-
Time Warner's Jeff Bewkes is Hurting the Cable Industry by Hyping "TV Everywhere"
Leading up to and during this week's Cable Show (the cable TV industry's big once-per-year conference), Time Warner CEO Jeff Bewkes continued to hype his company's "TV Everywhere" vision. Observing the media coverage of this initiative since the WSJ broke the news about it over a month ago, following how industry executives are responding to it, and listening to Mr. Bewkes's further comments, I've concluded that TV Everywhere - and Mr. Bewkes's hyping of it - is actually hurting the cable industry, not helping it. I don't think this was his intent, but I do believe it's the reality.
Let me say upfront, I think the idea that cable TV network programs being made available online, to paying multichannel video subscribers, but without an extra fee, is terrific. But it is a very long-term idea, requiring that lots of divergent constituent business models come into alignment. It also requires significant - and coordinated - technology development and implementation by numerous parties that have widely varying willingness and readiness to participate. And not least, someone has to actually pay for all this cross-industry technology development and testing to preclude it from becoming a hacker's paradise. It's a very tall order indeed.
Yet when I read Mr. Bewkes's comments about TV Everywhere and its implementation, he inevitably points to what Time Warner Cable (btw, not the company he runs any longer with the spinoff now almost complete) is doing with HBO in Milwaukee. By continuing to do so, I believe he is trivializing how complicated implementing something like TV Everywhere would be across the industry and across the country.
Mr. Bewkes's sketchiness with the details of how TV Everywhere would work is obvious in his interview with PaidContent's Staci Kramer here and here. There are plenty of generalizations and descriptions of the
 end-state, but little offered about how this would all be accomplished. One example: "...all of the video providers would have a link in their software where they could be pinged to see if the person is a video subscriber. That's not a complicated thing. It's simply a software program that asks does anybody have Staci as a sub and then Charter says, yes, I've got her and bang."
end-state, but little offered about how this would all be accomplished. One example: "...all of the video providers would have a link in their software where they could be pinged to see if the person is a video subscriber. That's not a complicated thing. It's simply a software program that asks does anybody have Staci as a sub and then Charter says, yes, I've got her and bang." Yeah, right! And if things were only that easy then maybe the cable and satellite industry wouldn't also have the 2nd lowest customer satisfaction score out of 43 industries measured by the American Customer Satisfaction Index (ahead of only airlines).
Meanwhile because the details have been so sparse, the media has been left to come to its own confusing and often conspiratorial conclusions about what TV Everywhere really means to consumers. Here's a sample of the recent headlines: "TV Everywhere - As Long As You Pay for It," "Time Warner Goes Over the Top," "Some Online Shows Could Go Subscription-Only" and "Pay Cable Tests Online Delivery." Talk about message mismanagement...
The cable industry - both operators and programmers - are getting hurt most by the hype and confusion around TV Everywhere. Consumers' expectations are being raised without any sense of timing or what will actually result. Many consumers already have no love lost for their cable operator and would jump at the chance to cut the cord. The flowery-sounding "TV Everywhere" suggests that day may be coming at exactly the moment when the industry should be collectively driving home a positive story that cable operators are investing in broadband - yet again - to provide more value to subscribers.
Meanwhile cable networks are also being hurt by TV Everywhere's hype. They are being forced to respond in public (as Disney's Bob Iger did in his keynote yesterday) to these vague ideas. But it is a PR nightmare-in-the-making for them, as they need to defend why consumers will have to continue paying subscription fees to watch their programs online, while broadcast TV network programs are freely available. That's a thankless job for them, and reading through Mr. Iger's speech yesterday, you could almost sense his resentment at being forced into this position.
Why Mr. Bewkes isn't modulating his comments about TV Everywhere in light of all this eludes me. Anyone who's ever created a product knows about "roadmaps," where product features are added over time, and customers are methodically messaged about enhancements to come. With TV Everywhere, it's as if all that matters to Mr. Bewkes is talking about the glorious end state, thereby erasing meaningful online benefits that can be delivered along the way. Contrast this with Comcast's OnDemand Online plan that offers the simple, but still highly-valuable near-term proposition of online cable programs on its own sites, and possibly the networks' as well.
Ironically, nobody should know the perils of hype better than Time Warner executives, since this was the company that brought us the ill-fated "boil-the-ocean" Full Service Network back in 1994. A reminder: those who ignore history are doomed to repeat it.
What do you think? Post a comment now.
Categories: Cable Networks, Cable TV Operators
Topics: Comcast, Disney, Time Warner
-
Blockbuster Follows Netflix Onto TiVo Boxes; Ho-Hum
Blockbuster and TiVo have announced that Blockbuster OnDemand movies will be available on TiVo devices. Though I'm all for creating more choice for viewers to gain access to the content they seek, in this
 case I don't see the deal creating a ton of new value in the market, as it comes 6 months after Netflix and TiVo announced that Netflix's Watch Instantly service would be available on TiVo devices and nearly 2 years after Amazon and TiVo made Amazon's Unbox titles available for purchase and download to TiVo users. It looks like the main differentiator here is that Blockbuster will begin selling TiVos in their network of physical stores.
case I don't see the deal creating a ton of new value in the market, as it comes 6 months after Netflix and TiVo announced that Netflix's Watch Instantly service would be available on TiVo devices and nearly 2 years after Amazon and TiVo made Amazon's Unbox titles available for purchase and download to TiVo users. It looks like the main differentiator here is that Blockbuster will begin selling TiVos in their network of physical stores. The deal underscores the flurry of partnership activity now underway (which I think will accelerate) between aggregators/content providers and companies with some kind of device enabling broadband access to TVs. I believe the key to these deals actually succeeding rests on 2 main factors: the content offering some new consumer value (selection, price, convenience, exclusivity, etc.) and the access device gaining a sufficiently large footprint. Absent both of these, the new deals will likely find only limited success.
Consumers now have no shortage of options to download or stream movies, meaning that announcements along the lines of Blockbuster-TiVo break little new ground. To me, a far more fertile area to create new consumer value is offering online access to cable networks' full-length programs. As I survey the landscape of how premium quality video content has or has not moved online, this is the category that has made the least progress so far. That's one of the reasons I think the recent Comcast/Time Warner Cable plans are so exciting.
With these plans in the works, but no timetables yet announced, non-cable operators need to be thinking about how they too can gain select distribution rights. There's still a lot of new consumer value to be created in this space. Given lucrative existing affiliate deals between cable networks and cable/satellite/telco operators, I admit this won't be easy. However, Hulu's access to Comedy Central's "Daily Show" and "Colbert Report" does prove it's possible.
We're well into the phase where premium video content is delivered to TVs via broadband. Those that bring distinctive content to large numbers of consumers as easily as possible will be the winners.
What do you think? Post a comment now.
Categories: Aggregators, Devices, FIlms, Partnerships
Topics: Amazon, Blockbuster, Comcast, Netflix, Time Warner Cable, TiVo
-
VideoNuze Report Podcast #10 - March 13, 2009
Happy Friday the 13th...
Below is the 10th edition of the VideoNuze Report podcast, for March 13, 2009.
This week Will adds some detail to his recent post, "Clarifying Comcast's and Time Warner's Plans to Deliver Cable Programming via Broadband to Their Subscribers." These plans are not fully locked in, but since there have been a lot of questions about them, it seemed worthwhile to provide a quick update.
Also, Daisy discusses a recent article she wrote about Clearleap, a new broadband-to-the-TV technology company that recently announced its platform. The whole broadband-to-the-TV area has been really hot recently and we expect a lot more activity to come.
Since this is the 10th edition of the VideoNuze Report podcast, we thought it would be a good time to check in with listeners and get you reactions. What do you think of the format and length? We thought the most meaningful content approach would be to provide some additional insight about what we've written recently, but does this feel fresh and substantive enough? Would it be better if we discussed recent market activities that we haven't necessarily written about yet? Or maybe answered some listener questions? Or something else?
The podcast format is very flexible and Daisy and I view the VideoNuze Report as a work in progress. We'd love to hear what listeners think and how we can change and improve. Either drop me an email (wrichmondATvideonuze.com) or leave a comment.
Click here to listen to the podcast (14 minutes, 29 seconds)
Click here for previous podcasts
The VideoNuze Report is available in iTunes...subscribe today!
Categories: Cable TV Operators, Podcasts, Technology
Topics: Clearleap, Comcast, Podcast, Time Warner
-
Broadband Subscriptions Chug Along in 2008
Last Friday, Leichtman Research Group released is quarterly roundup of broadband subscription growth sorted by major cable operators and telcos. LRG, run by my former colleague and friend Bruce Leichtman, has long been the bible for many in the industry for tracking broadband subscriber growth. LRG's numbers continue to demonstrate why broadband video has become such an exciting new distribution medium while adding context to Comcast's and Time Warner's recent moves to begin making online access to cable programming available to their subs.
To highlight a few key numbers, at the end of '08 the top broadband ISPs had 67.7 million subscribers, with top cable operators accounting for about 54.5% and top telcos the remainder. Top cable operators continue to maintain their edge in subscriber acquisition as well, grabbing 59% of all new broadband subs in '08.
