-
TiVo's Tom Rogers Puts TV Executives on Notice at NATPE
At the NATPE conference in Las Vegas yesterday I listened to TiVo CEO Tom Rogers send television executives an unmistakable message: either adopt a sense of urgency to address the two main forces upending the industry or prepare to watch the world as you've known it go away.
Rogers didn't mince words, forecasting for the TV industry a crisis comparable to the ones that have
 engulfed the financial services and newspaper industries if TV executives are complacent. Why Rogers didn't also cite the even more desperate U.S. auto industry was unclear....Is it possible that no other industry could ever find itself in that much pain?
engulfed the financial services and newspaper industries if TV executives are complacent. Why Rogers didn't also cite the even more desperate U.S. auto industry was unclear....Is it possible that no other industry could ever find itself in that much pain? The two forces underpinning Rogers' potential doomsday scenario are rampant time-shifting/ad-skipping by DVR-enabled households and fragmented viewing due to inevitable widespread broadband-connected TVs. On the DVR front, Rogers cited forecasts of DVR penetration in 60 million U.S. homes in several years, up from 30 million today. He explained that at that penetration level research suggests that brands will suffer major erosion from ad skipping.
I think Rogers is absolutely right. If you live in a DVR-enabled household, consider how different your (and your kids') viewing patterns are vs. in the pre-DVR age. Rogers noted that plenty of industry executives themselves have admitted to him that they too skip the ads.
As for broadband, Rogers said that 85% of TiVo HD buyers now connect their boxes to TiVo's broadband features. And he echoed a point that I'm fond of making: despite all of the broadband consumption on PCs that has occurred in recent years, for most consumers video isn't really "TV' until it is actually consumed on the TV. TiVo has been incredibly aggressive in introducing broadband features (see their site for a listing), and clearly its buyers are getting the message.
Rogers' comments were serving a larger purpose which is to position TiVo's new ad products as a key solution to these problems. For the past couple of years TiVo has begun promoting a slew of new ad units, targeting and measurement capabilities that it believes can make the TV ad model comparable or superior to the online advertising model (I wish you could see more details but oddly, information about TiVo's ad products sits behind a password-protected area of the company's site.) Rogers conceded the irony that the company most responsible for undermining the traditional ad model through ad-skipping adoption is now trying to ride to the industry's rescue.
Be that as it may, the main problem dogging TiVo's ad solution is that TiVo's subscriber base of under 4 million is just a tiny percentage of all U.S. TV households. And that's unlikely to change. The big driver of DVR penetration is service providers including the feature (sometimes from TiVo) in their set-top boxes.
Further, in the cable world at least, TiVo's ad solutions are going to run smack into Canoe, the industry's advanced advertising initiative. TiVo has already learned about how cable companies follow their own agenda; when TiVo is included in cable set-tops none of the broadband features are enabled. I know this first-hand. My old TiVo Series 2 in the basement gets all the broadband goodies, my Comcast TiVo in the family room gets none of them.
Rogers emphasized that his comments should be taken positively, in the context of the massive opportunities being created, rather than as an assertion that the industry is doomed to failure. I applaud Rogers for calling out the massive problems that lie ahead for the TV industry if it doesn't act with urgency to address these issues. TiVo is doing its part, but much more must also be done.
What do you think? Post a comment now.
Categories: Devices
Topics: TiVo
-
Netflix's Q4 Results Powered by Streaming; Further Growth Ahead
Netflix's Q4 earnings and business metrics released late Monday are resounding evidence of how important the company's Watch Instantly streaming feature is becoming to its future. Netflix ended '08 with just under 9.4 million subscribers, up 26% for the year. In Q4 '08 it added almost 2.1M gross subs (39% better than in Q4 '07) and 718K net subs (59% better than in Q4 '07). The company generated $51M in free cash flow in Q4 alone, more than in all of 2007. Did someone say there's a recession going? Not for Netflix it seems.
But here's the really interesting news: on the earnings call CEO Reed Hastings pinned the company's ability to beat its Q4 subscriber growth guidance on underestimating "the positive impact of the introduction of the multi-function CE devices from LG Electronics, Samsung, Microsoft and TiVo that promote Netflix streaming." He further added that "streaming is energizing our growth." Those are pretty strong validations of the company's broadband and CE strategy. (Btw, SeekingAlpha has the full transcript here. If you're a Netflix follower like me, it's a must-read.)
Hastings highlighted the LG and Samsung Blu-ray players as having a high connect rate in the 4th quarter,
 though noting that in terms of gross numbers Xbox and TiVo were more significant simply because their installed bases are so much larger. It's also important to know that Netflix is paying spiffs to CE partners to generate new Netflix subscribers. That further enhances the relationship between Netflix and its CE-partners. On the one hand Netflix content is both a competitive differentiator for these brands' and a generator of cash while on the other CE partners are a driver of both new subs and streaming adoption for Netflix.
though noting that in terms of gross numbers Xbox and TiVo were more significant simply because their installed bases are so much larger. It's also important to know that Netflix is paying spiffs to CE partners to generate new Netflix subscribers. That further enhances the relationship between Netflix and its CE-partners. On the one hand Netflix content is both a competitive differentiator for these brands' and a generator of cash while on the other CE partners are a driver of both new subs and streaming adoption for Netflix. Hastings noted that Netflix is in discussions with all major CE companies to "broadly cover the Blu-ray category and Internet TV category over the next few years." In the coming years, expect Netflix to be the content locomotive for marketing broadband-enabled devices the same way that "Intel Inside" was once the technology locomotive for marketing PCs. What other content provider is going to come close to such ubiquity? Possibly Amazon, whose pay-per-download model could actually be complimentary to Netflix in driving more device adoption. But certainly not Apple, which seems intent to yoke its massive iTunes video library to the proprietary Apple TV box in a fruitless (my opinion) attempt to recreate its iPod success.
Netflix's eventual device ubiquity is going to open up vast opportunities for the company. As I've said in prior posts, in combination with its affordable subscription model and well-respected brand name, Netflix could well become the prime potential "over-the-top" competitor to incumbent video service providers (cable/satellite/telco).
The fly in the ointment remains Watch Instantly's content selection, which is still a shadow of the DVD-by-mail catalog. VideoNuze readers know that I've been a forceful proponent of Netflix bolstering the number of broadcast network programs in its streaming catalog. Yet I think it's clear from Netflix CFO Barry McCarthy's comments on the call that Netflix isn't planning any home run initiatives when it comes to building the streaming catalog. He notes that the level of online content spending "will be paced by our success with streaming and our determination to continue to deliver strong earnings growth."
I generally favor that kind of steady-Eddie approach. But in this case I'd hate to see Netflix give too much weight to smoothly-growing earnings (which of course act to defend its stock price) at the expense of missing out on the big first-mover advantages it is sitting on. In fact, a key part of my prediction that Netflix could well be acquired this year (in my opinion by Microsoft, but who knows...) is that a deep-pocketed acquirer who can insulate Netflix from Wall Street's earnings expectations would be able to build Watch Instantly's library with far more vigor and hence make Netflix an even more formidable competitor.
Only time will tell on that front. Meanwhile Netflix's outstanding Q4 - in the face of a titanic economic slowdown - is tangible evidence that the company is on a path to play a far larger role in entertainment distribution in the broadband era.
What do you think? Post a comment now.
Categories: Aggregators, Devices
Topics: Amazon, Apple, Netflix
-
Recapping CES '09 Broadband Video-Related Announcements
CES '09 is now behind us. As has become typical, this year's show saw numerous broadband video product and technology announcements. As I wrote often last week, the key theme was broadband-enabled TVs. Assuming TV manufacturers deliver on their promises, Christmas '09 should mark the start of real growth in the installed base of connected TVs.
Here are the noteworthy announcements that I caught, in no particular order (I'm sure I've missed some; if so please add a comment and include the appropriate link):
Intel and Adobe to Extend Flash Platform to TVs
Adobe and Broadcom Bring the Adobe Flash Platform to TVs
Samsung and Yahoo Bring the Best of the Web to Television
Yahoo Brings the Cinematic Internet to Life and Revolutionizes Internet-Connected Television
LG Electronics First to Unveil "Broadband HDTVs" That Instantly Stream Movies From Netflix
LG Electronics Launches Broadband HDTVs with "Netcast Entertainment Access"
Sony Debuts Integrated Networked Televisions
Vizio Announces New and Exciting "Connected HDTV" Platform with Wireless Connectivity
Netflix Announces Partnership with Vizio to Instantly Stream Movies to New High Definition TVs
MySpace Partnerships Bring Web Site to TV Set
Macrovision to Bring Instant Access to Digital Content Directly to Internet-Connected Televisions
Cisco Brings Manufacturers Together to Make Connected Home Products Simple to Set-up and Easy to Use
blip.tv and ActiveVideo Networks Sign Deal to Bring Original Online Shows Directly to Television
Hillcrest Labs and Texas Instruments Showcase RF4CE Remote Controls with Freespace Technology
Categories: Aggregators, Devices
Topics: Ac, Adobe, Amazon, Broadcom, Intel, LG, Macrovision, Move Networks, MySpace, Netflix, Netgear, Roku, Samsung, Sony, Vizio, Yahoo
-
Where Does Advertising Fit In with Broadband-Enabled TVs?
