-
Tremor vChoice Ad Format Raises the Bar on Pre-rolls
I was intrigued by news yesterday from Tremor Media, the ad network and management company, of their rollout of a new ad format called vChoice. Advertising continues to be the primary business model for premium online video, yet there's wide consensus that pre-roll ads, the most popular ad format today, leaves a lot to be desired. I spoke to Tremor's CEO, Jason Glickman to learn more about vChoice, and its benefits vs. pre-roll.
With vChoice, there's still a video ad playing prior to the requested content, but at 5-15 seconds, it's shorter than typical 15 and 30 second spots. The big difference is that this short ad is meant to be a teaser; when it stops running, an explicit choice is given to the user to click for more video, or to continue on to the requested content.
By shortening the upfront message, and presenting more options to the user, the goal is to deepen engagement. vChoice is geared to advertisers who either already have videos that could be logically clustered and offered to users (e.g. a car model which multiple promo videos) or are interested in creating new stories for non-linear consumption (like the example below from Warner Bros). Either way, as Jason notes, vChoice offers much greater creative freedom and engagement potential than a typical 15 or 30 second passive spot.
Tremor just finished a beta of vChoice with Microsoft, P&G, Ubisoft and Warner Bros. The results are impressive: 200% lift in engagement, as defined by multiple metrics, and a click-through rate of 3-6% vs. sub-1% for typical pre-rolls. Tremor's also using Quantcast data to provide demographic profiling of these engaged users. The early results, plus the creative potential, is what Jason says has advertisers most excited.
Jason also added that there are two keys to making vChoice possible: the company's Acudeo management platform, which allows multiple in-stream ads to run within a single unit, while also delivering full analytics, and the scale represented by 900+ sites in Tremor's publisher network. Importantly, there's no extra charge for additional views in a vChoice experience. That means for users who watch multiple videos, the advertiser's cost/impression keeps declining.
Jason doesn't see vChoice obsoleting pre-rolls, but rather offering more value in the online video medium. vChoice's success depends on whether users will be sufficiently enticed by the enhanced choices the advertiser offers to divert from their original viewing intentions. Key to driving that behavior is getting media buyers and creatives to understand the new value of these units and to then to invest in them. As this happens, the full potential of online video advertising will begin to be realized.
What do you think? Post a comment now.
Categories: Advertising
Topics: Tremor Media
-
Other Analysts Waking Up to Concerns About Hulu's Business Model
I have to say, I chuckled a little when I read this morning's Online Media Daily story, "Opening a Pandora's Boxee" about a new report from Laura Martin at Soleil Securities titled "Content's $300B Gamble." I haven't read the report, but the article says that it expresses concern that ad revenues for programs watched online could be 60% lower than when watched on-air, "threatening TV's the TV platform's price umbrella."
The reason I chuckled is because I've been saying the same things for months now (for example, see "Broadcast Networks' Use of Broadband is Accelerating Demise of Their Business Model" and "OK, Hulu Now Has ABC. But When Will It Prove Its Business Model?") It's nice to see others starting to understand these important issues as well.
Recently I've had a number of conversations with TV and broadband executives who are similarly concerned about what role Hulu is going to play longer term for the broadcast industry, given the current absence of a proven business model for the site. There are some pretty strong feelings out there, ranging from "Hulu is totally misguided and will be the downfall of the broadcast industry" to "the Hulu team is so smart, they're bound to figure it out." One way or the other, with Hulu's growing popularity, I continue to believe that the broadcast industry's fortunes are increasingly tied to Hulu's financial success.
What do you think? Post a comment now.
Categories: Advertising, Aggregators
Topics: Hulu
-
NBC.com Bolsters Mobile Video Ad Model with Kiptronic's Help
While broadband video consumption continues to surge, mobile video usage is also now showing strong signs of growth, mainly due to the iPhone's popularity. In fact Nielsen just reported last week that iPhone users are 6 times as likely to watch mobile video as are other mobile subscribers. And for Q4 '08, it reported that 11.2M people watched mobile video, with 51% stating they're new to the medium, viewing for less than 6 months. This is still small compared with the 150M or so people (U.S.) watching broadband video each month, but with an onslaught of new or upgraded video-capable smartphones hitting the market, mobile video is poised to grow rapidly.
All of this is very good news for content providers, for whom this "3rd screen" (after TV and PC) opens up all kinds of new opportunities. Many have been participating to date in carrier-provided (e.g. VCast, FLO TV) and other (e.g. MobiTV) subscription services that have achieved solid growth. But with still advertising the primary business model for many content providers, they've been eager make ad-supported video available to growing base of mobile video users as well.
NBC for example has been pursuing ad-supported mobile video, and last summer, made a big mobile push with its Summer Olympics coverage. Still, as Stephen Andrade, NBC.com's SVP and GM and Robert Angelo director web/mobile, told me recently, inserting ads in its mobile-distributed video has been painfully laborious and grossly underoptimized. To address these issues, NBC recently struck a deal with Kiptronic, an ad serving firm that specialized in non web-based content.
Stephen and Robert explained that their overarching goal with NBC.com video is to "publish once, distribute everywhere" - a goal I often hear from other video content providers as well. However mobile-distributed video was siloed and not fully incorporated into its online/broadband work flows. This was especially problematic on the ad side, where mobile inventory wasn't exposed in DART, on which NBC has standardized its ads. As a result a lot of mobile inventory was unsold, and even when it was sold, advertisers were required to jump through a bunch of new hoops to get their ads to NBC, which itself then "hand-stitched" the ads to its mobile-distributed video.