And no surprise to anyone, with the rising penetration levels, the annual increases in total new subs have continued to slow: in '06 top cable and telco ISPs added 10.4M subs, in '07, 8.5M subs and in '08, 5.4M subs. Still, in the teeth of harsh economic downturn in Q4 '08, these ISPs were still able to add over 1M subs, growth that contracting industries like autos, retail and home-building would no doubt have killed for.
Broadband has long since become a utility for many American homes, a service that is as much expected as essentials like electricity and plumbing. A key reason broadband video is enjoying the success it is owes to the fact that broadband subscriptions have been driven for other reasons (e.g. faster email access, music downloads, always-on connectivity) over the years. Video has only recently become an additional and highly-valued benefit, which broadband ISPs now expect will drive interest in faster (and more expensive) broadband service plans.
Broadband's importance to the cable industry is demonstrated by the chart below showing #1 cable operator Comcast's performance over the last 2 years, which I originally posted on last November ("Comcast: A Company Transformed).

Note the company has now lost basic cable subscribers for 7 straight quarters, even as it continues to add digital video subs and broadband subs (and voice subs) at a healthy clip. I expect these trend lines will continue in their current pattern. No doubt this is the kind of picture that has helped spur Comcast (and #2 operator Time Warner Cable) to begin planning online distribution of cable programming, a feature that I believe will provide highly popular. Operators are in a tremendous position to capitalize on the shifting interests of their subscribers.
What do you think? Post a comment now.
Categories: Broadband ISPs, Cable TV Operators
Topics: Comcast, Leichtman Research Group, Time Warner Cable
-
The Video Industry's Winners and Losers 10 Years from Now: 5 Factors to Consider
Last week a publicly-traded communications-equipment company invited me to speak to a group of investment analysts it had assembled for its annual "investor day." In the Q&A session following my presentation I took a question that I'm not often asked, nor do I give much thought to: "10 years from now, who will be the video industry's winners and losers?"
It's a far-reaching question that doesn't lend itself well to an impromptu answer. Also, while it's great fun to prognosticate about the long run, I've found that it's also a complete crapshoot, which is why my focus is much shorter-term. I've long-believed there are just too many variables in play to predict with any sort of certainty what might unfold 10 years into the future.
Still, as I've thought more about the question, it seems to me that there are at least 5 main factors that will influence the video industry's winners and losers over the next 10 years:
1. Penetration rate of broadband-connected TVs -There's a lot of energy being directed to "convergence" technologies and devices which connect broadband to the TV. Broadband to the TV is a big opportunity for video providers outside the traditional video distribution value chain. It's also a minefield for those who have dominated the traditional model, such as broadcasters. The Hulu-Boxee spat demonstrates this. A high rate of adoption of broadband to the TV technologies will result in more openness and choice for consumers. That's a good or a bad thing depending on where you currently sit.
2. The effectiveness of the broadband video ad model - A large swath of broadband-delivered video is and will be ad-supported. But key parts of the broadband ad model such as standards, reporting and the buying process are still not mature. There's a lot of work going into these elements which is promising. The extent to which the ad model matures (and the economy rebounds) will have a huge influence on how viable broadband delivery is. Producers need to get paid to do good work or it won't get done. The imploding newspaper industry offers ample evidence. Those with robust online ad models like Google are likely to play a key role in helping distribute and monetize premium content.
3. How well the broadcast industry adapts to broadband delivery - The broadcast TV industry generates about $70 billion of ad revenue annually. But both broadcast networks and local stations are on the front lines of broadband's change and disruption, putting a chunk of that ad revenue up for grabs. With broadband-to-the-TV coming, broadcast networks must figure out how to make broadband-only viewership of their programs profitable on a stand-alone basis (i.e. when the online viewing is the sole viewing proposition). Local stations face bigger challenges. As the Internet was to newspapers, broadband delivery is to local stations. They face a slew of new competitors for ad dollars and audiences, while losing their exclusive access to network programming. To what extent they're able to reinvent themselves will determine how much share they hold on to and how much others peel off.
4. How aggressively today's video providers (cable/telco/satellite) and new paid aggregators pursue broadband video delivery - While anecdotes about "cord-cutting" will no doubt only intensify, the reality is that if today's video providers adapt themselves to broadband realities, they are likely to be as strong or stronger 10 years from now. The recent moves from Comcast and Time Warner are encouraging signs that the cable industry gets that being ostriches about the importance of broadband delivery is a road to nowhere. Consumers expect more flexibility and value; incumbents are in a tremendous position to deliver. Ownership of local broadband access networks that serve consumers' unquenchable bandwidth demands is going to be a very good business to be in. That all said, new paid aggregators like Netflix, Amazon and Apple could well steal some share if they aggressively beef up their content, offer a competitive user experience and deliver a better value. They could have a major impact on online movie distribution in particular.
5. The level of investment in startups - The venture capital industry, crucial to the funding of early-stage innovative technology companies, is going through its own turmoil. The industry's limited partners have been wounded by the market's drop, causing VCs to raise smaller funds (if they're even able to do this), limit the number of investments they make, and shy away from betting on big transformational startups. Plenty of strong video technology companies are still successfully raising money, but it's harder than ever. Lots of potentially promising ideas are going begging. The length and severity of the economic slowdown will have a big effect on just how much funding new technologies that can potentially reshape the video landscape over the next 10 years.
So there are 5 factors to consider in how the video landscape shapes up over the next 10 years. Now back to the here and now..
What's your crystal ball say? Post a comment now.
Categories: Advertising, Aggregators, Broadcasters, Cable TV Operators, FIlms
Topics: Boxee, Comcast, Google, Hulu, Time Warner
-
Clarifying Comcast's and Time Warner's Plans to Deliver Cable Programming Via Broadband to Their Subscribers
Summary:
What: Major cable operators Comcast and Time Warner intend to offer broadband access to cable programs for the first time, but they have provided few specifics to date, thereby creating a swirl of confusing interpretations. This post seeks to clarify their plans.
Important for whom: Cable networks, other content providers, cable operators, consumers
Potential benefits: Flexible access and first-time online availability of popular cable programs.
Background
Since the WSJ reported two weeks ago today that Comcast and Time Warner Cable plan to offer online access to cable TV programming to their subscribers, there has been a significant amount of confusion and misinterpretation about what these companies are actually planning to do. Absent official statements from either company, there has been an ongoing debate about whether cable operators, who want to defend their traditional model, were moving to choke off the largely open access to broadband video that users have grown accustomed to.
Things got more confusing this past Monday when AdAge ran an interview ("TV Everywhere -- As Long As You Pay For It") with Jeff Bewkes, CEO of Time Warner Inc. in which he elaborated on a company initiative dubbed "TV Everywhere" that major cable network owners such as Time Warner Inc. Viacom, NBCU, Discovery and others are said to be collaborating on. Bewkes outlined a broad online vision including the idea that cable programming could also be available on sites like Hulu, MySpace, Yahoo and YouTube as well, provided that users were paying a fee to some underlying service provider (cable/satellite/telco).
A wrinkle in the interview was exactly whom Bewkes was speaking for, since Time Warner Inc. (or "TWI" which owns the cable networks CNN, TNT, TBS, etc.) plans to spin off as an independent entity Time Warner Cable ("TWC"), which operates cable systems serving 14 million subscribers. After the split, set for next week, which of these companies would actually be sponsoring the "TV Everywhere" vision?
The NYTimes' technology reporter Saul Hansell then picked up on the interview and wrote a piece on the paper's widely-read "Bits" blog entitled "Time Warner Goes Over the Top," which provocatively began, "Just as soon as Time Warner has divested itself from the cable business, Jeff Bewkes, its chief executive, is preparing to stab the cable industry in the back. That's what I read in an interview with Mr. Bewkes in Advertising Age..."
Saul went on to describe his interpretation of one particular Bewkes comment as implying that Time Warner Inc. would offer its networks directly to consumers (or "over the top" of cable operators), thereby setting off a domino effect in which others' networks did the same, all of which would ultimately lead to the destruction of the cable industry business model.
The attention all of this received, particularly in the blogosphere, prompted a fair number of people to contact me and ask what's really going on here.
Time Warner's Plans
Yesterday I spoke with Keith Cocozza, TWI's spokesman, who said that Bewkes's comments do represent both TWI and TWC. Their mutual vision is to have cable programming offered not just at TWC's
 RoadRunner portal, but also at various third-party aggregators (Hulu, etc.) so long as they subscribe to any multichannel video service (whether from TWC, Verizon, DirectTV, etc.). They do envision offering a streaming-only service for those that don't want the traditional cable subscription, but it would only be available in their geographical footprint. All of that means that there's in fact no over-the-top threat involved here at all. TWI and TWC are "agnostic" about third-party aggregator access to the cable programs, because they recognize that people want to go to whatever sites make them most comfortable. And they do not plan to charge subscribers extra for online access.