If you haven't noticed, the theme at VideoNuze this week has been broadband-enabled TVs, since this has been one of the main themes of this week's CES. On Monday, when the dust has settled, I'll recap some of the key deals. For today though, I want to inject a small dose of reality into the hype that's starting to build up around broadband-enabled TVs.
First off, I'm thrilled to see an ecosystem of technology leaders, TV set manufacturers, content providers and aggregators taking shape around broadband-enabled TVs. It's looking increasingly inevitable that broadband access is going to be a staple feature of HDTVs in the years to come. Just as you wouldn't consider buying an HDTV without multiple HDMI ports today, at some point in the future you'll be unlikely to buy one without broadband capability. That's pretty cool.
Still, what's missing from the flurry of this week's announcements is how the exciting new broadband path to the TV will actually be monetized by video content providers. I know that mundane questions like this aren't what people tend to focus on at glitzy CES, but they are critical nonetheless. With services like Netflix or Amazon VOD - which have been in the middle of several announcements - it's obvious enough how they'll benefit. The more pertinent question is how video that is ad-supported is going to work, especially since ad-supported video will always represent the lion's share of the average consumer's viewership time.
The broadband video ad model itself is still nascent, and this week's J.P. Morgan report shows that there's no shortage of lingering skepticism still overhanging it. Nonetheless, I'd argue we're at least at a point now where most market participants have a pretty good handle on broadband video advertising's basics - serving technologies/vendors, formats, expected delivery quality, CPMs, user preferences, click-throughs, etc. In short, I believe the foundation is pretty well in place for a strong ramp up of spending (notwithstanding the larger economic issues) as the broadband video world exists today.
But how much of that foundation will still be valid for broadband-enabled TVs vs. how much will need to be re-built (as is the case with mobile video)? Many of the answers are driven by the chips from Intel, Broadcom and others that are going into these TVs. Understanding their respective capabilities and how they'll support broadband video advertising's existing ecosystem is key.
Here's why: in the broadband world to date, the computer's vast processing capabilities (along with the supporting cast of browser, media players, plug-ins, cookies and of course robust broadband access) has played an incredibly important, yet largely unsung role in raising the user experience bar to a point where broadband video has been massively adopted. Of course, this massive adoption has been THE key ingredient for the broadband video ad model to take off. And client-side capabilities only become more important in the highly syndicated broadband video world that I envision in the future. Ad servers need to know which site is playing the video so the right ad is dynamically served and everyone gets compensated properly. The new broadband TV chips need to support all of this and more.
One needs look no further than cable's VOD experience to date to recognize how important the building blocks for an effective advertising model are. While billions of VOD streams are now consumed, very little of it is monetized due to still-inadequate ad capabilities. Years after VOD's launch, these monetization constraints are curtail content providers' interest in participating in VOD. In fact, I'd argue that broadband has actually been a beneficiary of VOD's deficiencies: faced with a choice of where to allocate resources, many content providers have shifted attention to broadband because its monetization mechanisms are so robust.
Anyway, you get the point. Broadband-enabled TVs are very exciting. But to reach their potential, they must deliver a robust user experience and allow advertising to work effectively. In these penny-pinching, resource-constrained times, something that's cool is no longer enough to gain interest. People need to understand how they'll make money from it.
What do you think? Post a comment now.
Categories: Advertising, Devices
Topics: Amazon, Broadcom, Intel, J.P. Morgan, Netflix
-
Yahoo Gets Traction in Broadband-to-TV Market
At CES, Yahoo is making its presence felt in the budding broadband-to-the TV space with its "Yahoo Widget Engine." It has announced deals with TV manufacturers Samsung, LG, Sony and Vizio (see next post). It's an impressive list, and these Yahoo-enabled TVs are expected in the market later in '09.
Some of you may recall that the Yahoo Widget Engine debuted last summer as part of a broader alliance with Intel called the "Widget Channel". The two companies have come together to create an applications
 framework running on new Intel media processing chips. An SDK allows 3rd party developers to use web-standard technologies to develop applications for TVs and other CE devices. That's a mouthful, but the news coming out of CES appears to show that Yahoo/Intel are making progress building out the ecosystem of both TV manufacturers and 3rd parties applications.
framework running on new Intel media processing chips. An SDK allows 3rd party developers to use web-standard technologies to develop applications for TVs and other CE devices. That's a mouthful, but the news coming out of CES appears to show that Yahoo/Intel are making progress building out the ecosystem of both TV manufacturers and 3rd parties applications.In addition to Yahoo content like news, weather, finance and Flickr, there's 3rd party content from USA Today, YouTube, eBay and Showtime. And there are premium movie and TV programs from Netflix, Amazon VOD and Blockbuster. The list of others involved goes on.
All of this is very positive for the budding broadband-to-the-TV space and clearly demonstrates how much emphasis the non-incumbent video service provider (cable/satellite/telco) world is placing on "over the top" services. As expected, these incumbents have a big disruptive bull's-eye on their foreheads. For the numerous 3rd parties that have never had access to the consumers' TV, broadband's openness provides their first-ever entry pass.
As exciting as all this is, the jumble of TV, content, technology and aggregation brands coming to market is prime to create mass confusion for consumers being targeted with these services. Here's the scenario: a prospective TV buyer walks into a Best Buy just looking for a new HDTV, but pretty quickly starts hearing about all these different services and brands. Within minutes the consumer's head is going to be swimming. Which service and content is free and which costs extra? How does it all connect? What if I already have Netflix, Flickr or YouTube passwords - do they automatically work? Do I need to change something that's already in my house, like my home network? And who do I call if something's not working right? One sure winner with these new broadband TVs coming out is the Geek Squad!
Still, this is exciting stuff. A whole new world of broadband on the TV content and applications is finally poised to see the light of day and with it will come all kinds of new opportunities.
What do you think? Post a comment now.
Categories: Devices
Topics: Intel, LG, Samsung, Sony, Vizio, Yahoo
-
Vizio is Latest to Announce Broadband/TV Integration
Broadband video integrated TVs got another big boost as Vizio, one of the top 3 flat panel brands in the U.S. announced its new "Connected HDTV" platform at CES this afternoon. The move comes on top of Netflix's LG announcement, and other chip-based announcements from Adobe with Intel and Broadcom. More
 broadband TV announcements are sure to follow.
broadband TV announcements are sure to follow.The new Vizio TVs will incorporate the Yahoo Widget Engine and support for Adobe Flash Lite. Importantly, the TVs will allow access to a very broad range of content including Netflix Watch Instantly, Amazon VOD, Blockbuster OnDemand, Accedo, Flickr, Pandora, Rhapsody and Yahoo. For Netflix and Amazon specifically, the Vizio deal continues building out the portfolio of 3rd party devices that play their video libraries.
From a consumer standpoint, I think it's becoming increasingly clear that by late '09 into '10, buying an HDTV will almost always include the experience of bringing the set home, connecting it to your home wireless network and browsing a growing collection of paid and free broadband video choices. I envisioned for a while that 3 devices - game consoles, Blu-ray players and IP-enabled TVs - would be leading the charge into the "over-the-top" market. With these CES announcements and more to come, TVs could well become the most prolific of the three in the long run.
What do you think? Post a comment now.
Categories: Devices
Topics: Adobe, Broadcom, Intel, Netflix, Vizio
-
Amazon VOD Now On Roku; Battle with Apple Looms Ahead
Amazon and Roku announced yesterday that Amazon's VOD service will soon be available on Roku's $99 Digital Video Player. The deal starts to make good on Roku CEO Anthony Woods's intentions about "opening up the platform to anyone who wants to put their video service on this box."
With Amazon VOD's 40,000+ TV programs and movies added to the 12,000 titles already available to Netflix subscribers via its Watch Instantly service (plus more content deals yet to come), little Roku is starting to look like a potentially important link in the evolving "over-the-top" video distribution value chain.
More interesting though, is that I think we're starting to see the battle lines drawn for supremacy in the download-to-own/download-to-rent premium video category between Amazon on one side and Apple on the other. Though Apple dominates this market today, having sold 200 million TV programs alone, there are ample reasons to believe competition is going to stiffen.
Apple is of course in the video download business for the same reasons it was in the music download business: to drive sales of the iPod and more recently - and to a lesser extent - the iPhone. According to the latest info I could find, iTunes now has 32,000+ TV programs and movies, including a growing number in
 HD. For now that's slightly less than Amazon VOD, but my guess is that over time the two libraries will be virtually identical.
