for this is that the ad load in streaming programs is a small fraction vs. what it is in on-air. If all online viewing is incremental to on-air that wouldn't matter. But despite certain research that suggests online doesn't cannibalize on-air, for some viewers who have long since transitioned to time-shifted consumption, it surely does. More importantly, as convergence devices that link broadband to TVs gain penetration, the choice for viewers of how to watch a particular program - via online or via on-air - gets even more pronounced, putting further pressure on on-air.
Albert explained that ABC has been closely following the economics of programs' different viewing methods and recently concluded that it was more appropriate to compare online's economics to DVR's economics
 than to on-air's. Their reasoning is that because online is a "catch-up" medium it should be weighed against other comparable opportunities, not against on-air. Importantly, ABC "windows" the online release of its programs by 4-6 hours, so that hard-core fans who have to watch immediately will skew to on-air, rather than waiting. (Of course the question arises - in our increasingly on-demand, time-shifted world, how sizable is the "must-see" audience for all but the most popular programs like "Lost?" But that's a question for another day.)
than to on-air's. Their reasoning is that because online is a "catch-up" medium it should be weighed against other comparable opportunities, not against on-air. Importantly, ABC "windows" the online release of its programs by 4-6 hours, so that hard-core fans who have to watch immediately will skew to on-air, rather than waiting. (Of course the question arises - in our increasingly on-demand, time-shifted world, how sizable is the "must-see" audience for all but the most popular programs like "Lost?" But that's a question for another day.)When looked at this way, ABC believes online delivery compares favorably to DVR. No surprise, Albert would not disclose ABC's revenues or research, but he did give me a wink-and-a-nod when I shared my estimate that the on-air revenue per program per viewer is in the $.50-$.75 range (of course specific programs and specific episodes are above and below this range). To be clear, this only means the revenue generated is in this range. Because of bathroom breaks, channel flipping, viewers chit-chatting, etc. obviously not all of the ads are actually viewed.
Estimating the revenue per program per viewer range for DVR playback, given its attendant ad-skipping, is more complicated. Ad-skipping is surely high, but it's unclear exactly how high. For example, last Nov, the NY Times reported Nielsen research that somewhat remarkably showed that 46% of viewers age 18-49 still watched a program's commercials when in DVR playback mode. A different story is told by TiVo, which released data last Sept saying that for the programs that won the top Emmy awards, somewhere between 55-83% of the audience viewing these programs in DVR mode skipped the ads.
Just to round off, if we say that 60% of the ads in DVR playback are skipped, then DVR economics - and therefore ABC.com's economics - are in the $.20-$.30 range on a per program per viewer basis (i.e. 40% of $.50-$.75). Even on the low side of that range, that's better than my previous estimate of $.15 per program per viewer for Hulu in particular (which in reality was probably a little high anyway).
Further, Albert said that there's plenty of room for improving online's economics. One key focus is increasing the ad load, possibly to as much as double the current 5 ads per program. ABC.com has experimented with this and its research shows that neither the viewer nor the advertiser experience is diminished. As a result, ABC is inclined to increase the ad load to continue improving online economics further, but is somewhat constrained by advertisers' desire to minimize clutter and their own desire to remain consistent with non-ABC sites' ad loads.
Online distribution of full-length programs is still in its relative infancy. Yet as consumers hunger for it, broadcast networks have little choice but to provide it. The key is how to make this new delivery method profitable and also not harmful to the traditional network P&L. The use of windows for example, seems like an effective tactic insofar as there exists an audience intent on watching a program the moment it's shown on-air. Based on last week's conversation with Albert, along with prior ones, it seems like ABC is balancing things well - taking steps to pursue online, but doing so in a well-researched and analytically sound manner.
What do you think? Post a comment now (no sign-in required).
Categories: Advertising, Broadcasters
-
Why Did Online Video Consumption Spike in 2009?
If you want to get a sense of how significant an inflection year 2009 was for online video, have a look at the chart below.