RoadRunner portal, but also at various third-party aggregators (Hulu, etc.) so long as they subscribe to any multichannel video service (whether from TWC, Verizon, DirectTV, etc.). They do envision offering a streaming-only service for those that don't want the traditional cable subscription, but it would only be available in their geographical footprint. All of that means that there's in fact no over-the-top threat involved here at all. TWI and TWC are "agnostic" about third-party aggregator access to the cable programs, because they recognize that people want to go to whatever sites make them most comfortable. And they do not plan to charge subscribers extra for online access. From a consumer standpoint, all of this is quite enlightened. But from an operational standpoint, it feels incredibly complex. For example, I asked Keith about how a remote user, seeking to watch programs at a third party aggregator's site like Hulu, would be authenticated as an actual customer of a video service provider? While acknowledging it's too early to have all the answers, he said a test TWC has conducted in Wisconsin with HBO has shown this not to be a big technical problem. I don't agree. It's hard enough for companies to do a bilateral account integration (e.g. tying a user's Amazon account to a user's TiVo account); the idea of doing multilateral account integration (the numerous combinations of potential aggregators and service providers) is fraught with complexity and seems highly daunting.
Then there are financial issues to address. With no incremental subscriber payments, online program delivery needs to be sustained through ads alone. This would be quite workable if it were just cable operators and networks involved (they could split the ad avails proportionately as they've traditionally done with linear delivery), but by allowing third-party aggregators in too, a third mouth now needs to be fed. That will trigger a whole new negotiating dynamic, as each aggregator lobbies for a different share. And it's questionable whether there's even enough ad revenue for three parties to begin with, though Keith believes there is.
Comcast's Plans
Conversely, Kate Noel, Comcast's spokeswoman, told me yesterday that while it's still early to say anything definitive about Comcast's plans for distribution through third-party aggregators, their first priority is distribution of
 cable programs on their own sites (e.g. Fancast, Comcast.net) and the networks' own sites. Comcast seems to have more of a "walk, before you run" approach. It recognizes that protecting subscribers' privacy in any account integration is crucial so it plans to proceed carefully. I tried to pin Kate down on whether Comcast intends to charge for online access. Again she felt it was too early to be definitive, but it sounds like they're leaning toward a no-charge model as well. The timeline is to begin rolling out access in the 2nd half of '09.
cable programs on their own sites (e.g. Fancast, Comcast.net) and the networks' own sites. Comcast seems to have more of a "walk, before you run" approach. It recognizes that protecting subscribers' privacy in any account integration is crucial so it plans to proceed carefully. I tried to pin Kate down on whether Comcast intends to charge for online access. Again she felt it was too early to be definitive, but it sounds like they're leaning toward a no-charge model as well. The timeline is to begin rolling out access in the 2nd half of '09.Clearly there are a lot of moving pieces involved with these companies' plans. In general Time Warner has a more aggressive, yet I believe far less pragmatic, plan. They're trying to get all the way to the end zone right away, when just advancing the ball further downfield would be real progress for today's broadband users seeking improved access to premium content. Time Warner's "TV Everywhere" seems like a great vision, but it would take years to fully implement. Comcast's plan is probably achievable in a year or less. Either way, major cable operators finally seem to have the ball rolling toward broadband distribution of cable programming. As I pointed out last week, this can only be viewed as a positive.
What do you think? Post a comment now.
(btw, if you want to learn more about all this, come to the Broadband Video Leadership Evening on March 17th in NYC, where we'll dig deeply into these issues with our top-notch panel)
Categories: Cable Networks, Cable TV Operators
Topics: Comcast, Hulu, MySpace, Time Warner Cable, Yahoo, YouTube
-
New Research from TDG Sheds Light on Consumers' Three Screen Intentions
This past Tuesday I highlighted some of Nielsen's recent data which showed, among other things, significant online and mobile video usage by younger age groups. In that post I noted that marketers need to pay close attention to these trends to ensure their products and services meet these users' needs and expectations.
New research from The Diffusion Group (a long-time VideoNuze partner) provides a window into how users think about accessing video across multiple screens, and who the providers might be. TDG has recently completed a survey of 2,000 adults (18 or above) which tested interest in two-screen and three-screen services along with content and features. TDG has graciously provided a sample of the slides for complimentary download by VideoNuze. You can download the slides here.
TDG defined a three-screen service as "a single video service which feeds all your household TVs, PCs and mobile devices, for a single monthly fee, from a single service provider, and with relatively equal content, variety and quality of service for all three devices."
TDG found that almost 25% of those surveyed responded positively to such a package. Whereas video marketers would have traditionally considered heavy TV viewership (25 hours/week and above) to be the most important criterion for driving more video services adoption, these so-called "three-screen intenders" don't exhibit heavier TV viewership than non-intenders (though they're slightly higher in moderate viewership, 11-25 hours/week).
Rather, the behavior that distinguishes three-screen intenders is how much online viewing they're doing. The intenders are far higher consumers of online video in general, and of online TV programs in particular. In other words, their behaviors are already self-selecting them as the targets for a three-screen service offering. That of course makes it much easier for marketers to find and target them.
All of this certainly supports Comcast's and Time Warner Cable's recently revealed plans to offer their video subscribers online access to programs. Better news still for these companies is that TDG found that cable operators were the top choice by intenders as the preferred three-screen provider. Cable was chosen by 31.7% of intenders, almost double the amount that selected satellite operators. Translation: there is a sizable group of consumers interested in three-screen services and cable appears to be in the prime position to capitalize on this.
Of course, the next question then is whether cable operators should charge for these services or imitate Netflix's example with Watch Instantly by including them as a value add to existing digital services. In my opinion, at least some of the online viewing capability should be included for no extra charge. That would go a long way toward establishing loyalty, and position cable for even greater competitive gains.
Click here to download the complimentary slides.
What do you think? Post a comment now.
Categories: Cable TV Operators
Topics: Comcast, The Diffusion Group, Time Warner Cable
-
The Cable Industry Closes Ranks - Part 2
An article in Friday's WSJ "Cable Firms Look to Offer TV Programs Online" outlined a plan under which Comcast and Time Warner Cable, the nation's 2 largest cable operators, would give just their subscribers online access to cable networks' programming.
A Comcast spokesperson contacted me later Friday morning to explain that the plan, dubbed "OnDemand Online" is indeed in the works, though a release timeline is not yet set. The move is part of the company's
 "Project Infinity" a wide-ranging on-demand programming vision that was unveiled at CES '08, but oddly has not been messaged much since. Meanwhile, thePlatform, Comcast's broadband video management/publishing subsidiary also called me on Friday to confirm that - unsurprisingly - it would be powering the OnDemand Online initiative (thePlatform's CEO Ian Blaine explains more in this post).
"Project Infinity" a wide-ranging on-demand programming vision that was unveiled at CES '08, but oddly has not been messaged much since. Meanwhile, thePlatform, Comcast's broadband video management/publishing subsidiary also called me on Friday to confirm that - unsurprisingly - it would be powering the OnDemand Online initiative (thePlatform's CEO Ian Blaine explains more in this post).The idea of cable operators setting up online walled gardens for their subscribers alone was first signaled by Peter Stern, Time Warner's EVP/Chief Strategy Officer on the panel I moderated at VideoNuze's Broadband Leadership Breakfast last November. As I wrote subsequently in "The Cable Industry Closes Ranks" my takeaway from his and other cable executives' recent comments was that the industry was poised to collaborate in order to defend cable's traditional - and highly profitable - business model. Under that model, cable operators currently pay somewhere between $20-25 billion per year in monthly "affiliate fees" to programmers whose networks are then packaged by operators into various consumer subscription tiers.
It should come as a surprise to nobody that both cable networks and operators are mightily incented to defend their model against the incursions of free "over the top" distribution alternatives. Indeed what's surprising to me is why it has taken the industry so long to act forcefully when the stakes are so high and the market's moving so fast? I mean cable operators themselves are the largest broadband Internet access providers in the country, and they have watched for years as their networks have been engorged by surging online viewing, courtesy of YouTube, Hulu, Netflix and others. While they've made some tepid moves to push programming online (though to be fair Comcast's Fancast portal has evolved quite a bit recently), overall their broadband video distribution activities have been underwhelming, evidence of broadband distribution's lower priority status vis-a-vis TV-based video-on-demand.
Meanwhile Friday's article triggered plenty of hackles from the blogosphere that those evil cable operators were up to their old monopolistic tricks, this time moving to control the broadband delivery market and choke off open access to premium video. While it's indeed tempting to see these plans that way, I think that would be the wrong conclusion.