HD. For now that's slightly less than Amazon VOD, but my guess is that over time the two libraries will be virtually identical. While Apple has a near monopoly on portable viewing via the iPod and iPhone, it is a laggard in bridging broadband-to-the-TV. Its Apple TV device, introduced in January, 2007, and meant to give iTunes access on the TV, has been an underperformer. Certainly a detractor has been price, with the 40GB lower-end model still running $229. But more importantly, as an iTunes-only box, Apple TV perpetuates a closed, "walled-garden" paradigm that consumers are increasingly rejecting (as companies like Roku astutely understand).
For Amazon, the world's largest online retailer, video downloads are a rich growth market. The company brings significant advantages to the table, starting with tens of millions of existing customer relationships with credit cards or other payment options just waiting to be charged for video downloads. Amazon has strong brand name recognition and trust. And of course, it has a near-limitless ability to cross-promote downloads with DVDs and other products.
Determined not to be left behind in the great race to get broadband delivered video all the way to the TV, it has been integrating its VOD service with 3rd party devices like TiVo, Sony's Bravia Internet Video Link, Xbox 360 and Windows Media Center PCs. Its latest deal with Roku is far from its last.
 Amazon VOD's adoption will benefit from the fact that there are many non-Amazon reasons that people will be buying these devices. For example, consider Roku, TiVo and Xbox 360. With Roku, Netflix is fueling sales. As Netflix subscribers realize that new releases are generally not available in Watch Instantly, but are through Amazon VOD on Roku, they'll be prone to give Amazon VOD a try (the Netflix limitation is course due to Hollywood's windowing, and another reason why I believe it's crucial for Netflix to make deals with broadcast networks for online distribution of their hit programs). For TiVo and Xbox 360, each has a well-defined value proposition for consumers to purchase. Amazon VOD's availability is a pure bonus for buyers.
Amazon VOD's adoption will benefit from the fact that there are many non-Amazon reasons that people will be buying these devices. For example, consider Roku, TiVo and Xbox 360. With Roku, Netflix is fueling sales. As Netflix subscribers realize that new releases are generally not available in Watch Instantly, but are through Amazon VOD on Roku, they'll be prone to give Amazon VOD a try (the Netflix limitation is course due to Hollywood's windowing, and another reason why I believe it's crucial for Netflix to make deals with broadcast networks for online distribution of their hit programs). For TiVo and Xbox 360, each has a well-defined value proposition for consumers to purchase. Amazon VOD's availability is a pure bonus for buyers.Still, Amazon VOD's Achilles heel that it is missing a portable playback companion on a par with the iPod and iPhone. Users clearly value portability and Amazon needs to solve this problem (hmm, can you say "Kindle for Video?"). Yet another issue is that despite its various 3rd party device deals, the user experience will always be governed by these devices' strengths and weaknesses. In this respect, Apple's ownership of the whole hardware/software/services ecosystem gives it significant user experience advantages (which of course it has masterfully exploited with iTunes/iPod).
Apple and Amazon hardly have the market to themselves though. Others like Microsoft Xbox LIVE, Vudu and Sezmi are vying for a place in the market. And then of course there are the VOD offerings from the cable/satellite/telco video service providers, who have big-time incumbency advantages. Not to be forgotten in all of this is consumer inertia around the robust DVD market, which to a large extent all of these video download options seek to supplant.
In the middle of all this are Joe and Jane Consumer - soon to be overwhelmed by a barrage of competing and confusing offers for how to get on-demand TV program and movie downloads in better, faster and cheaper ways. In this market, I believe simplicity, content choices, brand and especially price will determine the eventual winners and losers. These are front and center considerations for Amazon, Apple and all the others going forward.
What do you think? Post a comment now.
Categories: Aggregators, Devices, Downloads, FIlms, HD
Topics: Amazon, Apple, iTunes, Roku, SezMi, TiVo, VUDU, XBox
-
Netflix and LG Go Over-the-Top with New "Broadband HDTVs"
Happy New Year and welcome to 2009.
The new year is picking up right where the old year left off - with Netflix adding yet another way for its subscribers to use its Watch Instantly streaming service on their TVs. Today's announcement that its WI software will be embedded in a select number of new LG "Broadband HDTVs" is more evidence of how content providers and consumer electronics companies are aiming to go "over the top" of cable/satellite/telco, driving high quality broadband video all the way to the TV.
The new LG Broadband HDTVs joins XBox 360, TiVo, Samsung and LG Blu-ray players and Roku as options
 for Netflix subscribers looking to watch WI on their TVs. The differentiator here is that this is the first "boxless" approach, so it offers a potentially simpler (though not less expensive) solution for consumers. No doubt it is the first of many deals Netflix will announce with TV manufacturers in '09.
for Netflix subscribers looking to watch WI on their TVs. The differentiator here is that this is the first "boxless" approach, so it offers a potentially simpler (though not less expensive) solution for consumers. No doubt it is the first of many deals Netflix will announce with TV manufacturers in '09.Still, my bet is that the group of box-based solutions will matter more to WI usage for a long time to come. That's because, even though LG is the #3 HDTV manufacturer, TV set replacement cycles are getting longer with the down economy, the new Broadband HDTVs will likely have a several hundred dollar price premium, and importantly, a solid portion of the existing Netflix subscriber target audience for these broadband sets may have long since been using one of the box-based alternatives and not see a lot of incremental benefit in buying one of the LG Broadband HDTVs.
Nevertheless, I think an interesting target market for these sets are non-Netflix subscribers, who are open to a "cord-cutting" proposition. Netflix is laying the groundwork for becoming a genuine alternative to today's multichannel subscription video services. As I've said before, to make itself more viable as an alternative, the most important thing Netflix can do is beef-up WI's broadcast network programming library.
 When top-tier broadcast network programming is combined with its movie catalog, Netflix could become very appealing for consumers who don't care much about cable network programs or sports. For $17/month for Netflix vs. $60/month or more for a typical digital TV package from cable/satellite/telco, the math on paying the premium for the Netflix-enabled LG TV becomes much more interesting. Importantly, the retailer has a much stronger hook to sell the LG Broadband HDTVs, especially if, as an added incentive, Netflix perhaps threw in a 3-4 month trial subscription.
When top-tier broadcast network programming is combined with its movie catalog, Netflix could become very appealing for consumers who don't care much about cable network programs or sports. For $17/month for Netflix vs. $60/month or more for a typical digital TV package from cable/satellite/telco, the math on paying the premium for the Netflix-enabled LG TV becomes much more interesting. Importantly, the retailer has a much stronger hook to sell the LG Broadband HDTVs, especially if, as an added incentive, Netflix perhaps threw in a 3-4 month trial subscription.The bottom line here is that Netflix continues to do the right thing by building out the portfolio of devices that play its WI streaming programming. The bigger the addressable audience is, the more that content providers of all stripes will take notice and want to do deals (Netflix's expansion of its promotional deal with Showtime is a useful data point on this subject). No other non-cable/satellite/telco subscription video service is close to Netflix in terms of number of subscribers, compatible streaming devices, library or brand name. In '09, Netflix is poised to build on these advantages as it morphs itself into an over-the-top broadband powerhouse.
What do you think? Post a comment now.
Categories: Aggregators, Devices
-
2009 Prediction #2: Mobile Video Takes Off, Finally
As promised, each day this week I'm sharing one prediction for 2009, with each one getting progressively bolder as the week progresses (and yes, I'll concede - as a number of you privately pointed out to me - yesterday's forecast that the Syndicated Video Economy would grow in '09 was a pretty wimpy start). So moving out a little further on the limb, today's prediction #2 is that video delivered directly to mobile/wireless devices will take off in '09, finally.
For those of you who have been following mobile/wireless video delivery, this has been a market that's perpetually been "just around the corner." In fact, a little over a year ago when I was planning VideoNuze, several people suggested that I shouldn't just focus on broadband delivery (as I define it to mean high-speed wired delivery of video to a home or business), but also mobile/wireless video. But after doing some due diligence I concluded that the market wasn't there yet, and that the vast majority of new video activity would be focused on wired broadband. Indeed, I think that's how '07 and much of '08 have shaped up.
However, having tracked recent activity in the mobile video space, I think '09 is going to be a big year of growth and recognition for this new medium (in fact, an old friend gently chastised me over lunch last week for even drawing a distinction between wired and wireless delivery, saying, "come on, it's ALL broadband!" I think he makes a very fair point.)
What has traditionally held back mobile delivery are a lack of video-capable devices, voice and text-focused wireless networks and a closed "on-deck" paradigm, which is the wireless carrier's version of the cable and satellite industry's proverbial walled-garden.
These limitations have now been mostly addressed, or are in the process of being addressed. On the device side, the most notable video-capable device is of course the iPhone, which by my calculations has already sold over 13 million units and is on its way to almost 20 million by the end of the year. Everyone I know who has an iPhone - especially kids - are infatuated with the video feature (if you've never seen it, especially now using AT&T's 3G network, get thee to an Apple store immediately!). In '09, the iPhone is poised for even greater popularity as Wal-Mart begins stocking it, possibly for just $99. Recession or not, the iPhone is going to remain white hot.