After looking at multiple solutions to address these issues, NBC chose Kiptronic's kipMobile. Stephen and Robert said the key was kipMobile's flexibility in plugging into NBC's existing content management system
 and work flow. Now when an NBC producer uploads video, upon preset instructions kipMobile transcodes the HD source file into relevant mobile formats and transfers them to Akamai (NBC's CDN). When a mobile user calls for a video, kipMobile determines which format is best-suited for that particular device, dynamically grabs appropriate ads from DART and combines the two into a file which Akamai then serves to the user.
and work flow. Now when an NBC producer uploads video, upon preset instructions kipMobile transcodes the HD source file into relevant mobile formats and transfers them to Akamai (NBC's CDN). When a mobile user calls for a video, kipMobile determines which format is best-suited for that particular device, dynamically grabs appropriate ads from DART and combines the two into a file which Akamai then serves to the user. Beyond dramatically simplifying NBC's work flow, Stephen and Robert are also excited about the new revenue potential, given NBC's booming mobile usage (Q1 '09 video streams jumped to 9.6M from 2.5M in Q1 '08 with mobile page views increasing from 32M to 96M in the same period). Looking deeper into the usage patterns, NBC sees more than half the mobile video usage occurring at home, as users increasingly look at their mobile device as an alternative screen when the TV isn't available. While 75% of NBC mobile usage is iPhone-based today, they're seeing strong adoption by non iPhone devices. Though still early, geo-identification is creating yet another ad opportunity unique to mobile.
NBC and many other content providers are going to be riding the wave of surging mobile video consumption. kipMobile and other monetization solutions will become increasingly important as these content providers seek to unify their online/broadband and mobile work flows and to fully monetize their views.
What do you think? Post a comment now.(Updated May 21st: Things move fast - Limelight just announced it has acquired Kiptronic.)Categories: Advertising, Broadcasters, Mobile Video, Technology
-
comScore Data Shows Tremor Media, Others Gaining in Premium Reach
Amid the steady stream of sneak peek press releases I'm sent each day, one I received late Tuesday from Tremor Media, the video ad network and monetization platform, caught my eye.
The release cited March data from comScore indicating that Tremor's network now had potential reach of 137M unique users and 57M unique video viewers (both unduplicated). The former number is from comScore's Media Metrix Ad Focus report and the latter from its Video Metrix Ad Focus report.
In particular, the latter number stuck out because I recalled comScore numbers from just 2 weeks ago that revealed the viewership for the top 10 video sites. Google (YouTube) was #1 with about 100M viewers, and Fox Interactive (mainly MySpace) was #2 with about half the amount, 55M.
comScore's new data meant that Tremor's potential reach was second only to YouTube's actual reach. And if you make the argument that much of YouTube's viewership is still UGC, while Tremor's network focuses
 solely on premium publishers, Tremor would be #1 in potential reach against premium video, a key point of the release. It's also worth noting that 2 other video ad networks focused on premium publishers also show up in comScore's top 10 for potential unique viewers- BrightRoll with 56M and YuMe with 41M.
solely on premium publishers, Tremor would be #1 in potential reach against premium video, a key point of the release. It's also worth noting that 2 other video ad networks focused on premium publishers also show up in comScore's top 10 for potential unique viewers- BrightRoll with 56M and YuMe with 41M. Tremor's VP of Marketing Shane Steele and market research manager Ryan Van Fleet walked me through the data further yesterday.
First, it's important to read these numbers carefully, as there's a little bit of apples vs. oranges going on. The Video Metrix Ad Focus report combines actual viewership by the destination sites (e.g. YouTube, MySpace, Yahoo, Hulu, etc.) with potential viewership by the ad networks. The report clearly denotes what's considered "potential." If I understand it correctly then, the comScore numbers for ad networks should be read as "here's the total potential audience of viewers you have access to." However, what percentage of this accessible audience actually gets an ad served by the ad network is only known by the ad network itself.
VideoNuze readers will recall there's been a lot of sensitivity around these comScore numbers, since last summer a minor kerfuffle broke out over comScore's ranking of YuMe's traffic. Initially it attributed MSN's full audience to YuMe, but later revised YuMe's ranking down by only included pages against which YuMe ads could be served. comScore also stated that on an ongoing basis it would report "potential" reach for ad networks based on documented agreements and "actual" reach for those networks that included certain tags. The new Tremor numbers reflect this potential reach measurement.
It's also important to remember that comScore filters its data to arrive at unduplicated reach. As I understand it that means that if for example Tremor had USAToday.com and Fox.com in its network (note Tremor doesn't disclose its publishers except to its advertisers) and a single user watched video at both sites, the user would only be counted once in Tremor's potential reach. I don't know how exactly comScore de-duplicates viewership, but let's assume it's accurate.
The extent of Tremor's reach (along with BrightRoll's and YuMe's), particularly against premium video is an encouraging sign. I've written in the past that key inhibitors of TV ad dollars moving over to online video are both scale and various friction points in the ad buying process. The comScore data demonstrates that a cluster of ad networks is emerging that can deliver against TV ad buyer's reach expectations, while adding new targeting and reporting capabilities unavailable in TV. There have also been recent enhancements to these companies' reporting/analytics (particularly around GRPs) to synch up with TV ad buyers' expectations.
The online video ad model continues to grow and evolve in spite of the current recession. This is particularly important for expensively-produced premium video where effective online monetization is crucial.
Chime in here with a comment if you think the comScore data or its implications needs further clarification.
Categories: Advertising
Topics: BrightRoll, comScore, Tremor Media, YuMe
-
Adap.tv Launches Player Partner Program
The ad management company Adap.tv has taken the wraps off its new "Player Partner Program" this morning. Initial partners include Brightcove, thePlatform, Mogulus, VMIX, Twistage and Kaltura. All are now integrated with Adap.tv's "OneSource" ad management system.
Yesterday, Dakota Sullivan, Adap.tv's VP of Marketing told me that though the company has been working with Brightcove and thePlatform informally to date, the new program will provide more structure to partners. Included are a central location on the Adap.tv web site for partners for promotional purposes along with other co-marketing and technology updates. No cash is changing hands with partners though, as Adap.tv tries to maintain neutrality.
These types of partnership programs are springing up all around the broadband video ecosystem, as companies continue to carve out their specific niches, and seek to benefit from partners' marketing efforts in a resource-constrained environment. I expect we'll continue to see them get rolled out.
Categories: Advertising, Partnerships
Topics: Adap.TV, Brightcove, Kaltura, Mogulus, thePlatform, Twistage, VMIX
-
VideoNuze Report Podcast #15 - May 8, 2009
Below is the 15th edition of the VideoNuze Report podcast, for May 8, 2009.
Daisy Whitney and I are back on track with our weekly VideoNuze Report podcast. This week Daisy adds more detail to a story she wrote for TV Week, "Targeted Ads: The Holy Grail?" which explores some recent ad targeting successes and ongoing challenges.