Rather, I look at the Comcast/TWC moves as both welcome and likely to spur more, not less, consumer
 access to broadband-delivered programming. That's because, if the cable networks are smart in their negotiations, they will gain from operators the approval to push more of their programs onto both their own web sites, and even to distribute some through others' sites. With net neutrality agitators hopeful in the wake of Barack Obama's election, Comcast and TWC need to tread carefully in these negotiations. Yet another part of the model I foresee is archived programs, which have been locked up in vaults due to programmers' concerns over operator reprisals if they leaked out online, becoming much more openly accessible.
access to broadband-delivered programming. That's because, if the cable networks are smart in their negotiations, they will gain from operators the approval to push more of their programs onto both their own web sites, and even to distribute some through others' sites. With net neutrality agitators hopeful in the wake of Barack Obama's election, Comcast and TWC need to tread carefully in these negotiations. Yet another part of the model I foresee is archived programs, which have been locked up in vaults due to programmers' concerns over operator reprisals if they leaked out online, becoming much more openly accessible. The Comcast/TWC hecklers need to remember one simple fact: to make quality programming requires solid business models. And in this economic climate, solid business models are far and few between. Despite having lost a total of over 500,000 video subscribers during the last 6 consecutive quarters, Comcast still owns one of those few sold models. And don't forget it is now investing to increase its broadband speeds, pledging 30 million, or 65% of its homes, will have 50 Mbps access by the end of '09 (a rollout which incidentally is all privately financed, without a dime of federal bailout money or other assistance).
In the utopian fantasy of some, all premium content flows freely, supported by a skimpy diet of ads alone. For some that works. Yet for cable networks accustomed to monthly affiliate fees this is completely unrealistic and uneconomic. One needs look no further than the wreakage of the American newspaper industry (including bankruptcy filings recently by the Chicago Tribune and today by the Philadelphia Inquirer) to understand the damage that occurs when business model disruption occurs in the absence of coherent, evolutionary planning.
Someday, when broadband video business models mature (as indeed they ultimately will), there will be lots of cable and other programming available for free online. For now though, getting Comcast and TWC to finally pursue an aggressive broadband distribution path is a welcome evolutionary step in unlocking this exciting new medium's ultimate potential.
What do you think? Post a comment now.
(Note: we'll be diving deep into this topic, and others, at VideoNuze's Broadband Video Leadership Evening on March 17th in NYC. More information and registration is here.)
Categories: Aggregators, Broadband ISPs, Cable Networks, Cable TV Operators
Topics: Comcast, Hulu, Netflix, Time Warner Cable, YouTube
-
Canoe and the Broadband Video Challenge
In 2008, Canoe Ventures, the JV of six large U.S. cable operators, became one of the hottest topics of conversation in the cable, programming and advertising industries. Last week, I was fortunate to get time with Vicki Lins, Canoe's Chief Marketing Officer, to learn more about the company's plans. Though Vicki has been pulling double duty between her role at Comcast Spotlight and Canoe in recent months, she had only just started full time with Canoe, so she readily admitted that she's still getting up-to-speed.
Ordinarily Canoe's advanced TV advertising mission would be off-center for VideoNuze's strictly broadband video-centric focus. But the reason it's relevant to understand is because I think long-term, the world that Canoe is trying to create on top of cable's digital set-top boxes is on a collision course with the world that broadband video is trying to create. I see both eventually competing for the same viewers, ad dollars and mind-share.
Canoe is critical to the cable industry because it recognizes that ever-better targeting, interactivity and ROIs are driving ad spending decisions. For 10+ years now, the Internet (and Google in particular) has been resetting marketers' expectations, thereby placing ever-greater pressure on TV ad executives to improve their game.
Vicki explained that first and foremost, Canoe is a service bureau, helping advertisers, programmers and
 cable operators wring more value out of their ad inventory. It does not intend to sell any ads itself. Canoe's key is leveraging its access to its cable partners' digital set-top boxes. First up is what's called "Creative Versioning" or zone-based addressability - the ability to break down users into logical segments that get specific ads. Another focus is productizing the viewership data being captured by those set-tops to out-Nielsen Nielsen (while of course respecting users' privacy). A third is trying to enable user interactivity - the ability to get deeper information, zero in on a product feature in an ad, order an item, etc.
cable operators wring more value out of their ad inventory. It does not intend to sell any ads itself. Canoe's key is leveraging its access to its cable partners' digital set-top boxes. First up is what's called "Creative Versioning" or zone-based addressability - the ability to break down users into logical segments that get specific ads. Another focus is productizing the viewership data being captured by those set-tops to out-Nielsen Nielsen (while of course respecting users' privacy). A third is trying to enable user interactivity - the ability to get deeper information, zero in on a product feature in an ad, order an item, etc. All of this would benefit cable and broadcast networks seeking to more effectively monetize their ad inventory, as well as cable operators which sell a portion of cable networks' ad inventory locally. Clearly these are key constituencies, but as Vicki points out, Canoe must also address ad agencies, brands, cable technologists, local operations teams where Canoe's technology is actually deployed, cable marketers and others who have a stake in this process. It's a pretty long list, and one wonders whether a start-up is able to handle all of this at once.
But there are two even bigger issues that I see. First, I find myself wondering whether Canoe is even aiming at the right target with these initial plans. Instead, why doesn't Canoe just focus 100% of its energies on monetizing these cable operators' billions of current VOD streams? It's amazing to me that years after VOD's launch, I don't see any ads on Comcast (my cable company) VOD. My kids watch lots of Ben 10, Hannah Montana, Wizards of Waverly Place, etc on VOD yet never see a single ad for a sugared cereal or wizzy new toy. As a parent this isn't something I'm complaining about, but if I were a Comcast shareholder it would sure have me scratching my head. It seems like such a big missed opportunity...is there something I don't understand here?
As Denise Denson, MTV's EVP of Content Distribution and Marketing recently told Multichannel News, "We have over a billion VOD orders this year on Comcast alone, but we've made virtually no money in advertising in that space....With the convergence of TV and the Internet, there is a danger that the Internet's interactive content could usurp it. It's unfortunate, but programmers will have to put their content where they can actually monetize it."
And that brings us back to broadband video's challenge to Canoe. The fact is that broadband is a parallel and fast-growing VOD platform that is generating significant content provider interest because of it offers substantial control of the user experience and relatively robust monetization. As I wrote yesterday, broadband advertising innovation is being adopted by major media companies like MTV. And because broadband ad innovation is diffused over many companies (as is all innovation in the hyper-competitive Internet realm), there are rapid and continuous improvements. Conversely, by concentrating its set-top box ad efforts through just Canoe I think the cable industry is limiting the platform's vast potential.
Denise Denson hit the nail on the head: resources are finite and programming networks will focus their attention on platforms that offer the best scale and monetization opportunities. With broadband coming to TVs very soon, it will soon be a de facto competitor to cable's digital set-top box delivery. To preserve the value of its video platform, cable needs to shore up its VOD advertising and user experience and not let broadband surpass it. For my money, that seems like the most productive place for Canoe to first focus its attention.
What do you think? Post a comment now.
Categories: Advertising, Cable TV Operators
-
Sony's Internet-to-the-TV Plans Are Confusing (and the NYTimes Coverage Isn't Helping Any)
Catching up on some reading last night, I got a chance to re-read a NYTimes piece by Saul Hansell from this past Tuesday rather sensationally entitled "How Comcast Controls Sony's Internet TV Plans." When I scanned it on Tuesday before posting a link to it from VideoNuze, I had one of those "This makes absolutely no sense, I need to read this again closer" reactions. Now, upon re-reading it, I'm having one of those "This really makes no sense" reactions.
The piece - which initially concerns Sony's efforts to bring broadband video to TVs, but then veers off into a somewhat unrelated discussion of the company's negotiations with the cable industry's tru2Way and CableCard technologies - quotes Sony Electronics U.S. president Stan Glasgow as saying: "We've worked with the cable companies for five years to develop a system that would allow us and the rest of the television manufacturers to have alternative content on the TV."
Why would Sony devote five years to such an undertaking? Because, again in Mr. Glasgow's words, "If you have to ask a consumer to switch sources constantly between cable and another source, it is not the normal consumer experience...There has to be a more integrated way to have cable and Internet content on the same user interface."
I'm all for making things easy on the consumer, but let's get this right: Sony devoted five years to negotiating with the cable industry so it could avoid viewers having to push the "Source" or "Input" button on their remote controls to toggle to broadband-delivered content via Sony devices?
Hello? According to comScore's recent numbers, 142 million people in the U.S. alone watched 558 million hours of online video. But amid that massive adoption, Sony thinks it might be setting the bar too high for its potential buyers if it asked them to push a button on their remotes so that they could enjoy some of that video on their TVs instead of on their PCs?
Is it just me, or does it appear that Sony completely misjudged both its potential buyers' technical aptitude and also their strong motivation to consume broadband-delivered video on their TVs?
While you consider those questions, let's also go back to basics: why is once-mighty Sony even bothering to integrate its Internet-to-the-TV products with the cable industry in the first place? The whole point of these kinds of Internet-to-the-TV devices is to disrupt the cable (and satellite and telco) industry's hold on consumer viewing time and spending for in-home video programming. Countless companies (Netflix, Hulu, Microsoft/Xbox, Apple/AppleTV, Vudu, Netgear, Sezmi, 2Wire, Blockbuster, LG, Samsung, Neuros, etc.) get this fundamental point and are implicitly or explicitly driving toward this goal each day.
That Sony doesn't seem to understand this suggests that the correct title of Saul's piece really should have been "Comcast Benefits by Exploiting Sony's Misguided Internet TV Plans."