Not to be lost in the iPhone's phenomenal wake are many other new video-capable phones. There's of course the new G1 from T-Mobile, powered by Android, Google's new mobile OS. I got my first look at one last week, and though not as sleek as the iPhone, I was able to watch excellent YouTube video. There are plenty of others to choose from as well, including the Samsung Propel, the LG Incite, the new BlackBerry Storm and the latest mother-of-all-phones, the Nokia N64, which comes with 16GB of internal memory (enough for 40 hours of video). Whereas many of us today carry phones incapable or barely capable of viewing video, in '09 the replacement process will be in full swing.
Of course, all the cool devices in the world don't matter unless you have a robust underlying network and the freedom to view what you want. On this front, the wireless carriers' push to build out their next generation 3G networks finally allows sufficient bandwidth to view high-quality video (though not HD yet). Next up is 4G, first from Clearwire, the SprintNextel-Intel-Google-cable industry consortium that's deploying its WiMax network with speeds of up to 6 Mbps downstream being promised. There's also MediaFLO, Qualcomm's mobile broadcasting platform that has steadily built out an ecosystem of technology, carrier and content partners.
Last but not least are the consumer-focused services and applications. Until recently, this market has mainly consisted of packaged subscription services like Verizon's VCast and MobiTV, which itself recently announced more than 5 million subscribers. The combination of new devices and networks promises to bring an increase in on-demand, web-based, ad-supported video consumption (plus paid downloads to be sure, courtesy of the iPhone mainly). Another interesting twist is the advent of live broadcasting from mobile devices, powered by providers like Qik, Kyte and Mogulus. These all supercharge the Twitter micro-blogging phenomenon.
All of this underscores why the distinction between wired and wireless broadband really becomes meaningless over time. The mobile experience is going to seem more and more like the one you have sitting at your computer, with the added benefit of portability. To throw a blue-sky variable into the mix, one wonders if at some point you'll simply plug your phone into your TV and watch streamed or downloaded video that way, rather than through a set-top box or a wired broadband connection. There's a convergence concept for you!
Years in the making, mobile/wireless video is finally upon us, and '09 is going to be a big year. That's good news for all of us as consumers, and it surely means I'll be working a lot harder to stay on top of things.
What do you think? Post a comment now.
Previous, Prediction #1: Syndicated Video Economy Grows
Tomorrow, 2009 Prediction #3
Categories: Devices, Mobile Video
Topics: Android, Apple, AT&T, BlackBerry, Clearwire, Google, iPhone, LG, Medi, Nokia, Samsung, SprintNextel, T-Mobile, Verizon, Wal-Mart
-
Reviewing My 6 Predictions for 2008
Back on December 16, 2007, I offered up 6 predictions for 2008. As the year winds down, it's fair to review them and see how my crystal ball performed. But before I do, a quick editorial note: each day next week I'm going to offer one of five predictions for the broadband video market in 2009. (You may detect the predictions getting increasingly bolder...that's by design to keep you coming back!)
Now a review of my '08 predictions:
1. Advertising business model gains further momentum
I saw '08 as a year in which the broadband ad model continued growing in importance as the paid model remained in the back seat, at least for now. I think that's pretty much been borne out. We've seen countless new video-oriented sites launch in '08. To be sure many of them are now scrambling to stay afloat in the current ad-crunched environment, and there will no doubt be a shakeout among these sites in '09. However, the basic premise, that users mainly expect free video, and that this is the way to grow adoption, is mostly conventional wisdom now.
The exception on the paid front continues to be iTunes, which announced in October that it has sold 200 million TV episode downloads to date. At $1.99 apiece, that would imply iTunes TV program downloads exceed all ad-supported video sites to date. The problem of course is once you get past iTunes things fall off quickly. Other entrants like Xbox Live, Amazon and Netflix are all making progress with paid approaches, but still the market is held back by at least 3 challenges: lack of mass broadband-to-the-TV connectivity, a robust incumbent DVD model, and limited online delivery rights. That means advertising is likely to dominate again in '09.
2. Brand marketers jump on broadband bandwagon
I expected that '08 would see more brands pursue direct-to-consumer broadband-centric campaigns. Sure enough, the year brought a variety of initiatives from a diverse range of companies like Shell, Nike, Ritz-Carlton, Lifestyles Condoms, Hellman's and many others.
What I didn't foresee was the more important emphasis that many brands would place on user-generated video contests. In '08 there were such contests from Baby Ruth, Dove, McDonald's, Klondike and many others. Coming up in early '09 is Doritos' splashy $1 million UGV Super Bowl contest, certain to put even more emphasis on these contests. I see no letup in '09.
3. Beijing Summer Olympics are a broadband blowout
I was very bullish on the opportunity for the '08 Summer Games to redefine how broadband coverage can add value to live sporting events. Anyone who experienced any of the Olympics online can certainly attest to the convenience broadband enabled (especially given the huge time zone difference to the U.S.), but without sacrificing any video quality. The staggering numbers certainly attested to their popularity.
Still, some analysts were chagrined by how little revenue the Olympics likely brought in for NBC. While I'm always in favor of optimizing revenues, I tried to take the longer view as I wrote here and here. The Olympics were a breakthrough technical and operational accomplishment which exposed millions of users to broadband's benefits. For now, that's sufficient reward.
4. 2008 is the "Year of the broadband presidential election"
With the '08 election already in full swing last December (remember the heated primaries?), broadband was already making its presence known. It only continued as the year and the election drama wore on. As I recently summarized, broadband was felt in many ways in this election cycle. President-elect Obama seems committed to continuing broadband's role with his weekly YouTube updates and behind-the-scenes clips. Still, as important as video was in the election, more important was the Internet's social media capabilities being harnessed for organizing and fundraising. Obama has set a high bar for future candidates to meet.
5. WGA Strike fuels broadband video proliferation
Here's one I overstated. Last December, I thought the WGA strike would accelerate interest in broadband as an alternative to traditional outlets. While it's fair to include initiatives like Joss Wheedon's Dr. Horrible and Strike.TV as directly resulting from the strike, the reality is that I believe there was very little embrace of broadband that can be traced directly to the strike (if I'm missing something here, please correct me). To be sure, lots of talent is dipping its toes into the broadband waters, but I think that's more attributable to the larger climate of interest, not the WGA strike specifically.
6. Broadband consumption remains on computers, but HD delivery proliferates
I suggested that "99.9% of users who start the year watching broadband video on their computers will end the year no closer to watching broadband video on their TVs." My guess is that's turned out to be right. If you totaled up all the Rokus, AppleTVs, Vudus, Xbox's accessing video and other broadband-to-the-TV devices, that would equal less than .1% of the 147 million U.S. Internet users who comScore says watched video online in October.
However, there are some positive signs of progress for '09. I've been particularly bullish on Netflix's recent moves (particularly with Xbox) and expect some other good efforts coming as well. It's unlikely that '09 will end with even 5% of the addressable broadband universe watching on their TVs, but even that would be a good start.
Meanwhile, HD had a banner year. Everyone from iTunes to Hulu to Xbox to many others embraced online HD delivery. As I mentioned here, there are times when I really do catch myself saying, "it's hard to believe this level of video quality is now available online." For sure HD will be more widely embraced in '09 and quality will get even better.
OK, that's it for '08. On Monday the focus turns to what to expect in '09.
What do you think? Post a comment now.
Categories: Advertising, Aggregators, Brand Marketing, Devices, HD, Indie Video, Politics, Predictions, Sports, Technology, UGC
Topics: Amazon, Apple, AppleTV, Barack Obama, Hulu, iTunes, NBC, Netflix, Olympics, Roku, VUDU, XBox
-
Sony's Internet-to-the-TV Plans Are Confusing (and the NYTimes Coverage Isn't Helping Any)
Catching up on some reading last night, I got a chance to re-read a NYTimes piece by Saul Hansell from this past Tuesday rather sensationally entitled "How Comcast Controls Sony's Internet TV Plans." When I scanned it on Tuesday before posting a link to it from VideoNuze, I had one of those "This makes absolutely no sense, I need to read this again closer" reactions. Now, upon re-reading it, I'm having one of those "This really makes no sense" reactions.
The piece - which initially concerns Sony's efforts to bring broadband video to TVs, but then veers off into a somewhat unrelated discussion of the company's negotiations with the cable industry's tru2Way and CableCard technologies - quotes Sony Electronics U.S. president Stan Glasgow as saying: "We've worked with the cable companies for five years to develop a system that would allow us and the rest of the television manufacturers to have alternative content on the TV."
Why would Sony devote five years to such an undertaking? Because, again in Mr. Glasgow's words, "If you have to ask a consumer to switch sources constantly between cable and another source, it is not the normal consumer experience...There has to be a more integrated way to have cable and Internet content on the same user interface."
I'm all for making things easy on the consumer, but let's get this right: Sony devoted five years to negotiating with the cable industry so it could avoid viewers having to push the "Source" or "Input" button on their remote controls to toggle to broadband-delivered content via Sony devices?