On the same targeting theme, I discuss a post I wrote earlier this week "Food2: A New Example of How Cable Networks Leverage Broadband." Scripps Networks, owner of Food Network and other lifestyle cable channels recently launched Food2, a destination targeted to the age 21-34 demo. It's a move that I believe will be closely watched by other channels looking to benefit from broadband's rise by "super-serving" specific audiences.
Click here to listen to the podcast (14 minutes, 38 seconds)
Click here for previous podcasts
The VideoNuze Report is available in iTunes...subscribe today!
Categories: Advertising, Cable Networks, Podcasts
Topics: Podcast
-
FreeWheel Raises $12M Series C Round, Video Sector Stays Strong
The syndicated video ad management company FreeWheel has announced that it has raised a $12M Series C round led by new investor Foundation Capital and existing investor Battery Ventures (prior funding
 rounds have not been disclosed). The up round provides continued evidence of fundraising strength in the broadband video sector, coming on top of at least $80M raised by industry companies in Q4 '08 and Q1 '09. Doug Knopper, co-founder/co-CEO gave me some additional background this afternoon.
rounds have not been disclosed). The up round provides continued evidence of fundraising strength in the broadband video sector, coming on top of at least $80M raised by industry companies in Q4 '08 and Q1 '09. Doug Knopper, co-founder/co-CEO gave me some additional background this afternoon.Funds will be used primarily for building headcount, integrating with broadband video ecosystem partners and continued product development. The company is up to 70 employees, spread between the U.S. (25 total between NYC and Silicon Valley) and China (45, all in development).
Doug echoed what industry CEOs have been telling me for months now - it's a brutal fundraising climate, but the video sector is very hot and companies with real traction are still highly sought-after. Investors recognize the shifts in consumer behavior and ad dollars and think we're still on the front end of these trends. While content investments have cooled, enabling technologies and services are still very attractive. At the NAB Show last week I got a heads up on additional financings to be unveiled soon.
FreeWheel has been very quiet about announcing customers, but Doug says there's plenty in the hopper and some news to come soon. No doubt there is given investors' continued confidence in the company.
What do you think? Post a comment now.
Categories: Advertising, Deals & Financings
Topics: Battery Ventures, Foundation Capital, FreeWheel
-
DVR Usage is Making Broadband Video Ads Look Better for Broadcast Networks
Data that TiVo released last week indicating that nearly 60% of broadcast TV programs in the 8pm and 9pm primetime slots are timeshifted for later viewing should be interpreted as another positive for broadband
 video advertising for two reasons.
video advertising for two reasons. First, because the high propensity of DVR users to skip ads means that broadband delivery can be increasingly considered the only way for big brands' ads to be guaranteed to be seen. And second, because all that ad-skipping is making the effective cost of each TV ad more expensive, thereby making broadband-delivered ads look like a better value.
In prior posts (here and here) I've outlined how a top network show drives around $.50-$.75 of ad revenue per on-air viewer. Said another way, advertisers are willing to pay $.50-$.75 to reach that show's audience. But now factor in that nearly 60% of the targeted viewers are watching via DVR, and that of this group maybe only 10% watch any ads at all. That means maybe only half or so of the intended audience actually see the ads. With half the audience, an advertiser is effectively paying 2x the CPM it thought it was.
Advertisers understand this as well, and as we know from newspapers' current plight, expecting they'll pay more to reach shrinking audiences is not a sustainable strategy. So, on the assumption that smaller and smaller targetable audiences long-term reduces the demand for on-air network ad inventory, CPMs should decline as well. On a relative basis that means that for broadcast networks, broadband video ads, which can't be skipped, have better targeting and more interactivity (all of which already drives higher broadband CPMs), start looking better and better. In short, DVRs' surging popularity is very good news for broadband video ads.
But as I explained in the posts cited above, the problem for networks today is that higher CPM broadband ads still result in lower total revenue per program for broadband vs. on-air. That's because networks are inserting a far smaller number of ad in a broadband-delivered program vs. an on-air delivered program (my estimate is somewhere around 3 minutes for broadband vs. 20 minutes for on-air). Hence the broadcasters' challenge - get total broadband ad revenue up while DVR usage acts to drive on-air revenue down.
Doing so requires better strategy and better execution. On the strategy side, I've said it before (and it always pains me to say it again), but broadcast networks have to increase ad avails in their broadband-delivered programs. That probably means more ads per pod, but could also mean other types of non-intrusive units like banners. On the execution side, it means more attention to each stream to ensure well-targeted ads that are actually delivered.
With broadband revenue still accounting for a miniscule amount of total broadcast network revenue, it's tempting to deprioritize addressing these issues. I think that would be a mistake. TiVo's stats on DVR usage in primetime (combined with other shifting consumer behaviors) should be a major wake-up call for networks about how their business models need to change. Fortunately for them, broadband offers an even-higher value delivery option if it is exploited properly.
What do you think? Post a comment now.
Categories: Advertising, Broadcasters, DVR
Topics: TiVo
-
YuMe/Mindshare's iGRP is Another Important Building Block for Video Ads
This week's announcement by YuMe and Mindshare to introduce an "iGRP" calculation for online video ad campaigns is another important building block in the online video industry's maturation process. Under the plan, YuMe and Mindshare will offer a reach and frequency metric for ad campaigns running across YuMe's network, which will correlate to GRPs that media planners use for TV ads. I spoke to YuMe's president and co-founder Jayant Kadambi about the iGRP plan yesterday.
Jayant explained that as the online video medium has grown, YuMe's sales team has begun interacting with more and more TV ad buyers, in addition to online ad buyers it customarily dealt with. While a lot of the
 spending for online video ads is still based on number of uniques and impressions, recently virtually all of the TV ad buyers YuMe deals with have been asking for a way to correlate and compare online video ad buys with TV buys. To address this need YuMe introduced the iGRP calculation a little while back and this week took the wraps off of it publicly. For those interested in understanding GRPs better, and the iGRP calculation, YuMe also released this useful white paper.
spending for online video ads is still based on number of uniques and impressions, recently virtually all of the TV ad buyers YuMe deals with have been asking for a way to correlate and compare online video ad buys with TV buys. To address this need YuMe introduced the iGRP calculation a little while back and this week took the wraps off of it publicly. For those interested in understanding GRPs better, and the iGRP calculation, YuMe also released this useful white paper.The white paper suggests that in addition to measuring reach and frequency, iGRPs can also capture an "interactivity factor" which would measure things like mouseovers, click-throughs and leads. YuMe and Mindshare plan to work with agencies and advertisers on various experiments testing the performance of different ad formats, durations, content types and targeting schemes.