What's profoundly different about the broadband era is that neither Comcast nor any other incumbent controls how consumers get video on their TVs, just as neither the NYTimes nor any other single news provider has ever controlled how we've gotten our news. If would-be "over-the-top" competitors don't get this basic idea - and instead waste precious time and resources on perpetuating the traditional world order - then shame on them.
What do you think? Post a comment now.
Categories: Cable TV Operators, Devices
-
Video is the Killer App Driving Coming Bandwidth Explosion
A short interview in Multichannel News with Rouzbeh Yassini before the Thanksgiving break last week caught my eye.
Rouzbeh's name is likely unfamiliar to many of you. But for others who have been in and around the cable and broadband industries since the '90s, he is semi-famous. In those days Rouzbeh ran a company called LANCity, which was a pioneer in designing and manufacturing cable modems. These of course are the devices that now reside in tens of millions of homes around the world, enabling broadband Internet access and the high-quality video services like YouTube, Hulu, iTunes and others that run through them.
Though it's only been about 15 years, the early-to-mid '90s seem like another age entirely. Can you remember dial-up Internet access? Busying up your phone line if you wanted to be online? Listening to all those weird tones as your creaky 56K modem connected you to Prodigy, CompuServe, AOL, or eventually this thing everyone seemed to be talking about called the "World Wide Web?"
In my opinion, Rouzbeh deserves as much credit as anyone for the transformation of the dial-up Internet era
 to the broadband world we now enjoy. He played a crucial role in articulating broadband's business potential to scores of senior cable executives who barely knew what a computer was, much less this new-fangled thing called the Internet. Importantly, he was a key technical architect of modern cable networks, which today barely resemble the passive, one-way networks of old.
to the broadband world we now enjoy. He played a crucial role in articulating broadband's business potential to scores of senior cable executives who barely knew what a computer was, much less this new-fangled thing called the Internet. Importantly, he was a key technical architect of modern cable networks, which today barely resemble the passive, one-way networks of old. In short, I've learned to take notice of Rouzbeh's prognostications. Though he can be irrepressibly optimistic, he's directionally right more often than not.
All of that brings me to his Multichannel interview. Rouzbeh now envisions the era of gigabit or 1,000 megabit Internet access within a decade. To put this in perspective, today's cable modems typically deliver around 10 megabit service or 1% of a gigabit. Spurred by competitive pressures, Comcast has recently announced the rollout of 50 megabit service to certain regions, with expansion to its entire footprint by 2010. These new rollouts are part of the cable industry's "DOCSIS 3.0" standards, covering a new generation of modems and channel management techniques.
There's an axiom in the broadband industry that usage always rises to the level of bandwidth provided. Yet when we're talking 1 gigabit service, one has to rightly ask, "what in the world are people going to do with all that bandwidth?" Rouzbeh posits things like corporate networking, remote offices, medical services and the like, but only touches briefly on video delivery.
From my perspective, video is the killer application that will drive this bandwidth explosion. As I wrote recently in "Video Quality Keeps Improving - What's it All Mean?" we are on the front end of a shift toward dramatically higher video quality, with near HD delivery already becoming common (Hulu, Netflix and Vudu are among the most recent to announce HD initiatives). This shift will only accelerate going forward. And to accommodate it will require lots more bandwidth from network providers.
In reality, the trickiest part of bandwidth expansion is less the technology development and deployment and more the business models that support the investments and make the most strategic sense. Questions abound: Is the right model to charge $150/mo for 50 megabit access as Comcast plans? Or to build a content service available only to those high-powered users? Or act like a CDN and provide services so as to charge content providers themselves to deliver higher-quality video? Maybe some hybrid of these, or some other model? And of course, what impact do these models have on the incumbent multichannel subscription video offering?
While there's murkiness now, like Rouzbeh, I'm a big believer that these things will ultimately be worked out and that bandwidth expansion is inevitable. Just as we now look back on the dial-up era and wonder how we got by, eventually we'll look at the mid-to-late 2000s and wonder how we survived on so little bandwidth.
What do you think? Post a comment now.
Categories: Aggregators, Broadband ISPs, Cable TV Operators, People
Topics: Comcast, DOCSIS, Hulu, Netflix, VUDU
-
November '08 VideoNuze Recap - 3 Key Themes
Welcome to December and to the home stretch of 2008. Following are 3 key themes from VideoNuze in November:
Cable programming's online distribution narrows - Last month I concluded that cable programmers (e.g. Discovery, MTV, Lifetime) are going to become much more sparing when it comes to distributing their full programs online. As noted in "The Cable Industry Closes Ranks," after hearing from industry executives at the CTAM Summit and on the Broadband Video Leadership Breakfast, it has become apparent that the industry is going to defend its traditional multichannel video subscription model from broadband and new "over-the-top" incursions.
Both programmers and operators have a lot vested in this successful model, and are surely wise to see it last as long as possible. Subscription and affiliate fees are particularly precious in this economy, as the WSJ wrote on Saturday. Still, many VideoNuze readers pointed out the music industry's folly in trying to maintain its business model, only to see it turned upside down. Many predicted the cable industry is doomed to follow suit. Truth-be-told though, as I wrote in "Comcast: A Company Transformed," major cable operators are already far more diversified than they used to be. Broadband, phone and digital TV (+ add-ons like DVR, HD and VOD) have created huge new revenue streams. Surging broadband video consumption only helps them, even as "cord-cutting" looms down the road.
Netflix moves to first ranks of cord-cutting catalysts - Three posts in November highlighted the significant role that Netflix is poised to play in moving premium programming to broadband distribution. Most recently, in "New Xbox Experience with Netflix Watch Instantly: A 'Wow' Moment," I shared early reactions from a VideoNuze reader (echoed by many others) to receiving a subset of Netflix's catalog through Xbox's recently upgraded interface. Netflix CEO Reed Hastings highlighted the increasing importance of game devices in bridging broadband to the TV in his keynote at NewTeeVee Live this month (recapped here).
Still, Netflix lacks the rights to deliver many movies online, a problem unlikely to be rectified any time soon given Hollywood's stringent windowing approach. As such, in "Netflix Should be Aggressively Pursuing Broadcast Networks for Watch Instantly Service," I offered my $.02 of advice to the company that it should build on its recent deal with CBS to blow out its online library of network programs. In this ad-challenged environment, I believe networks would welcome the opportunity. Hit TV programs would help drive device sales, which is crucial for building WI's adoption. While the Roku box is a modest $99, other alternatives are still pricey, though becoming cheaper (the Samsung BD-P2500 Blu-ray player is down $100, now available at $300, I spotted the LG BD300 over the weekend for $245). A robust Netflix online package would be poised to draw subscribers away from today's cable model.
Lousy economy still looms large - Wherever you go, there it is: the lousy economy. Though the market staged a nice little rebound over the last 5 days, things are still fragile. Across the industry broadband companies are doing layoffs. This is only the most obvious of the side effects of the economic downturn. Another, more subtle one could be downward price pressure. As I wrote in "Deflation's Risks to the Broadband Video Ecosystem," economists are now growing concerned that the credit crunch could lead to collapsing prices and profits across the economy. I noted that such an occurrence would be particularly damaging for the broadband industry, where business models are still nascent, so ROIs and spending are softer.
Here's to hoping for some good economic news in December...
What do you think? Post a comment now.
Categories: Aggregators, Broadcasters, Cable Networks, Cable TV Operators, Devices, Games
Topics: CBS, Comcast, LG, Microsoft, Netflix, Roku, Samsung, XBox
-
Watching Reed Hastings at NewTeeVee Live
Yesterday I had my own positive broadband video experience, remotely watching portions of the
 NewTeeVee Live conference held in SF from the comfort of my office. Om Malik and crew put together a packed agenda and I had wanted to go, but a personal conflict kept me in Boston.
NewTeeVee Live conference held in SF from the comfort of my office. Om Malik and crew put together a packed agenda and I had wanted to go, but a personal conflict kept me in Boston. I caught most of Netflix CEO Reed Hastings' keynote (until the UStream feed froze up, arghh...) and thought he offered some interesting tidbits about how he sees the broadband video market unfolding. VideoNuze readers know I've been avidly following Netflix's recent moves with Watch Instantly and I've come to think of the company as one of three key aggregators best-positioned to disrupt the cable model (the other two being YouTube and Apple).
Three noteworthy points that Hastings made:
Standards needed to interface broadband to the TV - Hastings catalogued the efforts Netflix is making to integrate with various devices like Roku, LG, TiVo, Xbox, etc, but concluded by saying that these one-off, ad hoc integrations are not scalable and are really slowing the market's evolution. Most of us would agree with this assessment. Still, he was quite pessimistic about a standards setting process's ability to move quickly enough - saying this could be a 10-30 year endeavor. Instead, if I understood him correctly, he thinks the TV approach should just be browser- based, and also that today's remotes should be scrapped in favor of pointer-driven (i.e. mouse-like) navigation.