Hello? According to comScore's recent numbers, 142 million people in the U.S. alone watched 558 million hours of online video. But amid that massive adoption, Sony thinks it might be setting the bar too high for its potential buyers if it asked them to push a button on their remotes so that they could enjoy some of that video on their TVs instead of on their PCs?
Is it just me, or does it appear that Sony completely misjudged both its potential buyers' technical aptitude and also their strong motivation to consume broadband-delivered video on their TVs?
While you consider those questions, let's also go back to basics: why is once-mighty Sony even bothering to integrate its Internet-to-the-TV products with the cable industry in the first place? The whole point of these kinds of Internet-to-the-TV devices is to disrupt the cable (and satellite and telco) industry's hold on consumer viewing time and spending for in-home video programming. Countless companies (Netflix, Hulu, Microsoft/Xbox, Apple/AppleTV, Vudu, Netgear, Sezmi, 2Wire, Blockbuster, LG, Samsung, Neuros, etc.) get this fundamental point and are implicitly or explicitly driving toward this goal each day.
That Sony doesn't seem to understand this suggests that the correct title of Saul's piece really should have been "Comcast Benefits by Exploiting Sony's Misguided Internet TV Plans."
What's profoundly different about the broadband era is that neither Comcast nor any other incumbent controls how consumers get video on their TVs, just as neither the NYTimes nor any other single news provider has ever controlled how we've gotten our news. If would-be "over-the-top" competitors don't get this basic idea - and instead waste precious time and resources on perpetuating the traditional world order - then shame on them.
What do you think? Post a comment now.
Categories: Cable TV Operators, Devices
-
Blockbuster Online with New 2Wire MediaPoint Player Has a Tough Climb Ahead
Have you received the email pitch from Blockbuster Online yet, to rent 25 movies and get the new 2Wire MediaPoint Digital Media Player "free?" I've received a couple already this week (see below), and after reviewing the offer and its details, and comparing it to other alternatives, my conclusion is that the new service has a tough climb ahead.
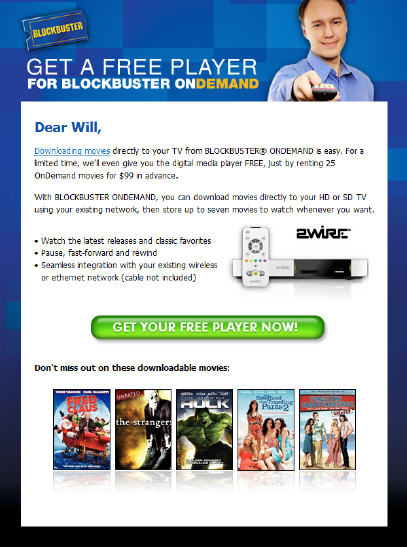
The new 2Wire box itself is in the same general family as other single-purpose boxes such as AppleTV, Vudu and Netflix's Roku. There are some differences among them in hard drive size, pricing, outputs and streaming vs. downloading orientation. But they all serve the same basic purpose: connecting you via your home broadband connection to one source of "walled garden" premium-quality video content.
VideoNuze readers know I've been quite skeptical of the standalone box model, especially when box prices start in the $200-300 range. There's no question there's an upscale, early adopter audience that will buy in, but mainstream consumers will be uninterested for all kinds of reasons including: financial considerations (especially in this economy), resistance to connecting another box in already crowded consoles, perceived technical complexity, strong existing substitutes (e.g. cheap ubiquitous DVD players) and indistinct value propositions.
My judgment is based on a pretty simple set of criteria I rely on to gauge a new product or service's likelihood of success: Does it offer meaningful new value (some combination of better price, quality or speed) with minimal adoption effort required? Can a large target audience for this new value be clearly defined, served and acquired in an economically-reasonable manner? Is this new value attainable without sacrificing meaningful benefits of existing alternatives?
Miss on any one of these and the odds of success lengthen. Miss on any two and you're in long-shot territory. Miss on all three and you're dead on arrival. After evaluating the Blockbuster Online/MediaPoint current offer, my sense is that it misses on at least two and possibly all three.
Value: As explained below, for certain movies renters, the offer is valuable. It provides convenience at a relatively low financial commitment for the new device. But explaining these benefits just to the relevant target audience at an economic cost per acquisition is going to be nearly impossible. I'm dubious that even in-store promotions - which on the surface seem Blockbuster's strength - will work. First, there may be franchisee issues, as there were with previous "Total Access" promotions. And second, Blockbuster has closed so many stores in prime target neighborhoods - due to the rise of Netflix and other options eroding their business - that they'll be missing many prospects (example: in my upscale home town of Newton, MA there is not a single Blockbuster store left).
Audience: There's only one real target audience I can see for this offer, and it seems very narrow to me: low-volume renters of movies only, who are not iTunes users. Think about it - if you rent a lot of movies, you've likely been subscribing to Netflix for years (more so if you also rent TV shows). If you want to own your content instead of rent it, then you buy DVDs or maybe more recently have been buying digital version, most likely with iTunes primarily. If that's the case, then when it comes to watching on TV, you're going to buy an Apple TV (even then, few have done so to date), not a 2Wire MediaPoint. The eligible target audience left for Blockbuster/MediaPoint seems pretty slim.
Sacrificing existing benefits: Inevitably all digital distribution options need to be compared to the incumbent DVD format, which is remarkably strong (no wonder a billion units have been shipped to date). Against the DVD standard, Blockbuster/MediaPoint is inferior in a number of ways: limited viewing windows (the usual online limitations of 24 hour expiration after starting, and 30 day automatic file deletion), no portability to view rented movies on other TVs not connected to a MediaPoint, no TV shows available for rent, and at this point, smallish storage that only keeps up to 5 movies at a time.
Add it all up, and it's a pretty daunting set of issues. To be sure, much of this isn't specific to Blockbuster. To succeed, all new digital delivery options must be mindful of the above criteria as well.
What do you think? Post a comment now.
Categories: Aggregators, Devices
Topics: 2Wire, AppleTV, Blockbuster, Netflix, VUDU
-
November '08 VideoNuze Recap - 3 Key Themes
Welcome to December and to the home stretch of 2008. Following are 3 key themes from VideoNuze in November:
Cable programming's online distribution narrows - Last month I concluded that cable programmers (e.g. Discovery, MTV, Lifetime) are going to become much more sparing when it comes to distributing their full programs online. As noted in "The Cable Industry Closes Ranks," after hearing from industry executives at the CTAM Summit and on the Broadband Video Leadership Breakfast, it has become apparent that the industry is going to defend its traditional multichannel video subscription model from broadband and new "over-the-top" incursions.
Both programmers and operators have a lot vested in this successful model, and are surely wise to see it last as long as possible. Subscription and affiliate fees are particularly precious in this economy, as the WSJ wrote on Saturday. Still, many VideoNuze readers pointed out the music industry's folly in trying to maintain its business model, only to see it turned upside down. Many predicted the cable industry is doomed to follow suit. Truth-be-told though, as I wrote in "Comcast: A Company Transformed," major cable operators are already far more diversified than they used to be. Broadband, phone and digital TV (+ add-ons like DVR, HD and VOD) have created huge new revenue streams. Surging broadband video consumption only helps them, even as "cord-cutting" looms down the road.
Netflix moves to first ranks of cord-cutting catalysts - Three posts in November highlighted the significant role that Netflix is poised to play in moving premium programming to broadband distribution. Most recently, in "New Xbox Experience with Netflix Watch Instantly: A 'Wow' Moment," I shared early reactions from a VideoNuze reader (echoed by many others) to receiving a subset of Netflix's catalog through Xbox's recently upgraded interface. Netflix CEO Reed Hastings highlighted the increasing importance of game devices in bridging broadband to the TV in his keynote at NewTeeVee Live this month (recapped here).
Still, Netflix lacks the rights to deliver many movies online, a problem unlikely to be rectified any time soon given Hollywood's stringent windowing approach. As such, in "Netflix Should be Aggressively Pursuing Broadcast Networks for Watch Instantly Service," I offered my $.02 of advice to the company that it should build on its recent deal with CBS to blow out its online library of network programs. In this ad-challenged environment, I believe networks would welcome the opportunity. Hit TV programs would help drive device sales, which is crucial for building WI's adoption. While the Roku box is a modest $99, other alternatives are still pricey, though becoming cheaper (the Samsung BD-P2500 Blu-ray player is down $100, now available at $300, I spotted the LG BD300 over the weekend for $245). A robust Netflix online package would be poised to draw subscribers away from today's cable model.
Lousy economy still looms large - Wherever you go, there it is: the lousy economy. Though the market staged a nice little rebound over the last 5 days, things are still fragile. Across the industry broadband companies are doing layoffs. This is only the most obvious of the side effects of the economic downturn. Another, more subtle one could be downward price pressure. As I wrote in "Deflation's Risks to the Broadband Video Ecosystem," economists are now growing concerned that the credit crunch could lead to collapsing prices and profits across the economy. I noted that such an occurrence would be particularly damaging for the broadband industry, where business models are still nascent, so ROIs and spending are softer.