I've believed for a while, as have others, that while there will be experimental ad dollars flowing into online video advertising, in order for the industry to truly scale, it is going to have to draw spending away from TV advertising. This is especially true in the down economy where advertisers are paring budgets, not increasing them. The $60 billion or so that's spent per year on TV ads is a rich pot of gold for online video to tap into. And given how reliant the online video industry is on advertising (vs. the paid model), the urgency to do so is quite high.
But actually making this happen is no easy feat. The TV ad industry is well-understood by all its
 participants, and despite its shortcomings and recent pressures such as surging DVR usage, many in the industry have little incentive to change. As a result, I believe online video ad executives must address and resolve all the friction points in shifting ad spending. Learning to speak in the same language - GRPs in this case - that traditional TV buyers have used in building media plans and doing post-campaign analysis is essential for the online video industry's growth.
participants, and despite its shortcomings and recent pressures such as surging DVR usage, many in the industry have little incentive to change. As a result, I believe online video ad executives must address and resolve all the friction points in shifting ad spending. Learning to speak in the same language - GRPs in this case - that traditional TV buyers have used in building media plans and doing post-campaign analysis is essential for the online video industry's growth.YuMe's and Mindshare's GRP plan comes on the heels of Tremor Media's own GRP announcement with comScore from February. No doubt others will follow with their own approaches as well. This will make for a noisy period until the industry coalesces around standard ways of calculating GRPs and other metrics. Nonetheless, this awkward adolescence should be viewed as an expected part of the maturation process for an industry seeking to convert an already massive, and still rapidly growing amount of monthly eyeballs into meaningful ad revenues.
What do you think? Post a comment now.
Categories: Advertising, Analytics
Topics: comScore, Mindshare, Tremor Media, YuMe
-
6 Reasons Why the Disney-YouTube Deal Matters
Late yesterday's announcement that Disney-ABC and ESPN would launch a number of ad-supported channels focused on short-form content was yet another meaningful step in broadband video's maturation process. Here are 6 reasons why I think the deal matters:
1. It validates YouTube as a must-have promotional and distribution partner
For many content providers it's long since become standard practice to distribute clips, and often full-length content, on YouTube. Yet aside from CBS, no broadcast TV network has seriously leveraged YouTube.
 That's been a key missed opportunity, as YouTube is simply too big to ignore. It's not just that YouTube notched 100M unique viewers in Feb. '09 according to comScore, it's that the site has achieved dramatically more market share momentum over the past 2 years than anyone else, increasing from 16.2% of all streams to 41% of all streams.
That's been a key missed opportunity, as YouTube is simply too big to ignore. It's not just that YouTube notched 100M unique viewers in Feb. '09 according to comScore, it's that the site has achieved dramatically more market share momentum over the past 2 years than anyone else, increasing from 16.2% of all streams to 41% of all streams. Increasingly, YouTube is not the 800 pound gorilla of the broadband video market; it's the 8,000 pound gorilla. Disney has acknowledged what has long been tacitly understood - as a video content provider, it's impossible to succeed fully without a YouTube relationship.
2. It creates a path for full-length Disney-ABC programming to appear on YouTube and elsewhere
While this deal only contemplates short-form video, and more than likely, mostly promotional clips, it almost certainly creates a path for full-length episodes to appear as well, as the partners build trust in each other and learn how to monetize. Full-length content is most likely to come from ABC, not ESPN (the release
 pointedly states no long-form content from ESPN's linear networks is included) as part of a newly expanded distribution approach.
pointedly states no long-form content from ESPN's linear networks is included) as part of a newly expanded distribution approach.For YouTube, which has been aggressively evolving from its UGC roots in its quest to generate revenues, the current clip deal alone is a big win; gaining distribution rights to full-length programs would be an even more significant step. Underscoring YouTube's flexibility, the current deal allows ESPN's player to be embedded, and for Disney-ABC to retain ad sales. YouTube's reported redesign, which places more emphasis on premium content, is yet another way it is getting its house in order for premium content deals.
3. It opens up a new opportunity for original short-form video to flourish
When you think about broadcast TV networks and studios, you immediately think of conventional long-form content. Yet all of these companies have been producing short-form content that either augments their broadcast programs, or is originally produced for broadband, as Disney's own Stage 9 is pursuing. The levels of success of this content have been all over the board.
With YouTube as a formal partner, Disney can aggressively leverage it as its primary distribution platform, gaining more direct access to this vast audience. Facing unremitting market pressures on many fronts, broadcast TV networks themselves need to reinvent their business models. Short-form original content married to strong distribution from YouTube would be a whole new strategic opportunity.
4. It puts pressure on Hulu and other aggregators
It's hard not to see YouTube's gain as Hulu's - and other aggregators' - loss. For sure nothing's exclusive here, and as PaidContent has reported, discussions about Disney distributing full-length programs on Hulu (as well as YouTube) are also underway. But the Disney deal underscores something important that differentiates YouTube from Hulu: YouTube is both a massive promotional vehicle and a potential long-form distributor, while Hulu is really only the latter.
YouTube's benefit derives from its first-mover status. Hulu has done a tremendous job building traffic and credibility in its short life, but it is still distant to YouTube in terms of reach. I continue to believe it is far easier for YouTube to evolve from its UGC roots to become also become a premium outlet than it is for Hulu - or anyone else - to ever compete with YouTube's reach.
5. It raises threat warning to incumbent service providers by another notch
It's also hard not to see the Disney deal moving YouTube's threat level to incumbent video service providers (cable/satellite/telco) up another notch. We discussed YouTube's importance to these companies at the Broadband Video Leadership Evening 2 weeks ago (video here), and I thought the panelists generally did not give YouTube much credit as it deserves.