Cable should evolve to focus on broadband delivery and de-emphasize multichannel packaging - Of course this is incredibly self-serving from Netflix's standpoint, but Hastings made the case that broadband margins for cable operators are nearly 100%, because they have no content costs, whereas on the cable side, they have high and ever-increasing programming costs. He cited Comcast's recent announcement of 50 Mbps service as evidence that cable operators should focus on winning the broadband war, and eventually letting go of the multichannel model. Nice try Reed, but I don't see that happening anytime soon. However, as I recently wrote in "Comcast: A Company Transformed," there's no question that broadband is becoming an ever greater part of its revenue and cash flow mix.(Reed emailed to clarify the above point. He didn't say cable should focus on broadband delivery over the current multichannel model; rather that cable - and satellite/telco - should focus more on web-like viewing experiences through improved navigation and VOD/DVR to be more on-demand, personalized and browser-friendly. And he added that with the shift to heavier broadband consumption, cable is a winner either way. Note - I thought I interpreted him correctly, but between UStream choking and my own scribble, it seems I was a bit off here. Thanks for correcting Reed.)Game consoles in leading position to bridge broadband to the TV - Hastings made a pretty strong case for the Wii - and to a lesser extent the PlayStation and Xbox - as the leading bridge devices. The Wii in particular could be a real broadband winner if it could support HD and Flash. As I've been thinking about broadband to the TV, I've concluded - barring anything from left field - that game devices, IP-enabled TVs and IP-enabled Blu-ray players are where the action will be concentrated for the next 3-4 years (this doesn't take account of forklift substitutes like a Sezmi or others sure to come).
NewTeeVee has a good wrap-up of Hastings' talk as well, here. The video replay isn't up yet, but when I see it, I'll post an update.
What do you think? Post a comment now!
Categories: Aggregators, Cable TV Operators, Devices
Topics: Apple, Comcast, LG, Netflix, PlayStation, Roku, TiVo, Wii, XBox, XBox, YouTube
-
The Cable Industry Closes Ranks
First, apologies for those of you getting sick of me talking about the cable TV industry and broadband video; I promise this will be my last one for a while.
After attending the CTAM Summit the last couple of days, moderating two panels, attending several others and having numerous hallway chats, I've reached a conclusion: the cable industry - including operators and networks - is closing ranks to defend its traditional business model from disruptive, broadband-centric industry outsiders.
Before I explain what I mean by this and why this is happening, it's critical to understand that the cable business model, in which large operators (Comcast, Time Warner Cable, etc.) pay monthly carriage or affiliate fees to programmers (e.g. Discovery, MTV, HGTV, etc.) and then bundle these channels into multichannel packages that you and I subscribe to is one of the most successful economic formulations of all time. The cable model has proved incredibly durable through both good times and bad. In short, cable has had a good thing going for a long, long time and industry participants are indeed wise to defend it, if they can.
It's also important to know that the industry is very well ordered and as consolidation has winnowed its ranks to about half a dozen big operators and network owners, the stakes to maintain the status quo have become ever higher. All the executives at the top of these companies have been in and around the industry for years and have close personal and professional ties. There's a high degree of transparency, with key metrics like cash flow, distribution footprint, ratings and even affiliate fees all commonly understood.
One last thing that's worth understanding is that the cable industry has very strong survival instincts, or as a long-time executive is fond of saying, "Real cable people (i.e. not recent interlopers from technology, CPG or online companies that have joined the industry) were raised in caves by wolves." The fact is that the industry started humbly and experienced many very shaky moments. Yet it has managed to survive and continually re-invent itself (for those who want to know more, I refer you to "Cable Cowboy: John Malone and the Rise of the Modern Cable Business" by Mark Robichaux, still the best book on the industry's history that I've read).
All of that brings us to broadband and its potential impact on the cable model. As I've said many times, broadband's openness makes it the single most disruptive influence on the traditional video distribution value chain. Principally that means that by new players going "over the top" of cable - using its broadband pipes to reach directly into the home - cable's model is at serious risk of breaking down, once and for all.
The cable industry now gets this, and I believe has closed ranks to frown heavily on the idea of cable programming, which operators pay those monthly affiliate fees for, showing up for free on the web, or worse in online aggregators' (e.g. Hulu, YouTube, Veoh, etc.) sites. The message is loud and clear to programmers: you'll be jeopardizing those monthly affiliate fees come renewal time if your crown jewels leak out; worse, you'll be subverting the entire cable business model.
And this message isn't being delivered just by cable operators such as Peter Stern from Time Warner who said on my Broadband Video Leadership Breakfast panel that "a move to online distribution by cable networks would directly undermine the affiliate fees that are critical to creating great content." It's also coming from the likes of Discovery CEO David Zaslav who said on a panel yesterday that "there's no economic value from online distribution," and that "great brands like Discovery's must not be undervalued by making full programs available for free online."
The issue is, as a practical matter, can the industry really control all this? If there's zero online distribution, then as Fancast's impressive new head, Karin Gilford said on my panel yesterday, "pressure builds up and another channel inevitably opens" (read that as The Piracy Channel). The problem is that if, for example, an operator does put programs up on its own site - as Fancast is doing - they're available to ALL the site's visitors, not just existing cable subscribers, unless other controls are put in place like passwords, IP address authentication, geo-targeting, etc. But these are confusing and cumbersome to users whose expectations are increasingly being set by broadcasters who are making their primetime programs seamlessly available to all comers.
So what does this closing ranks suggest? Going forward, I think we'll still see cable networks putting up plenty of clips and B-roll video from their programs, maybe the occasional online premiere, some made-for-the-web stuff, paid program downloads (iTunes, etc.) and promotional/community building contests, as Deanna Brown from Scripps described with "Rate My Space" or Zaslav discussed with "MythBusters."
But when it comes to full cable network programs going online, I think that spigot's going to dry up. That has implications for online aggregators like Hulu, who will continue to have big holes in their libraries until they're ready to pay up for these carriage rights. And it also means that broadband-to-the-TV plays are also going to be hampered by subpar lineups unless these companies too are willing to pay for cable programming.
By closing ranks the cable industry's making a bold bet that its ecosystem can withstand broadband's onslaught and the rise of the Syndicated Video Economy. In yesterday's post I noted that the music industry tried a similar approach; we know where that got them. There are plenty of reasons to think things could indeed be different for the cable industry, but there are as many other reasons to think the cable industry is massively deluding itself and could someday be grist for a chapter in the updated version of Clay Christensen's "The Innovator's Dilemma," (my personal bible for how to pursue successful disruption), right alongside the inevitable chapter about how the once mighty American auto industry spectacularly lost its way.
For my part, there are just too many moving parts for me to call this one just yet.
What do you think? Post a comment now!
Categories: Aggregators, Broadcasters, Cable Networks, Cable TV Operators, Devices, Syndicated Video Economy
Topics: Comcast, CTAM Summit, Discovery, Fancast, Scripps, Time Warner
-
Comcast: A Company Transformed
Three numbers in last week's third quarter Comcast earnings release underscored something I've believed for a while: Comcast is a company transformed, now reliant on business drivers that barely existed just ten short years ago. Comcast's transformation from a traditional, plain vanilla cable TV operator to a digital TV and broadband Internet access powerhouse is profound proof of how consumer behaviors' are changing and value is going to be created in the future.
The three numbers that caught my attention were the net additions of 382,000 broadband Internet subscribers and 417,000 digital subscribers, with the simultaneous net loss of 147,000 basic subscribers. The latter number is the largest basic sub loss the company has sustained and, based on the company's own earnings releases, the sixth straight quarter of basic sub contraction. In the pre-digital, pre-broadband days, when a key measure of cable operators' health was ever-expanding basic subscribers, this trend would have caused a DEFCON 1 situation at the company. (see graph below for 2 year performance of these three services)
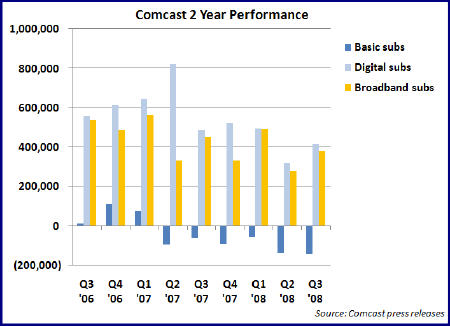
That it doesn't any longer owes to the company's ability to bolster video services revenue and cash flow through ever-higher penetration of digital services into its remaining sub base (at the end of Q3 it stood at 69% or 16.8 million subs). Years after Comcast and other cable operators introduced "digital tiers," stocked with ever-more specialized channels that consumers resisted adopting, the industry has hit upon a winning formula for driving digital boxes into Americans' homes: layering on advanced services like HD, VOD and DVR that are only accessible with digital set top boxes and then bundling them with voice and broadband Internet service into "triple play" packages. Comcast has in effect gone "up-market," targeting consumers willing and able to afford a $100-$200/month bundle in order to enjoy the modern digital lifestyle.