Here's to hoping for some good economic news in December...
What do you think? Post a comment now.
Categories: Aggregators, Broadcasters, Cable Networks, Cable TV Operators, Devices, Games
Topics: CBS, Comcast, LG, Microsoft, Netflix, Roku, Samsung, XBox
-
New Xbox Experience with Netflix Watch Instantly: A "Wow" Moment
Wow.
That was the reaction that VideoNuze reader and digital media public relations executive Jeff Rutherford had after downloading the "New Xbox Experience" (or NXE) to his Xbox 360 and activating Netflix Watch Instantly. Jeff relayed the details to me in an email and phone call yesterday, adding that it felt comparable to his (and many others') first experience with TiVo.
Hyperbole? Maybe. I'm always mindful about how gadgeteers' early wows seem to melt away when new technology products reach the broader mass market. Still, the Xbox 360/Netflix Watch Instantly integration seems promising on at least three fronts.

First, Xbox 360 is a relatively mainstream device that has its own clear value propositions, thereby driving a sizable footprint that is only going to grow. Second, Netflix's Watch Instantly is a value-add to its subscription service, requiring no incremental fees, or special new add-on hardware to Xbox 360. And third, as Jeff reported, it was very easy to get going: he was given a code to input online and when he returned to his Xbox, his Watch Instantly queue was displayed there, awaiting his on-demand selections.
These benefits - large distribution, no extra fees, no new hardware and easy install/strong user experience - are all key to a successful broadband-to-the-TV service. But equally, if not more important is content selection and value. This is where the Xbox 360/Netflix implementation hits a speed bump, at least for now.
As I explained recently in "Netflix Should be Aggressively Pursuing Broadcast Networks for Watch Instantly Service," today's windowing model puts the company is in a serious bind with respect to getting top-flight Hollywood films. While Jeff reported seeing some strong titles like Disney's Ratatouille (and other films he noticed carrying the Starz watermark), the reality is that Watch Instantly's catalog is still a small sliver of Netflix's DVD-by-mail catalog and will remain so for some time to come.
Further portending the difficulties of what's ahead for Netflix as it navigates Hollywood's minefields is early word, courtesy of Joystiq and other blogs, that all of Sony's Columbia Pictures movies have been disabled for XBox 360 Netflix users, due to licensing issues. While we may all be rooting for Netflix to find deal terms with Sony and the others, the realist side of me says that Hollywood's overseers understand that the Xbox 360 integration (and others TBD) have real significance in the relentless push to digital delivery. So before the proverbial horse gets out of the barn, they want to ensure the right deals are in place for them to capture appropriate value.
While that drama plays itself out, Netflix would be wise to do everything else it can to bolster Watch Instantly content value and selection. As I wrote in the prior post, incorporating broadcast programs should be a top priority. Also high on the list should be well-branded, high-quality broadband-only content.
Netflix has a very interesting opportunity to accelerate the Watch Instantly adoption curve, leveraging the huge installed base of Xbox 360 users and Microsoft's UI improvements (more on NXE's new look at Engadget if you're interested). With proof of its success in hand, Netflix's negotiations with recalcitrant studios can only be helped along. Meantime, Xbox 360 is getting another strong (albeit likely temporary) value proposition to compete in the game console space. And consumers win - as Jeff pointed out - by gaining ever-better access to the content they want.
What do you think? Post a comment now.
Categories: Aggregators, Devices, Games
Topics: Microsoft, Netflix, Xbox 360
-
Here Comes Sling.com
Does the world need another broadband video aggregation site for premium quality video content?
The answer to that question will start to come early next week when Sling.com, the latest entrant in this already crowded space, officially launches. Recently Jason Hirschhorn, president of Sling Media's entertainment group and Brian Jaquet, Sling's Director of Public Relations came through Boston and caught me up on their plans to launch commercially on Nov. 24th.
Many of you know that Sling is the maker of the Slingbox, which connects to your TV or DVR, allowing you
 to remotely watch programs on your computer. It's a very clever product, though I have to admit its use case has always been a little confounding to me. Nonetheless, just over a year ago, Sling was acquired by EchoStar in a $380 million deal. Shortly thereafter, EchoStar split itself into two parts, Dish Network, the satellite-delivered programming company, and EchoStar Corporation, which includes Sling and other technology-based businesses.
to remotely watch programs on your computer. It's a very clever product, though I have to admit its use case has always been a little confounding to me. Nonetheless, just over a year ago, Sling was acquired by EchoStar in a $380 million deal. Shortly thereafter, EchoStar split itself into two parts, Dish Network, the satellite-delivered programming company, and EchoStar Corporation, which includes Sling and other technology-based businesses.Sling.com, developed by Jason's entertainment group, is the first Sling offering not tethered to any of its devices and therefore open to all users. Acknowledging that Hulu has set a high bar on user experience, Jason explained that Sling.com is attempting to go one step further on usability, and will also differentiate itself with updated social networking capabilities and highly focused editorial content.
In particular, Sling.com offers a slew of Facebook-like features that allow users to subscribe to and favorite programs and networks, with users in turn able to follow these activities. As Jason aptly put it, the goal is to "digitize the water cooler conversation." The whole experience is geared toward engaging the user at a far deeper level than we're accustomed to in passive linear viewing, or even typical at other aggregators' sites.
The real differentiator for Sling long-term though is the integration of Sling.com with the remote viewing offered by Slingbox. Enabled by a new web-based player (instead of the prior downloadable client), users are able to seamlessly browse back and forth between watching live TV and cataloged programs, as shown below.
Taking this one step further, Sling's goal is to get its remote viewing technology embedded in others' set-top boxes as well. So for example, a Comcast STB with Sling inside would allow you to have live TV integrated into your Sling.com, without having to go buy another box.
That's an enticing prospect, but making it happen will be no small feat; the STB giants like Motorola and SA (now part of Cisco) will get on board only when their biggest customers - America's cable operators - ask for it. The prospect of these cable executives wanting to incorporate any technology controlled by Charlie Ergen, Echo's founder/CEO and the cable industry's arch-enemy, stretches my mind. However, stranger deals have been done, so who knows. In the meantime, there are a whole lot of other non-cable homes globally Sling can address first.
But much of that is down the road anyway. For now, Sling.com is going to compete head on with Hulu (which by my count supplies virtually the entire current movie catalog at Sling.com, in turn begging the question of how many different ways one relatively small ad revenue stream can get carved up?), Fancast, the portal sites, YouTube and so on. Jason readily admits that these sites will not compete on content exclusivity; ultimately they'll all have access to everything that's available.
So in this incredibly crowded space, is there room for a newcomer? On the surface, it's tempting to say "no." But history teaches us that "better mousetraps" can elbow their way into even the most crowded spaces. Remember how many search engines already existed when Google burst onto the scene? On a totally different level, I can relate to this challenge myself. A year ago I wondered whether there was room for a new broadband video-centric blog when so many others already existed; now here we are.
The reality is that newcomers succeed because they don't accept the status quo as final. Rather, they find smart ways of delivering new and better value to customers who didn't necessarily even know what they wanted, but when they got it, were delighted. That's Sling.com's challenge. Whether it can meet it remains to be seen. But in this crummy economy, their deep-pocketed backing certainly gives them a leg up on any VC-funded competitors when it comes to long-term staying power.
What do you think? Post a comment now!
Categories: Aggregators, Cable TV Operators, Devices, Satellite
Topics: Cisco, DISH Network, EchoStar, Fancast, Hulu, Motorola, SA, Sling, YouTube
-
Watching Reed Hastings at NewTeeVee Live
Yesterday I had my own positive broadband video experience, remotely watching portions of the
 NewTeeVee Live conference held in SF from the comfort of my office. Om Malik and crew put together a packed agenda and I had wanted to go, but a personal conflict kept me in Boston.
NewTeeVee Live conference held in SF from the comfort of my office. Om Malik and crew put together a packed agenda and I had wanted to go, but a personal conflict kept me in Boston. I caught most of Netflix CEO Reed Hastings' keynote (until the UStream feed froze up, arghh...) and thought he offered some interesting tidbits about how he sees the broadband video market unfolding. VideoNuze readers know I've been avidly following Netflix's recent moves with Watch Instantly and I've come to think of the company as one of three key aggregators best-positioned to disrupt the cable model (the other two being YouTube and Apple).
Three noteworthy points that Hastings made:
Standards needed to interface broadband to the TV - Hastings catalogued the efforts Netflix is making to integrate with various devices like Roku, LG, TiVo, Xbox, etc, but concluded by saying that these one-off, ad hoc integrations are not scalable and are really slowing the market's evolution. Most of us would agree with this assessment. Still, he was quite pessimistic about a standards setting process's ability to move quickly enough - saying this could be a 10-30 year endeavor. Instead, if I understood him correctly, he thinks the TV approach should just be browser- based, and also that today's remotes should be scrapped in favor of pointer-driven (i.e. mouse-like) navigation.