I continue to believe that of all the various "over-the-top" threats to the current world-order, YouTube is the most meaningful ad-supported one. It has massive audience, a potent monetization engine in Google's AdWords, and with the Disney deal, increased credibility with premium content providers. Especially for younger audiences, the YouTube brand means a lot more than any incumbent service provider's. If I were at Comcast, Verizon or DirecTV, I'd be keeping very close tabs on YouTube's evolution.
6. It exposes the absurdity of the ongoing Viacom-Google litigation
Two weeks ago at the Media Summit I listened to Viacom CEO Philippe Dauman describe the status of his company's $1 billion lawsuit against Google and YouTube. As he talked of mounds of data and reams of documentation being collected and reviewed, I found myself slumping in my chair, thinking about how well all the lawyers involved in the case must be doing, and yet how pointless it all seems.
The old adage "2 wrongs don't make a right" fits this situation perfectly. There is no question that in the past YouTube was lax about enforcing copyright protection on its site and cavalier about how it responded publicly to the concerns of rights-holders. But it has made much progress with its Content ID system and a good faith effort to become a trusted partner. All of this is evidenced by the fact that Disney wouldn't even be talking to YouTube, much less cutting a deal, if it didn't view YouTube as reformed. While the media world is moving on, adapting itself to the new rules of video creation, promotion and distribution, Viacom continues to waste resources and executive attention pursuing this case. To be sure, Viacom has been plenty active on the digital front, but it is long overdue that these companies figure out how to resolve their differences and instead focus on how to work together to generate profits for themselves, not their lawyers.
What do you think? Post a comment now.
Categories: Advertising, Aggregators, Broadcasters, Cable Networks, Partnerships, UGC
Topics: Disney, ESPN, Google, Viacom, YouTube
-
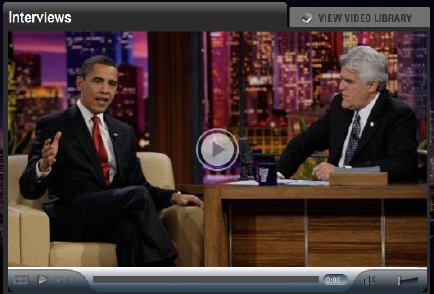
NBC.com is Missing At Least 75% of Potential Ad Revenue in Obama-Leno Video
Watching President Obama's appearance on "The Tonight Show with Jay Leno" on NBC.com over the weekend was a classic reminder of how so many sites miss out on so much of their total broadband video advertising opportunity.
The interview, which lasts over 24 minutes, carried just one 15 second pre-roll ad, (for Subway, when I watched it) along with a companion banner. Twice during the interview, Leno interrupted the President to pause for a TV commercial break, but when he did so, there was no mid-roll ad inserted by NBC.com. There was also no post-roll ad appended, just a promo graphic for the show itself.
If you figure there were at least 4 potential 15 second avails (1 pre-roll, 1 post-roll and 2 mid-rolls), but only the pre-roll was filled, it means that NBC.com missed out on 75% of the potential ad revenue that each full stream viewer would have generated. In reality the percentage is probably even higher because the mid-rolls could likely be 30 seconds or more.
That degree of under-monetization is pretty disappointing. Don't get me wrong, I'm not advocating that broadband video streams become overwhelmed with ads, which would surely cause a consumer backlash. But I do believe that providers of premium content like NBC.com (and there are few videos more premium than the first time ever a U.S. President has appeared on the "Tonight Show") must recognize and monetize their opportunities effectively. There are at least three reasons why:
First, and most obviously, broadcast networks' poor recent financial performance demands that they seize every available money-making opportunity. Not doing so is just bad business. How many businesses succeed long-term when they don't execute on all chances to generate revenue?
Second, NBC.com and other premium video providers are setting a bad precedent for consumers' expectations. If I can watch 24 minutes of Leno with just one 15 second ad, then if and when NBC.com tries to increase the ad load, I'm inevitably going to be displeased. In short, NBC is devaluing its own content by not serving notice to broadband viewers NOW, that a "price" - in the form of watching ads - must be paid for access.
Third, and tying together the first two reasons, is that it is urgent that networks learn how to achieve economic parity between programs viewed via broadband delivery vs. on-air delivery.
That's because the era of broadband-connected TVs has already begun, and is poised to gain further steam as new devices and connected TVs proliferate.
As this happens, online viewing will no longer be merely supplemental for many viewers to on-air, as it often (thought not exclusively) is today. Rather it will be substitutive. That means viewers will watch Leno via broadband on their TVs, instead of via cable/satellite/telco or over-the-air delivery. Just as "Tonight" would never go 24 minutes on-air without an ad pod (which consists of more than one just 15 second ad btw); NBC.com should never let this happen online. Doing so will cause major damage to its future P&L.
In his Media Summit interview last week, NBCU's Jeff Zucker said the company has already evolved from "digital pennies" to "digital dimes." Yet Hulu's recent stiff-arming of Boxee underscores the reality that networks are nowhere close to economic parity between online and on-air delivery of their programs today. Neither consumers nor technology are standing still waiting for them to catch up. Behaviors, expectations and future economics are being formed right now.
NBC.com - and others - need to be mindful of this and ensure that when they put their premium video online they're fully capitalizing on their ad opportunities. If they don't, then 5 years from now Mr. Zucker will wind up like so many of today's newspaper CEOs - lamenting, not praising, his company's "digital dimes," long after his "analog dollars" have evaporated.
What do you think? Post a comment now.
Categories: Advertising, Broadcasters
-
NBCU's Zucker: "We're at digital dimes now"
NBCU CEO Jeff Zucker provided the opening keynote interview at the Media Summit in NYC this morning with Businessweek Executive Editor Ellen Pollock. I've seen him speak a number of times and true to form he was pragmatic, quite candid and humorous. Highlights below:
"We're at digital dimes now" - Zucker of course famously worried aloud about the risk of "exchanging analog dollars for digital pennies," the notion that half-baked online delivery models would only serve to cannibalize traditional profitability. Zucker sees progress, saying Hulu is "well ahead of plan" and is yes, is now making money. Zucker repeatedly praised the success of the company's wide-ranging digital initiatives, but also noted often there is still a lot of work to do. He also wondered aloud whether digital would ever be a 1 to 1 revenue substitute for traditional revenue streams, but that further cost rationalization would help drive profitability.