Still, in a sense the new advanced video services represent just the latest in a continuum of improved video services. Far more impressive to me is the broadband growth that both Comcast and other cable operators have experienced. Comcast's approximately 15 million YE '08 broadband subscribers will generate almost $8 billion in annual revenue for Comcast, up dramatically from its modest days as part of @Home 10 years ago. (It's also worth noting the company now also provides phone service to over 6 million homes today vs. zero 10 years ago)
The cable industry as a whole will end 2008 with approximately 37 million broadband subs, again up from single digit millions 10 years ago. And note that the 387,000 net new broadband subs Comcast added in Q3 '08 compares with just 277,000 net broadband subs that the two largest telcos, AT&T and Verizon added in quarter, combined. As someone who was involved in the initial trials of broadband service at Continental Cablevision less than 15 years ago, observing this growth is nothing short of astounding.
While broadband's financial contribution to Comcast is unmistakable, its real impact on the company is more
 keenly felt in its newfound importance in its customers' lives. Broadband Internet access has become a true utility for many, as essential in many homes as heat, water and electricity. A senior cable equipment executive told me recently that research done by cable companies themselves has shown that in broadband households, broadband service would be considered the last service to get cut back in these tough economic times. In these homes cable TV itself - long thought to be recession-resistant - would get cut ahead of broadband.
keenly felt in its newfound importance in its customers' lives. Broadband Internet access has become a true utility for many, as essential in many homes as heat, water and electricity. A senior cable equipment executive told me recently that research done by cable companies themselves has shown that in broadband households, broadband service would be considered the last service to get cut back in these tough economic times. In these homes cable TV itself - long thought to be recession-resistant - would get cut ahead of broadband.But Comcast and other cable operators must not rest on their laurels. Their next big challenge is to figure out how to take this massive base of broadband subs and start delivering profitable video services to it. If Comcast allows its broadband service to be turned into a dumb pipe, with "over the top," on demand video offerings from the likes of Hulu, YouTube, Neflix, Apple and others to ascend to dominance, that would be criminal. Not only would it devalue the broadband business, it would dampen interest in the company's advanced video services (VOD in particular) while making the company as a whole vulnerable in the coming era of alternative, high-quality wireless delivery.
Comcast is indeed a company transformed from what it was just 10 years ago. Technology, changing consumer behaviors and a little bit of "being in the right place at the right time" dumb luck have combined to allow Comcast to remake itself. Comcast itself must fully recognize these changes and aggressively build out Fancast and other initiatives to fully capitalize on its newfound opportunities.
What do you think? Post a comment now.
Categories: Aggregators, Broadband ISPs, Cable TV Operators, Telcos
Topics: Apple, AT&T, Comcast, Netflix, Verizon, Verizon, YouTube
-
Digital Media and Broadband Video Executives Play Musical Chairs
It's been hard not to notice the recently growing roster of digital media/broadband video executives who are either leaving their jobs or jumping to other companies.
Among the many recent changes:
- Bill Day (moved to CEO, ScanScout from Chief Media Officer, Marchex)
- Ned Desmond (leaving as President, Time, Inc Interactive)
- Tony Fadell (leaving as SVP, iPod Division, Apple)
- Karin Gilford (moved to SVP, Fancast/Comcast from VP/GM, Yahoo Entertainment)
- Bob Greene (left as EVP, Advanced Services, Starz)
- Kevin Johnson (moved to CEO, Juniper Networks from President, Platforms & Services Division, Microsoft)
- George Kliavkoff (leaving as Chief Digital Officer, NBCU)
- Michael Mathieu (moved to CEO, YuMe from President, Freedom Communications Internet Division)
- Scott Moore (leaving as SVP, Media Group, Yahoo)
- Herb Scannell (moved from CEO to Executive Chairman, Next New Networks)
- David Verklin (moved to CEO, Canoe Ventures from CEO, Aegis Media Americas)
Of course there are many more as well.
There's no blanket explanation for all of this movement. Senior executives - particularly those with strong track records in unchartered territory like digital media and broadband video - are always in demand by competitors. And established companies who can't execute or who are losing altitude in their core businesses become fertile ground for executive recruiters. Then there are always personal reasons for causing executive change (family matters, geographic restrictions, etc.).
The whole digital media and broadband space is extremely dynamic. Major incumbents continue to struggle with defining their strategies and how to organize themselves properly to execute. The financial meltdown has caused huge profit pressure, prompting operational streamlining.
Still, I'm hoping that all this executive movement doesn't slow broadband's growth. In particular, prematurely folding a digital operation into an incumbent product area can limit innovation as executives who are primarily focused on the core business and who lack detailed domain knowledge will inevitably shy away from riskier or more complex digital initiatives. I've seen this myself first hand. Broadband is still early in its evolution; hopefully executive change will foster, not hinder, its continued progress.
What do you think? Post a comment now.
Categories: People
Topics: Aegis, Apple, Canoe, Comcast, Juniper, Marchex, Microsoft, NBCU, Next New Networks, ScanScout, Starz, Time, Yahoo, YuMe
-
October '08 VideoNuze Recap - 3 Key Themes
Welcome to November. October was a particularly crazy month with the unfolding financial crisis. Here are 3 key themes.
1. Financial crisis hurts all industries; broadband is no exception
In October the financial crisis was omnipresent. During the month I addressed its probable effects on the broadband industry here and here so I'm not going to spend much more time on it today. Suffice to say, for the foreseeable future, the key industry metrics are financing, staffing and customer spending. Conserving cash and getting to breakeven are paramount for all.
In particular, in "Thinking in Terms of a 'GOTI' Objective" I tried to provide some food for thought about why focus is so important right now. Industry CEOs' jobs have gotten a whole lot harder in the wake of the meltdown; those with the best strategic and financial skills will come through the storm, others will encounter significant challenges.
2. Broadband video is still in very early stages of development
I'm constantly trying to gauge just how developed the broadband video industry actually is. All kinds of indicators continue to suggest to me that we're still in the very early days. For example, in one post this month comparing iTunes and Hulu, it was evident that iTunes is currently far outpacing Hulu in TV episode-related revenues. Remember that Hulu is the undisputed premium ad-supported aggregator. And that the ad-supported business model itself is predicted by most to eventually be far larger than the paid model. That iTunes is so far ahead for now shows how young Hulu really is (in fact, just celebrating its first anniversary) and how much more development the ad-supported model still has ahead of it.
I think another relevant indicator of progress is how well the broadband medium is distinguishing itself from alternatives by capitalizing on its key strengths. In "Broadband Video Needs to Become More Engaging," I noted that while there have recently been positive signs of progress, overall, much of broadband's engagement potential is still untapped. That's why I'm always encouraged by compelling UGV contests like the one Fox and Metacafe unveiled this month or by technology like EveryZing's new MetaPlayer that drives more granular interactivity. To truly succeed, broadband must become more than just an online video-on-demand medium.
3. Cable operators are central to broadband video's development
As ISPs, cable operators account for the lion's share of broadband Internet access. Further, their ongoing efforts to increase bandwidth widens the universe of addressable homes for high-quality content delivery. Still, their multichannel subscription-based business model is increasingly threatened by broadband's on-demand, a la carte nature. As delivery quality escalates and consumer spending remains pinched, the notion of dropping cable in favor of online-only access become more alluring.
Yet in "Cutting the Cord on Cable: For Most of Us It's Not Happening Any Time Soon," I explained why restricted access to popular cable network programs and an inability to easily view broadband video on the TV will keep cable operators in a healthy position for some time to come. Still, it's a confusing landscape; this month I noticed Time Warner Cable itself helped foster cable bypass, when in the midst of its retransmission standoff with LIN TV, it offered an instructive video for how to watch most broadcast network programming online. Comcast also got into the act, unveiling "Premiere Week" on its Fancast portal. These kinds of initiatives remind consumers there's a lot of good stuff available for free online; all you need is a broadband connection.
Lots more to come in November, stay tuned.
Categories: Broadband ISPs, Broadcasters, Cable Networks, Cable TV Operators, Technology, UGC
Topics: Comcast, EveryZing, FOX, Hulu, iTunes, LIN TV, MetaCafe, Time Warner Cable
-
Comcast's Fancast Becomes Hub for Premieres; But Where's Project Infinity?
Here's a clever move from Comcast's Fancast broadband portal to create new value for users and generate excitement in the broadband market: this week it is running "Premiere Week," an aggregation of 168 premiere TV episodes. The episodes span series premieres ("Desperate Housewives," "Dexter," "The Office"), season premieres ("Fringe," "Sons of Anarchy," "Crash") and classic pilots ("Dynasty," "The A-Team," "Miami Vice"). It's great fun and a visitor could get lost on the site for hours, as I nearly did.
These are the kinds of promotions that Comcast should be all over. Given its extensive reach and programming muscle, the company has definite - though not insurmountable - advantages over other aggregators to pull this kind of promotion together.
The competition for aggregating premium programming continues to intensify. Business models are all over the board as are approaches for getting video all the way to the TV. For example, last week Amazon launched its pay-per-use VOD initiative which includes a page of info for how to watch using TiVo, Sony Bravia Internet Video Link, Xbox 360, etc. Then yesterday, Netflix announced that it will incorporate about 2,500 of Starz's movies, TV shows and concerts in its Watch Instantly feature, along with a feed of its linear channel. Still other moves are forthcoming.