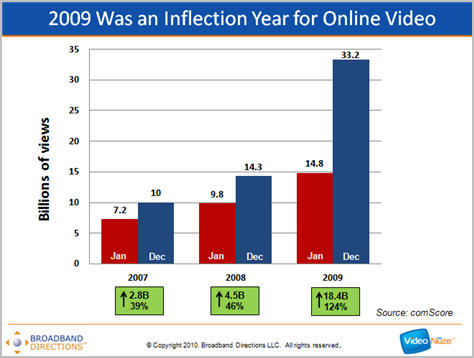
As you can see, according to comScore data, while Jan-Dec growth in 2007 (up 2.8 billion views or 39%) and 2008 (up 4.5 billion views or 46%) were impressive by any standard, the Jan-Dec 2009 growth of 18.4 billion views, up 124%, completely blows them away. Growth was so significant in 2009 that I think years down the road it will be pointed to as the year that online video really turned the corner.
But if that's the case, the question begs, "Why did growth accelerate so much in 2009 vs. prior years?" That's what I've been asked several times by industry colleagues since posting "comScore Data Shows 2009 Was a Blistering Year for Online Video" 2 weeks ago. It's a great question and though I don't have a really precise answer, here's my best sense of what happened.
No surprise, the most important contributor to the year's growth was YouTube. It zoomed from 6.3 billion views in Jan '09 to 13.2 billion in Dec. '09. That increase of 6.9 views accounts for 38% of the 18.4 billion delta between Jan and Dec. So what did YouTube do to generate such significant growth? Part of the reason is surely organic; more people uploading, sharing and viewing YouTube videos. But in 2009 YouTube also made strides in professionalizing the content on YouTube, broadening its value proposition to users. For example, its "Content ID" program, which lets media companies manage and monetize user-uploaded videos, has largely addressed the copyright infringement concerns from past years (the Viacom suit is a notable exception).
In 2009, among other things, YouTube also signed up Disney/ESPN, Univision and others as content partners, began implementing FreeWheel's ad system so 3rd party content providers could better monetize their views, engaged a number of leading brands to use it as a promotional platform, and with "YouTube Direct" engaged news organizations as partners. In short, YouTube continues to immerse itself into the fabric of the Internet. Whether users are viewing videos at its site or through its wildly popular embeds, YouTube has become omnipresent. YouTube now also claims to be the 2nd largest search site.
A second, but distant contributor to 2009's growth was Hulu, which saw its views increase by over 763 million from Jan to Dec, accounting for about 4% of the 18.4 billion increase in total views during that period. Hulu's mindshare leaped following its 2009 "Evil Plot" Super Bowl ad featuring Alec Baldwin and the subsequent ones. No doubt the addition of ABC programs throughout the year, plus other new content partners, also helped generate more viewership, along with the hugely popular SNL clips.
Once you get beyond these top 2 sites, the individual contributions to 2009's growth are more dispersed. The comScore data shows that across all video sites, usage intensified significantly during the year. For example, the number of videos viewed per viewer increased from 101 in Jan to 187 in Dec. The number of minutes watched jumped from 356 in Jan (almost 6 hours) to 762 in Dec (more than 12 1/2). There were also 31 million more U.S. Internet users watching video in Dec vs. Jan (178 million vs 147 million).
Looking beyond the numbers and thinking more qualitatively, it's also fair to conclude than in '09 online video reached a certain level of awareness that made it almost ubiquitous. There is just so much video online, and it is shared so widely, and highlighted so frequently by mainstream media, that it is unavoidable, even for the least technically-savvy among us. People are increasingly entertaining themselves with online video, but they're also finding new uses for it in their daily personal and professional lives.
I think it's unlikely we'll see the same level of growth in 2010 as in 2009, but I do believe the growth curve over the next 5 years will be very steep. The primary contributor will be convergence devices (e.g. game consoles, Blu-ray players, Roku, etc.) that are bridging online video to the TV where longer-form consumption will be the norm. Another key contributor will be TV Everywhere services, which are just now getting off the starting blocks. Lastly, I think growth in mobile consumption will be another important contributor. Add them all up and the 33.2 billion videos viewed in Dec. '09 will look relatively small 5 years from now.
What do you think? Post a comment now (no sign-in required).
Categories: Aggregators
Topics: comScore, Hulu, YouTube
-
VideoNuze Report Podcast #49 - February 12, 2010
Daisy Whitney and I are pleased to present the 49th edition of the VideoNuze Report podcast, for February 12, 2010.