Cable should evolve to focus on broadband delivery and de-emphasize multichannel packaging - Of course this is incredibly self-serving from Netflix's standpoint, but Hastings made the case that broadband margins for cable operators are nearly 100%, because they have no content costs, whereas on the cable side, they have high and ever-increasing programming costs. He cited Comcast's recent announcement of 50 Mbps service as evidence that cable operators should focus on winning the broadband war, and eventually letting go of the multichannel model. Nice try Reed, but I don't see that happening anytime soon. However, as I recently wrote in "Comcast: A Company Transformed," there's no question that broadband is becoming an ever greater part of its revenue and cash flow mix.(Reed emailed to clarify the above point. He didn't say cable should focus on broadband delivery over the current multichannel model; rather that cable - and satellite/telco - should focus more on web-like viewing experiences through improved navigation and VOD/DVR to be more on-demand, personalized and browser-friendly. And he added that with the shift to heavier broadband consumption, cable is a winner either way. Note - I thought I interpreted him correctly, but between UStream choking and my own scribble, it seems I was a bit off here. Thanks for correcting Reed.)Game consoles in leading position to bridge broadband to the TV - Hastings made a pretty strong case for the Wii - and to a lesser extent the PlayStation and Xbox - as the leading bridge devices. The Wii in particular could be a real broadband winner if it could support HD and Flash. As I've been thinking about broadband to the TV, I've concluded - barring anything from left field - that game devices, IP-enabled TVs and IP-enabled Blu-ray players are where the action will be concentrated for the next 3-4 years (this doesn't take account of forklift substitutes like a Sezmi or others sure to come).
NewTeeVee has a good wrap-up of Hastings' talk as well, here. The video replay isn't up yet, but when I see it, I'll post an update.
What do you think? Post a comment now!
Categories: Aggregators, Cable TV Operators, Devices
Topics: Apple, Comcast, LG, Netflix, PlayStation, Roku, TiVo, Wii, XBox, XBox, YouTube
-
Sezmi Update: Technical Trial Complete, New Round Raised, Q1 Launch Planned
Sezmi, a company I wrote about enthusiastically back in May as a big potential disruptor of cable/satellite multichannel services, is making steady progress toward commercial launch. Phil Wiser, the company's co-founder/president gave me an update this week.
Most important, the company has completed technical trials in Seattle with three local broadcasters (Fisher, Tribune and Daystar), to prove in its "FlexCast" distribution model. Sezmi uses a portion of over-the-air spectrum, along with broadband connectivity, to its set-top box to bypass traditional cable infrastructure.
 Phil explained that broadcasters are motivated to work with Sezmi for several reasons: incremental revenue from leasing spectrum, enhanced positioning in the Sezmi UI vs. current EPGs, and new ad-driven destination areas or "Zones," that broadcasters can use to create more customized and monetizable viewing experiences.
Phil explained that broadcasters are motivated to work with Sezmi for several reasons: incremental revenue from leasing spectrum, enhanced positioning in the Sezmi UI vs. current EPGs, and new ad-driven destination areas or "Zones," that broadcasters can use to create more customized and monetizable viewing experiences. On the cable networks side, Sezmi pulls down signals to its operational center in Melbourne, FL, processes them and uplinks them. Then, with dishes and other equipment installed at its local broadcast partners' facilities, Sezmi combines all channels for distribution to the home. That gives the viewer three ways to access programming: through traditional linear feeds, through VOD and through DVR.
Phil's confident that these technical trials validate the Sezmi delivery model as well as the feasibility of a national rollout. The next step is a beta trial, with "hundreds" of consumer homes, with a limited, geographically-based commercial rollout intended for sometime in Q1 (no doubt driven by its partners' priorities). Phil confirmed several other broadcast deals, including ones where multiple cities are covered, have been signed, and that several distribution partners are on board, including one with a national footprint (hmm, AT&T? Verizon? Someone else?)
Importantly, I also extracted from Phil that the company has closed another round of financing - greater than the earlier round of $17.5M. Sezmi has a big vision and with 3 pieces of consumer premise hardware (antenna, set top and remote), plus backend equipment and national/local delivery infrastructure to fund, this is a big dollar project for sure.
I remain optimistic about Sezmi's opportunity. As I said in the May post, I haven't seen the whole thing work at scale yet, so there are significant technology unknowns. There's also a sizable customer education mountain to climb (though hopefully mitigated by large well-branded partners' assistance). Then there's the small matter of signing up the local broadcasters, as well as the cable networks.
Still, Sezmi's core value proposition - a better viewing experience at a lower cost than today's cable/satellite incumbents - is right on the mark. The old adage about execution mattering more than strategy has rarely been truer than with Sezmi. It's going to be interesting to watch its continued progress.
What do you think? Post a comment now!
Categories: Cable Networks, Cable TV Operators, Devices, Startups
Topics: Daystar Television Network, Fisher Communications, SezMi, Tribune Broadcasting
-
The Cable Industry Closes Ranks
First, apologies for those of you getting sick of me talking about the cable TV industry and broadband video; I promise this will be my last one for a while.
After attending the CTAM Summit the last couple of days, moderating two panels, attending several others and having numerous hallway chats, I've reached a conclusion: the cable industry - including operators and networks - is closing ranks to defend its traditional business model from disruptive, broadband-centric industry outsiders.
Before I explain what I mean by this and why this is happening, it's critical to understand that the cable business model, in which large operators (Comcast, Time Warner Cable, etc.) pay monthly carriage or affiliate fees to programmers (e.g. Discovery, MTV, HGTV, etc.) and then bundle these channels into multichannel packages that you and I subscribe to is one of the most successful economic formulations of all time. The cable model has proved incredibly durable through both good times and bad. In short, cable has had a good thing going for a long, long time and industry participants are indeed wise to defend it, if they can.
It's also important to know that the industry is very well ordered and as consolidation has winnowed its ranks to about half a dozen big operators and network owners, the stakes to maintain the status quo have become ever higher. All the executives at the top of these companies have been in and around the industry for years and have close personal and professional ties. There's a high degree of transparency, with key metrics like cash flow, distribution footprint, ratings and even affiliate fees all commonly understood.
One last thing that's worth understanding is that the cable industry has very strong survival instincts, or as a long-time executive is fond of saying, "Real cable people (i.e. not recent interlopers from technology, CPG or online companies that have joined the industry) were raised in caves by wolves." The fact is that the industry started humbly and experienced many very shaky moments. Yet it has managed to survive and continually re-invent itself (for those who want to know more, I refer you to "Cable Cowboy: John Malone and the Rise of the Modern Cable Business" by Mark Robichaux, still the best book on the industry's history that I've read).
All of that brings us to broadband and its potential impact on the cable model. As I've said many times, broadband's openness makes it the single most disruptive influence on the traditional video distribution value chain. Principally that means that by new players going "over the top" of cable - using its broadband pipes to reach directly into the home - cable's model is at serious risk of breaking down, once and for all.
The cable industry now gets this, and I believe has closed ranks to frown heavily on the idea of cable programming, which operators pay those monthly affiliate fees for, showing up for free on the web, or worse in online aggregators' (e.g. Hulu, YouTube, Veoh, etc.) sites. The message is loud and clear to programmers: you'll be jeopardizing those monthly affiliate fees come renewal time if your crown jewels leak out; worse, you'll be subverting the entire cable business model.
And this message isn't being delivered just by cable operators such as Peter Stern from Time Warner who said on my Broadband Video Leadership Breakfast panel that "a move to online distribution by cable networks would directly undermine the affiliate fees that are critical to creating great content." It's also coming from the likes of Discovery CEO David Zaslav who said on a panel yesterday that "there's no economic value from online distribution," and that "great brands like Discovery's must not be undervalued by making full programs available for free online."
The issue is, as a practical matter, can the industry really control all this? If there's zero online distribution, then as Fancast's impressive new head, Karin Gilford said on my panel yesterday, "pressure builds up and another channel inevitably opens" (read that as The Piracy Channel). The problem is that if, for example, an operator does put programs up on its own site - as Fancast is doing - they're available to ALL the site's visitors, not just existing cable subscribers, unless other controls are put in place like passwords, IP address authentication, geo-targeting, etc. But these are confusing and cumbersome to users whose expectations are increasingly being set by broadcasters who are making their primetime programs seamlessly available to all comers.
So what does this closing ranks suggest? Going forward, I think we'll still see cable networks putting up plenty of clips and B-roll video from their programs, maybe the occasional online premiere, some made-for-the-web stuff, paid program downloads (iTunes, etc.) and promotional/community building contests, as Deanna Brown from Scripps described with "Rate My Space" or Zaslav discussed with "MythBusters."
But when it comes to full cable network programs going online, I think that spigot's going to dry up. That has implications for online aggregators like Hulu, who will continue to have big holes in their libraries until they're ready to pay up for these carriage rights. And it also means that broadband-to-the-TV plays are also going to be hampered by subpar lineups unless these companies too are willing to pay for cable programming.