Comcast's real lever though is unifying its currently siloed worlds of digital TV, broadband Internet access and Fancast. When converged they're a blockbuster; companies like Netflix, Amazon and others cannot replicate this combination. In particular, Comcast, and other cable operators are ideally positioned to bridge broadband all the way to the TV. That's the last big hurdle to unlock broadband's ultimate value. Whether they'll do so is an open question.
Earlier this year Comcast CEO Brian Roberts unveiled the company's "Project Infinity" which suggested Comcast was looking to unify its various video offerings and bring broadband to its subscribers' TV. It seemed like a promising move, though there was no timeline disclosed. Now, nearly 9 months later I can't find any updates on the status of Project Infinity. It would be great for the company to publicly release a progress report or sense of upcoming milestones.
Promotions like "Premiere Week" are a positive step from Comcast, but real competitive advantage for the company lies in launching services which are truly impossible for others to match.
What do you think? Post a comment.
Categories: Aggregators, Cable TV Operators, Portals
Topics: Amazon, Comcast, Fancast, Netflix, Starz, TiVo
-
Fancast Gets a Facelift
Comcast's Fancast broadband portal has received a much-needed facelift, adding new features and content to compete with other well-funded players in this space. (Note: before you conclude that VideoNuze has become obsessed with covering Comcast - since just yesterday I dug into its ISP policies - rest assured, tomorrow I'll move on!)
Fancast is by far the most ambitious portal effort among the major cable operators. In fact, while other operators' portals target just their own ISP customers, Comcast's goal is to have Fancast compete for ANY broadband user's attention. That means that Fancast goes head to head with ad-based broadband aggregators like Hulu, Veoh, Joost, Metacafe, etc. And now with Fancast's new video download store, it also butts up against folks like iTunes, Amazon Unbox, Xbox LIVE Marketplace, etc. Then of course there's YouTube, the 800 pound gorilla of the broadband video world, which all aggregators, compete with on one level or another.
With such a formidable array of competitors, Fancast has a high bar to succeed. Still, I've maintained for a while that Comcast, with its 14 million+ broadband subscribers and 22 million+ cable subscribers is extremely well-positioned and needed to play aggressively in broadband video distribution. To date though I've been underwhelmed by Fancast, which seemed to have a solid vision, but sub-par execution. (For more on this, see 2 previous posts, here and here, comparing Hulu and Fancast.)
Now, with Fancast's facelift, the portal is getting some mojo. Fancast's director of communications Kate Noel recently took me on a spin through what's new. First up is a new home page (see below) that nicely showcases premium content that is curated by an in-house editorial team. Clicking on a selection reveals an oversize video player (which can be further enlarged to full screen). New features include embedding and sharing, along with a handy tool to be notified when a new episode is offered.
There's also a noticeable improvement in content selection, which Kate says now includes over 37,500 video assets; 320+ individual TV programs, 250+ movies and countless trailers and clips from over 100 content partners. Fancast is also putting a heavy emphasis on editorial differentiation, and has created sections such as "Today's Top 5," "Daily Buzz (blog)" and "Discover All Your Favorites." to help orient users on the site and provide editorial perspective.
This all plays to what Kate says is Fancast's larger mission to not just "offer TV online," but rather to "use Fancast as a cross-platform hub" that draws value from and drives value to Comcast's other offerings - digital cable, VOD and DVR service in particular.
With Comcast's huge cable subscriber base, that sounds right in theory. But how exactly Fancast fully executes on that potential still feels squishy. For example, doing a search for a current episode of "Mad Men" reveals a nice option to watch on VOD (since it's not currently on Fancast - that's a whole other story...), but is this really a game-changer? A much more significant lever at Comcast's disposal would be getting Fancast onto their digital cable boxes, so all that great Fancast content could be consumed in the living room (maybe along with YouTube, Funnyordie, NYTimes.com and other video?). The nagging question remains: will that day ever come?
One last thing that struck me about Fancast was its seemingly murky relationship with Hulu, which supplies many of Fancast's movies, and some of its TV programs. Is Hulu a Fancast competitor, a partner, both? Kate says Hulu is not competitive. Yet at the end of the day, aren't both Hulu and Fancast competing for the same ad dollars, and eyeballs? Here's another question: with Comcast's vast programming arm, why can't it procure movies directly from studios, instead of cutting Hulu in on the action? I must say, it's all very confusing.
Still, to the average user, the new Fancast is an improvement, and there is more progress yet to come.
What do you think? Post a comment now!
Categories: Aggregators, Cable TV Operators, Portals
Topics: Comcast, Fancast, Hulu
-
Debunking the Paranoia Around Comcast's ISP Policies
While much of the world was on vacation last week, yet another Comcast-related fracas broke out in the blogosphere, this time over the company's latest update to its broadband internet access policies. While this latest flap cements Comcast's status as the favorite target of those who put a totally unfettered Internet on a par with life, liberty and the pursuit of happiness, my immediate reaction was more "what's the big deal?"
The latest fracas centers on a seemingly innocuous, yet possibly longer-term significant change in
 Comcast's "Acceptable Use Policy" which governs how much use you can get out of your Comcast High-Speed Internet service each month. In the past there was no theoretical limit, though Comcast says it always had on eye on its heaviest users (under 1% of its total base of 14 million) who would be contacted when an undisclosed threshold was reached. Last Thursday, Comcast posted a change in its AUP stating that starting October 1st, the usage cap would be 250GB/mo.
Comcast's "Acceptable Use Policy" which governs how much use you can get out of your Comcast High-Speed Internet service each month. In the past there was no theoretical limit, though Comcast says it always had on eye on its heaviest users (under 1% of its total base of 14 million) who would be contacted when an undisclosed threshold was reached. Last Thursday, Comcast posted a change in its AUP stating that starting October 1st, the usage cap would be 250GB/mo.The blogosphere's reaction was immediate and sometimes raucously over-the-top (one well-known blogger pronounced the change "the end of the Internet as we know it"). While Comcast tried to translate the 250GB cap into say, how many emails a user could send each month (50 million) or songs that could be downloaded (62,500), others began furiously crunching the numbers to see more extreme scenarios, like how many HD movies/mo you'd be able to download.
For my part, I believe that Comcast's new cap - like much of the swirl surrounding its recent BitTorrent throttling - is much ado about nothing, at least for now. Where others see a raging fire threatening to burn down the Internet, I barely see signs of smoke just yet.
Yesterday I peppered Comcast spokesman Charlie Douglas with questions about the cap. While I had to ask several times whether it is intended to stifle broadband video consumption in any way (a favorite conspiracist belief), Charlie finally did provide an emphatic "no." He cited Comcast's own Fancast broadband portal as a key company priority, which itself would be harmed by any sort of broadband crackdown.
For sure some of you are thinking, "yeah but Will, he's their PR guy, what do you expect him to say?! Why do you believe him?!"
Fair questions. But contrary to the end-of-the-world crowd, I don't think Comcast has any sinister hidden motives with the cap, or with its network management policies. I do however think that Comcast does not take enough care in determining its policies or communicating them to its broadband users and other constituencies. Combined, these feed the distrust and dislike of Comcast that seems to be pervasive.
Even in my conversation with Charlie yesterday I found myself having several "huh?" moments that seem to strain credulity. For example:
Q: Why set a cap and especially one that's so high that it has little practical effect? A: Well, our customer feedback told us we needed to have a cap.
Q: How was the cap size determined? A: We thought it was a generous amount. Q: But the specific size? A: We thought it was a generous amount.
Q: Why release news of the cap in the last week of the summer (when many are on vacation and not paying attention) and in the midst of the ongoing FCC network management issue, instead of rolling out a comprehensive new plan that could be messaged accordingly? A: The cap and the FCC network management have nothing to do with each other, they are separate issues. Q: But in the media's coverage and public's perception, they are all considered part of the same picture. A: The cap and the FCC network management have nothing to do with each other, they are separate issues.
Q: Now that there's a formal cap, how about providing a simple tool so users can monitor their monthly usage, like cell phone companies do? A: Heavy users know how to find these tools; someone just told me last week that a Google search for "bandwidth meter" yields 290,000 hits. Q: Yes, but how about just offering a tool as a "good neighbor" gesture that your customers would appreciate? A: The cap is irrelevant to 99% of our users.
No doubt you'll find these answers as confounding as I do. All I can conclude is that 10+ years into the broadband game, Comcast still hasn't recognized how vital its broadband service is to its users nor how it has become part of a far-larger tableau including freedom of speech, the economy and American competitiveness. Comcast's seeming tone-deafness to all of this was fully evident in its continuously revised responses to the FCC's BitTorrent inquiry earlier this year.
This explanation will strike many as too generous and trusting. However, until I see real evidence of perniciousness on Comcast's part, to think anything else just feels like paranoia to me.
What do you think? Post a comment now.
Categories: Broadband ISPs
Topics: Comcast, FCC, Net Neutrality