"We're in process of finding new economic models" - On the above point, Zucker was candid in saying that the work to be done on new economic models is still experimental and that "a lot of success is often accidental." He readily concedes that nobody has all the answers, and that a key challenge is bridging from the traditional business models to new ones, balancing the interests of older audiences comfortable with the status quo with younger ones that are aggressively embracing the new. Describing his own kids' media activity, which focuses on Hulu, generating their own content and being interactive must give Zucker ample perspective.
"Technology is unbelievably exciting" - Zucker has always emphasized the importance of technology on NBCU's various businesses and today was no exception. He noted that technology is increasing access to TV programs and movies in unprecedented ways, which is a good thing. However he also candidly observed that it has fundamentally changed the broadcast business, primarily through consumers' use of DVRs and online delivery. All of that, plus NBC's lagging primetime performance, has caused it to completely re-think the broadcast model. He observed that newspapers' current woes can be traced to them not being willing to quetion the fundamentals of their model and the role of technology. Like other video providers, he seems determined to confront realities and avoid repeating this mistake.
"NBCU is first and foremost a cable programming company" - Zucker has often highlighted the benefits of the two revenue stream cable programming model (affiliate fees and advertising), but this was the first time I've heard him so clearly position the company as being mainly in the cable business. NBCU's stable of channels, USA, SciFi, Oxygen, MSNBC, Bravo, etc. contributed 60% of NBCU's operating profit last year. The networks' ability to "outperform the market, especially in women's programming and news" is key to NBCU's overall success. Zucker noted that USA is increasingly a "must buy" for advertisers, and with its mass appeal, should justifiably be considered the 5th broadcast network.
"We're hopeful we'll resolve TV.com-Hulu issues soon" - Zucker only briefly touched on Hulu's recent decision to pull its programming from TV.com, which is fast emerging as a Hulu competitor. As has been previously reported, Hulu's attorneys obviously believe TV.com compromised its Hulu distribution agreement as part of its new configuration subsequent to CBS's acquisition of CNET. With a battle looming between aggregators especially in the down economy, I think it remains to be seen whether a settlement can be found.
Categories: Advertising, Aggregators, Broadcasters
Topics: NBCU
-
The Video Industry's Winners and Losers 10 Years from Now: 5 Factors to Consider
Last week a publicly-traded communications-equipment company invited me to speak to a group of investment analysts it had assembled for its annual "investor day." In the Q&A session following my presentation I took a question that I'm not often asked, nor do I give much thought to: "10 years from now, who will be the video industry's winners and losers?"
It's a far-reaching question that doesn't lend itself well to an impromptu answer. Also, while it's great fun to prognosticate about the long run, I've found that it's also a complete crapshoot, which is why my focus is much shorter-term. I've long-believed there are just too many variables in play to predict with any sort of certainty what might unfold 10 years into the future.
Still, as I've thought more about the question, it seems to me that there are at least 5 main factors that will influence the video industry's winners and losers over the next 10 years:
1. Penetration rate of broadband-connected TVs -There's a lot of energy being directed to "convergence" technologies and devices which connect broadband to the TV. Broadband to the TV is a big opportunity for video providers outside the traditional video distribution value chain. It's also a minefield for those who have dominated the traditional model, such as broadcasters. The Hulu-Boxee spat demonstrates this. A high rate of adoption of broadband to the TV technologies will result in more openness and choice for consumers. That's a good or a bad thing depending on where you currently sit.
2. The effectiveness of the broadband video ad model - A large swath of broadband-delivered video is and will be ad-supported. But key parts of the broadband ad model such as standards, reporting and the buying process are still not mature. There's a lot of work going into these elements which is promising. The extent to which the ad model matures (and the economy rebounds) will have a huge influence on how viable broadband delivery is. Producers need to get paid to do good work or it won't get done. The imploding newspaper industry offers ample evidence. Those with robust online ad models like Google are likely to play a key role in helping distribute and monetize premium content.
3. How well the broadcast industry adapts to broadband delivery - The broadcast TV industry generates about $70 billion of ad revenue annually. But both broadcast networks and local stations are on the front lines of broadband's change and disruption, putting a chunk of that ad revenue up for grabs. With broadband-to-the-TV coming, broadcast networks must figure out how to make broadband-only viewership of their programs profitable on a stand-alone basis (i.e. when the online viewing is the sole viewing proposition). Local stations face bigger challenges. As the Internet was to newspapers, broadband delivery is to local stations. They face a slew of new competitors for ad dollars and audiences, while losing their exclusive access to network programming. To what extent they're able to reinvent themselves will determine how much share they hold on to and how much others peel off.
4. How aggressively today's video providers (cable/telco/satellite) and new paid aggregators pursue broadband video delivery - While anecdotes about "cord-cutting" will no doubt only intensify, the reality is that if today's video providers adapt themselves to broadband realities, they are likely to be as strong or stronger 10 years from now. The recent moves from Comcast and Time Warner are encouraging signs that the cable industry gets that being ostriches about the importance of broadband delivery is a road to nowhere. Consumers expect more flexibility and value; incumbents are in a tremendous position to deliver. Ownership of local broadband access networks that serve consumers' unquenchable bandwidth demands is going to be a very good business to be in. That all said, new paid aggregators like Netflix, Amazon and Apple could well steal some share if they aggressively beef up their content, offer a competitive user experience and deliver a better value. They could have a major impact on online movie distribution in particular.
5. The level of investment in startups - The venture capital industry, crucial to the funding of early-stage innovative technology companies, is going through its own turmoil. The industry's limited partners have been wounded by the market's drop, causing VCs to raise smaller funds (if they're even able to do this), limit the number of investments they make, and shy away from betting on big transformational startups. Plenty of strong video technology companies are still successfully raising money, but it's harder than ever. Lots of potentially promising ideas are going begging. The length and severity of the economic slowdown will have a big effect on just how much funding new technologies that can potentially reshape the video landscape over the next 10 years.
So there are 5 factors to consider in how the video landscape shapes up over the next 10 years. Now back to the here and now..
What's your crystal ball say? Post a comment now.