This week Daisy and I dig into the 2009 comScore data that I detailed in my post on Tuesday (slides available for download too). It was a blistering year for online video, with total streams growing from 14.8 billion in Jan '09 to 33.2 billion in Dec '09. All the other relevant metrics also recorded strong growth. I share more details on the numbers and what they mean, focusing particularly on the top 2 sites YouTube and Hulu.
Then Daisy discusses her takeaways from the recent iMedia conference she helped organize. She talks about how brands are trying to break through the clutter, and the role of online video ad networks. Finally, she also discusses recent interviews she conducted with Facebook executives.
Click here to listen to the podcast (13 minutes, 55 seconds)
Click here for previous podcasts
The VideoNuze Report is available in iTunes...subscribe today!
Categories: Advertising, Podcasts
Topics: comScore, Hulu, iMedia, YouTube
-
comScore Data Shows 2009 Was a Blistering Year for Online Video (Slides Available)
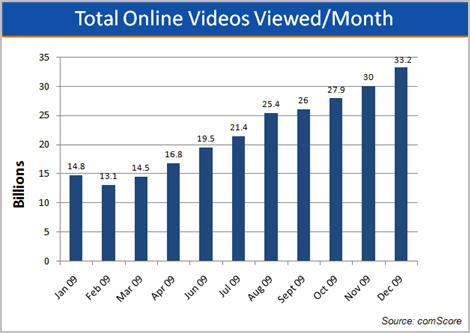
Last Friday, comScore released its Dec. '09 data for online video usage. I've been tracking comScore's data for the last 3 years and Dec put an exclamation mark on what many of us already knew: 2009 was a blistering year of growth in online video consumption. Below are graphs of the most important data (Click here if you'd like a complimentary PDF download of all of the slides.)
The first graph shows total online video views more than doubled from 14.8 billion in Jan '09 to 33.2 billion in Dec '09. The historical growth is even more impressive. Just two years ago, in Dec '07, comScore reported 10 billion video views.
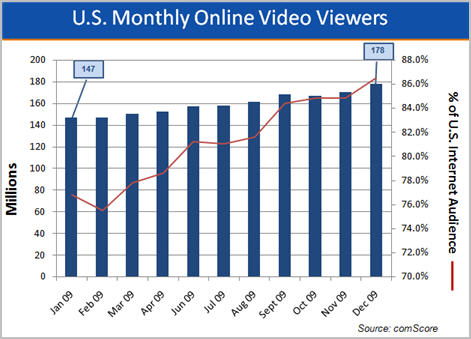
Online video usage is now nearly ubiquitous in the U.S. According to comScore, in Dec '09, 86.5% of all U.S. Internet users watched online video, up nearly 10 percentage points from the 76.8% in Jan '09. That translates to 178 million people watching video in Dec '09, up from 147 million in Jan '09. Back in Jan '07, there were 123 million viewers.
Those users are watching a whole lot more videos as well. For Dec '09, comScore reported that 187 videos were watched per average viewer, up 85% from 101 in Jan '09, and more than triple the 59 watched in Jan '07.
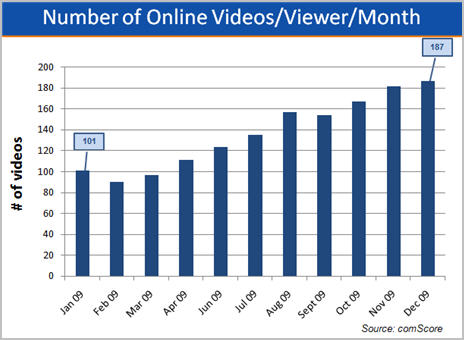
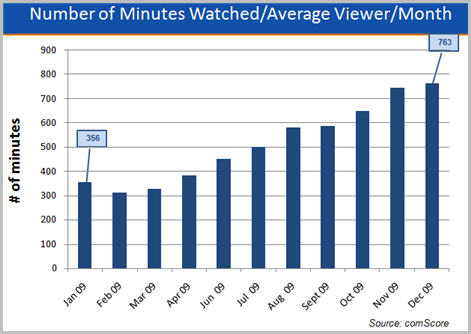
As well, those viewers spent a lot more time watching online video. In Dec '09 comScore said that the average online viewer watched 762.6 minutes or 12.7 hours, more than double the 356 minutes viewed on average in Jan '09. Here's the really incredible stat: back in Jan '07, comScore pegged this number at just 151 minutes or about 2 1/2 hours, meaning average viewing time has more than quintupled in the last 3 years.