By closing ranks the cable industry's making a bold bet that its ecosystem can withstand broadband's onslaught and the rise of the Syndicated Video Economy. In yesterday's post I noted that the music industry tried a similar approach; we know where that got them. There are plenty of reasons to think things could indeed be different for the cable industry, but there are as many other reasons to think the cable industry is massively deluding itself and could someday be grist for a chapter in the updated version of Clay Christensen's "The Innovator's Dilemma," (my personal bible for how to pursue successful disruption), right alongside the inevitable chapter about how the once mighty American auto industry spectacularly lost its way.
For my part, there are just too many moving parts for me to call this one just yet.
What do you think? Post a comment now!
Categories: Aggregators, Broadcasters, Cable Networks, Cable TV Operators, Devices, Syndicated Video Economy
Topics: Comcast, CTAM Summit, Discovery, Fancast, Scripps, Time Warner
-
Netflix Should be Aggressively Pursuing Broadcast Networks for Watch Instantly Service
Over the past several months Netflix has made a series of announcements related to its "Watch Instantly" feature. On the device side, there are new partnerships with TiVo (for Series 3, HD and HD XL models), Microsoft Silverlight (for Mac viewing), Samsung (for Blu-ray players), LG (for Blu-ray players), Xbox 360 and of course Roku. All allow Netflix Watch Instantly content to be delivered directly to users' TVs. Meanwhile on the content side, there have been deals with Starz, CBS and Disney Channel, with more no doubt yet to come.
Our household has been an enthusiastic subscriber to Netflix for years and I welcome the commitment that
 Netflix appears to be making to Watch Instantly. However, as I pointed out in May, in "Online Movie Delivery Advances, Big Hurdles Still Loom," Watch Instantly is hobbled by its limited catalog, now totaling around 12,000 titles, just 10% of Netflix's total catalog, even after including the recently added Starz titles.
Netflix appears to be making to Watch Instantly. However, as I pointed out in May, in "Online Movie Delivery Advances, Big Hurdles Still Loom," Watch Instantly is hobbled by its limited catalog, now totaling around 12,000 titles, just 10% of Netflix's total catalog, even after including the recently added Starz titles. The fundamental problem Netflix is bumping up against in building out Watch Instantly's film catalog is Hollywood's well-established windowing process. Studios have wisely and methodically maximized their films' lifetime financial value by doling out the rights to air them to a series of distribution outlets. These rights unfold in a carefully calibrated timeline and have become wrapped up in a thick layer of contractual agreements extending to all parties in the value chain. It is a system that has served all constituencies well, generating billions of dollars of value. It is also unlikely to change in any material way any time soon.
As such, Netflix, the "world's largest online movie rental service," as it calls itself, is increasingly discordant. On the one hand, growing the Watch Instantly service is crucial to Netflix's long term success in the digital/broadband era but on the other, it doesn't have the ability to offer a competitive catalog that meets consumers' online delivery expectations. So what to do?
My recommendation is for Netflix to incorporate the delivery of TV programming, via Watch Instantly, into its core value proposition. Specifically, Netflix should be making an all-out effort (if it is not already doing so) to secure next-day rights to deliver all prime-time broadcast network programs to its subscribers.
This strategy provides Netflix with many clear benefits and positions it well for long-term success. First, in these tight economic times, it dramatically expands the value of the Watch Instantly feature, turning it into both a bona fide subscriber retention tool to battle churn as well as a high-profile subscriber acquisition lever (not to mention an exciting pull-through offer big box retailers could use in their Sunday circulars to generate traffic).
Second, it is a clever competitive strike against four primary alternative ways whereby consumers can watch network programs on demand: cable-based VOD, a la carte paid downloads at iTunes/Amazon/others, free online aggregators like Hulu/Fancast/others and DVRs (though note the TiVo deal addresses this last option).
A comprehensive Netflix prime-time catalog compares well with each alternative. Against cable VOD it offers familiar, superior navigation plus a viable revenue stream for broadcasters while cable tries to get Canoe ready; against paid downloads, the obvious advantage of being a value-add service; against online aggregators, commercial free delivery; and against DVRs, the lack of consumer hardware purchases and persistent recording space limitations.
All of this should make Netflix a very appealing partner for the broadcast networks. They are getting hammered by ad-skipping, audience fragmentation, quality programming migrating to cable and an inferior single revenue source business model. The prospect of Netflix offering payments for their programs should be well-received. There may be concerns about programs' long term syndication value and also the potential enablement of a new gatekeeper. In better times these might be deal-killers; in this climate they shouldn't be.
Finally, there's the big potential long-term Netflix prize: if it can stitch together a large-scale network of compatible devices for Watch Instantly distribution, it could create a viable "over-the-top" alternative to today's multichannel subscription services (cable/telco/satellite). As I described in my recent "Cord Cutters" post, to really succeed, Netflix would have to eventually incorporate cable network programming. But if its reach is wide and its economics sound, that's within the realm of possibility as well.
But those are long-term issues. For now, while the recent CBS deal is a great start, Netflix should be working double-time to build out a full library of broadcast programs. It would dramatically improve Watch Instantly's appeal and value, while positioning Netflix well for the broadband era.
What do you think? Post a comment now.
Categories: Aggregators, Broadcasters, Devices, Partnerships
Topics: CBS, Disney, LG, Microsoft, Netflix, Roku, Samsung, Silverlight, Starz, TiVo
-
Cutting the Cord on Cable: For Most of Us It's Not Happening Any Time Soon
Two questions I like to ask when I speak to industry groups are, "Raise your hand if you'd be interested in 'cutting the cord' on your cable TV/satellite/telco video service and instead get your TV via broadband only?" and then, "Do you intend to actually cut your cord any time soon?" Invariably, lots of hands go up to the first question and virtually none to the second. (As an experiment, ask yourself these two questions.)
I thought of these questions over the weekend when I was catching up on some news items recently posted to VideoNuze. One, from the WSJ, "Turn On, Tune Out, Click Here" from Oct 3rd, offered a couple examples of individuals who have indeed cut the cord on cable and how their TV viewing has changed. My guess is that it wasn't easy to find actual cord-cutters to be profiled.
There are 2 key reasons for this. First it's very difficult to watch broadband video on your TV. There are special purpose boxes (e.g. AppleTV, Vudu, Roku, etc.), but these mainly give access to walled gardens of pre-selected content, that is always for pay. Other devices like Internet-enabled TVs, Xbox 360s and others offer more selection, but are not really mass adoption solutions. Some day most of us will have broadband to the TV; there are just too many companies, with far too much incentive, working on this. But in the short term, this number will remain small.
The second reason is programming availability. Potential cord-cutters must explicitly know that if they cut their cord they'll still be able to easily access their favorite programs. Broadcasters have wholeheartedly embraced online distribution, giving online access to nearly all their prime-time programs. While that's a positive step, the real issue is that cord-cutters would get only a smattering of their favorite cable programs. Since cable viewing is now at least 50% of all TV viewing (and becoming higher quality all the time, as evidenced by cable's recent Emmy success), this is a real problem.
To be sure, many of the biggest ad-supported cable networks (MTV, USA, Lifetime, Discovery) are now making full episodes of some of their programs available on their own web sites. But these sites are often a hodgepodge of programming, and there's no explanation offered for why some programs are available while others are not. For example, if you cut the cord and could no longer get Discovery Channel via cable/satellite/telco, you'd only find one program, "Smash Lab" available at Discovery.com. Not an appealing prospect for Discovery fans.
Then there's the problem of navigation and ease of access. Cutting the cord doesn't mean viewers don't want some type of aggregator to bring their favorite programming together in an easy-to-use experience. Yet full streaming episodes are almost never licensed to today's broadband aggregators. Cable networks are rightfully being cautious about offering full episodes online to aggregators not willing to pay standard carriage fees.
For example, even at Hulu, arguably the best aggregator of premium programming around, you can find Comedy Central's "The Daily Show" and "Colbert Report." But aside from a few current episodes from FX, SciFi and Fuel plus a couple delayed episodes from USA like "Monk" and "Psych," there's no top cable programming to be found.
As another data point, I checked the last few weeks of Nielsen's 20 top-rated cable programs and little of this programming is available online either. A key gap for cord-cutters would be sports. At a minimum, they'd be saying goodbye to the baseball playoffs (on TBS) and Monday Night football (on ESPN). In reality, sports is the strongest long-term firewall against broadband-only viewing as the economics of big league coverage all but mandate carriage fees from today's distributors to make sense.
Add it all up and while many may think it's attractive to go broadband only, I see this as a viable option for only a small percentage of mainstream viewers. Only when open broadband to the TV happens big time and if/when cable networks offer more selection will this change.
What do you think? Post a comment now.
Categories: Aggregators, Broadcasters, Cable Networks, Cable TV Operators, Devices, Telcos
Topics: AppleTV, Comedy Central, Discovery, ESPN, FX, Hulu, Lifetime, Roku, SciFi, TBS, USA, VUDU, Xbox360