Categories: Advertising, Aggregators, Broadcasters, Cable TV Operators, FIlms
Topics: Boxee, Comcast, Google, Hulu, Time Warner
-
Adap.tv Releases OneSource 2.0
Adap.tv is announcing its upgraded OneSource 2.0 ad management platform this morning. The Adap team explained to me on Friday what's new in this release.
OneSource 2.0 builds on the product's initial vision of improving ad optimization while reducing complexity. Adap noted that the main pain point that its customers are expressing especially given the weak economy, is
 the need to spend more time focused on selling ads and less time on operationalizing the ad relationships. The need to improve their ROIs through both higher ad rates and higher fill rates is driving them to source ads from multiple sources and to want to refine those sources to find the optimal mix. All of this increases implementation and reporting complexity.
the need to spend more time focused on selling ads and less time on operationalizing the ad relationships. The need to improve their ROIs through both higher ad rates and higher fill rates is driving them to source ads from multiple sources and to want to refine those sources to find the optimal mix. All of this increases implementation and reporting complexity.OneSource 2.0's new features are meant to address these issues. The video provider can now accept ad tags from virtually any source, and do so more efficiently. In addition, through a management dashboard, the provider's ad ops manager can specify and adjust the fill order for the ad sources on a per ad basis. That means that for a specific piece of content there can be one queue for pre-rolls and another for overlays or for two pieces of content there can be two different pre-roll queues, and so on.
By sequencing multiple sources, OneSource creates a failover system so that an ad is likely always served, thereby increasing fill rates. Adap pointed to one provider who has been able to increase their fill rate from 20% to 70%.
In addition, OneSource 2.0 allows reporting by revenue source, video positions and geographic regions, which, at least in the demo screens that I saw, looked quite powerful. The ad ops manager can track performance on a daily basis and re-order sources accordingly. Lastly, there are enhanced tools for managing ads when content is syndicated, along with performance reporting.
I continue to see OneSource in a competitive set with Tremor Media's Acudeo ad management system, and also to some extent with Panache and FreeWheel. All of these systems are, in one way or another trying to improve video content providers' monetization and/or syndication efforts. Adap notes that by not also operating an ad network, it can be more agnostic about ad sources and solely focused on its technology. It now has 300+ publishers on board, helping monetize "high 100s of millions" of impressions per month, which it said is a 10x increase from OneSource's launch in May '08.
What do you think? Post a comment now.
Categories: Advertising, Technology
Topics: Adap.TV, FreeWheel, Panache, Tremor Media
-
Local Video Ad Space is Bustling with Innovation
The ad business in general may be in the doldrums due to the economic downturn, but one space that's bustling with innovation is online video ads for local, small-to-medium (SMB) sized businesses.
Local advertising has of course been around since the beginning of time. And even the idea of allowing local SMBs to create video ads is not a new concept; cable operators' local ad divisions have been doing this for years. What's relatively new in the local ad space are companies that allow a far higher degree of self-service video ad creation and campaign management by the client, online placements of their ads, and much improved analytics and ROI measurement capabilities vs. traditional cable TV.
For some local merchants, engaging in this process will be overwhelming and they'll stick with the tried and true local options like newspaper, radio and yellow page listings. But I believe that for many others, who recognize that their customers are increasingly going online to find local merchants and understand that a video packs far higher emotional punch than a text ad, this new alternative will be highly compelling.
There are multiple fairly well-funded players covering the local SMB video ad space, each with their own particular points of differentiation. They include Spot Runner, Spot Mixer, Jivox, Mixpo, PixelFish and others. Some like Spot Runner don't limit themselves to online distribution only, they're targeting TV as well. But the basics are relatively similar: a low-cost, often self-service ad creation process, a pretty well-defined way of targeting the intended audience through locally-oriented sites, and fairly flexible campaign/spending options. A persistent goal is to make it incredibly easy and cost-effective for local SMBs, who have most likely never done anything like this, to get up and running quickly.
To get a better feel for this all works and how SMBs are benefitting, I recently spoke with both Jim Gustke, VP of Worldwide Marketing at Jivox and Stephen Condon, VP of Marketing at PixelFish. Jivox, which raised
 $10.5 million last summer, reported that it doubled its customer base in Q4 '08. Jim said a real differentiator for the company is its publishing network of 800 premium sites and 65 million monthly unique visitors. This allows it to offer advertisers improved targeting and analytics vs. competitors who can only promise placements on affiliated sites. Jivox video ads auto-play in a 300x250 window on the publisher's site with audio off until initiated by the user. Better still for the advertiser, Jivox only charges for ads when 100% of the video has been viewed, thereby providing a pay-for-performance value proposition as well.
$10.5 million last summer, reported that it doubled its customer base in Q4 '08. Jim said a real differentiator for the company is its publishing network of 800 premium sites and 65 million monthly unique visitors. This allows it to offer advertisers improved targeting and analytics vs. competitors who can only promise placements on affiliated sites. Jivox video ads auto-play in a 300x250 window on the publisher's site with audio off until initiated by the user. Better still for the advertiser, Jivox only charges for ads when 100% of the video has been viewed, thereby providing a pay-for-performance value proposition as well.Jim said the most popular local categories include cosmetic surgeons, dentists, contractors, hospitality and legal. Demonstrating how active the category is, most of Jivox's new business has come through search. New advertisers pay as little as $250 to get started.
Meanwhile, Stephen explained that PixelFish employs a more customized and channel-centric approach, getting 80% of its business through partners like YellowBook, Google TV and others who are interfacing
 directly with the SMBs. That means PixelFish overlaps a bit with TurnHere and other video production networks. When one of its partners generates an order, PixelFish taps into its network of videographers to shoot specific footage which is then centrally edited and produced for the client. Through online editing tools recently acquired from EyeSpot, the advertiser can make changes to the ad himself and continue to make updates to it as offers change.
directly with the SMBs. That means PixelFish overlaps a bit with TurnHere and other video production networks. When one of its partners generates an order, PixelFish taps into its network of videographers to shoot specific footage which is then centrally edited and produced for the client. Through online editing tools recently acquired from EyeSpot, the advertiser can make changes to the ad himself and continue to make updates to it as offers change."Democratization" is a much-overused word, but here I think it really does apply. Even with local cable advertising, the cost of producing and running a TV ad has been prohibitive for many local merchants. These new companies are changing that, making video advertising accessible and affordable for the first time for broad swaths of local SMBs. Incumbents like local cable, newspapers and radio need to prepare themselves as the power of broadband and search-based marketing disrupt their status quo. I'm expecting this new crop of companies is going to drive a lot of change in this space.