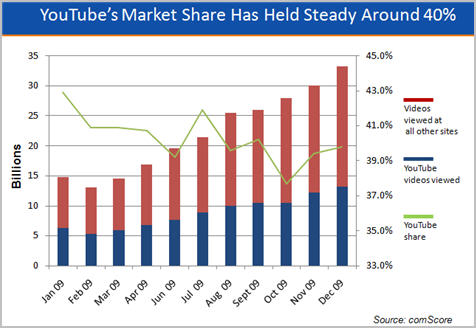
I've talked many times about how YouTube is the 800 pound gorilla of the online video market, and 2009 only further cemented this. Videos viewed at YouTube surged from 6.3 billion in Jan '09 to 13.2 billion in Dec '09. To put this in perspective, Google closed its acquisition in Nov '06. In Jan '07 (the first month comScore publicly released online video data), YouTube notched 1.2 billion views. That means that in the 3+ years that Google has owned YouTube, it has grown more than 10x in size. More amazing is that even with all the growth by other sites (particularly Hulu), YouTube has kept up its approximate 40% share of the overall online video market, starting the year at 42.9% and ending at 39.8%.
Speaking of Hulu, in its first full year of operation, the site surged from 250 million views in Jan '09 to 1,013 billion views in Dec '09. Unique viewers increased from 24.4 million in Jan '09 to 44.1 million in Dec '09. But if you look at the red line in the graph below, you'll see that uniques jumped to 41.6 million by Mar '09 which I believe must be due, at least in part, to a likely measurement change by comScore. Since Mar you'll notice that uniques hovered right around 40 million each month, dipping below during the summer and then bouncing back in Q4.
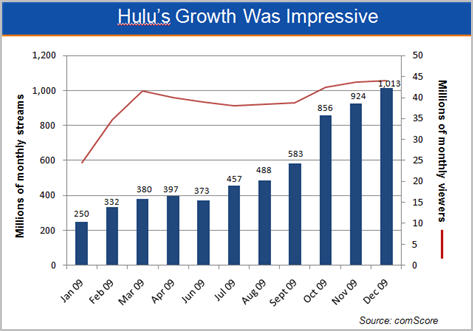
A few months ago I speculated that Hulu's relatively flat pattern in uniques could suggest that, in its current configuration, Hulu may have saturated the market for its content and user experience (for example, contrast Hulu with YouTube, which grew its uniques by 33% in '09 to 135.8 million by Dec '09). I'll be looking to see if Hulu can notch more noteworthy increases in uniques during '10; if not, then I think my thesis will be proven correct.
Nonetheless, Hulu's viewers clearly love the site, with average number of videos per viewer more than doubling to 22.9 in Dec '09, up from 9.8 in Dec '08. Users are spending more time on Hulu, increasing the amount of total minutes on the site from 58 in Mar '09 to 132 in Dec '09. What's remarkable though is that the average minutes watched per video (the yellow line below), has stayed virtually constant at around 6 minutes each month. That shows that while there's plenty of long-form consumption happening at Hulu, clips are still very popular too.
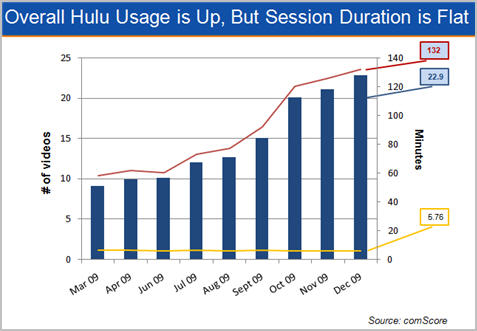
comScore is a great source of month in and month out online video data, but as always my caveat is that no third party can ever track usage as closely as the sites themselves, so take these numbers with a small grain of salt!
Click here if you'd like a complimentary PDF download of all of the slides.
What do you think? Post a comment now (no sign-in required).
Categories: Aggregators
Topics: comScore, Hulu, YouTube