What do you think? Post a comment now.
Categories: Advertising
Topics: Jivox, Mixpo, PixelFish, Spot Mixer, Spot Runner
-
Tremor Media Raises $18 Million Further Validating Broadband Video's Impact
Tremor Media announced this morning that it has raised a Series C round of $18 million, led by Meritech Capital Partners, with participation from existing investors Canaan Partners, Masthead Venture Partners and European Founders Fund. Tremor has now raised nearly $40 million to date. Tremor's CEO Jason Glickman gave me a short update on the company yesterday and a little more background on the financing.
Tremor believes it is now the largest video ad network, with 1,400 publishing partners aggregating 137 million unique visitors per month. Tremor focuses exclusively on premium video (i.e. non user-generated)
 and Jason said the company has access to 1 billion "advertisable impressions" per month. According to Jason, this critical mass has been a big source of the company's recent success as it has been able to appeal to advertisers by segmenting its network to target certain types of users.
and Jason said the company has access to 1 billion "advertisable impressions" per month. According to Jason, this critical mass has been a big source of the company's recent success as it has been able to appeal to advertisers by segmenting its network to target certain types of users. Jason explained that as Tremor has grown and usage of broadband video has surged, the company has increased its efforts to shift traditional TV ad dollars over. Though it's hard to know exactly what budgets ad dollars were originally earmarked for, based on the size of the RFPs Tremor's responding to, Jason thinks this shift is indeed underway. And as he correctly points out, you don't need a lot of the $70 billion that's spent on TV annually to move over to make a big impact in broadband advertising. To help compete more effectively with TV, Tremor also recently announced that it would use comScore's Post Buy and Ad Effectiveness reports to offer GRP (gross ratings points) campaign metrics.
To give some sense of Tremor's relative size, comScore reported 14.3 billion total U.S. video views in Dec. '08. Of that YouTube accounted for approximately 5.9 billion views. If you assume that somewhere between half and two-thirds of YouTube's views are UGC (and don't even consider UGC views at all other sites), then premium U.S. video views might be somewhere around 11.3-12.3 billion per month. According to these calculations, that would mean Tremor has access to around 8-9% of premium U.S. video views per month.
While acknowledging the economic downturn has created new challenges, Jason said the company has met or beat all of its metrics, is still on track for profitability in '09 and had multiple financing offers. Meritech's media and advertising experience in other portfolio companies (e.g. Facebook, Quigo, Revenue Science, etc.) was a real draw. The funding will be used to build its network, enhance its Acudeo monetization platform and continue international expansion.
There's no denying the economic pain being felt these days, but Tremor's ability to raise, coupled with other market leaders' ability to do so, is solid evidence that the broadband video market is a rare bright spot in the media landscape today. I constantly remind people that the underlying fundamentals of broadband video consumption are only increasing each month. The companies that figure out how to capitalize on these trends will still be able to raise money.
What do you think? Post a comment now.
(Note: Tremor Media is a VideoNuze sponsor)
Categories: Advertising, Deals & Financings
Topics: comScore, Meritech, Tremor Media
-
Betawave TV: Video Syndication Aimed at Kids and Moms
The "syndicated video economy" continues to mature with today's announcement of Betawave TV, a video distribution network offering video content and ads to kids age 6-17 and moms. Betawave TV is being launched by Betawave Corp., which was until recently called GoFish (and which also recently raised $22.5M). The company has amassed a U.S. publisher network totaling 25 million monthly unique visitors. I recently spoke to Betawave's executive chairman Jim Moloshok to learn more.
Betawave TV illustrates how broadband is helping merge the traditional concept of an ad network with the
 potential for widespread distribution of video to contextually targeted publisher sites. The bet here is that Betawave TV's content and ads can generate more value on its publishers' pages than just pure advertising could. Since Betawave TV's network has a heavy emphasis on gaming sites (e.g. GamesGecko, Hallpass, etc.) that don't have really have video strategies themselves, Betawave TV's offering seems like a good augment. Betawave TV will be released on sites totalling 6 million monthly uniques by the end of Q1.
potential for widespread distribution of video to contextually targeted publisher sites. The bet here is that Betawave TV's content and ads can generate more value on its publishers' pages than just pure advertising could. Since Betawave TV's network has a heavy emphasis on gaming sites (e.g. GamesGecko, Hallpass, etc.) that don't have really have video strategies themselves, Betawave TV's offering seems like a good augment. Betawave TV will be released on sites totalling 6 million monthly uniques by the end of Q1. Of course, these sites are by nature very immersive, so drawing users' attention away from their primary purpose requires compelling content. Betawave TV has a broad content strategy, including licensing from producers like Cookie Jar Entertainment, MGM and Young Hollywood to creating its own series. First up is the fashion-oriented and brand-sponsored "Raven Symone Presents." My guess is that much of Betawave TV's programming is relatively inexpensive to acquire or to produce, all the more so if Betawave TV can do more brand-sponsored deals.
Ultimately, Betawave TV is competing for audience attention and ad dollars that have traditionally flowed to major kids' TV programmers like Disney, Nickelodeon and Cartoon Network. As a piece in Mediaweek just yesterday suggested, 50-75% of ad dollars spent on kids' sites are no longer a part of integrated TV packages. The massive fragmentation of kids' attention away from just watching TV is certainly the underlying cause for this and what Betawave is banking on for success. I can attest to this trend myself: when my 8 1/2 year-old daughter gets together with friends they are far more likely to play games at AmericanGirl.com than watch Disney Channel.
No doubt Betawave TV won't be alone in pursuing kids online with syndicated video and ads. While Jim says they own 100% of the target inventory on their publishers' sites, there's no question these publishers will be evaluating plenty of competing offers in the future. Betawave TV's results will be an interesting test of how mature the video syndication opportunity actually is.
What do you think? Post a comment now.
Categories: Advertising, Syndicated Video Economy
Topics: Betawave
-
Media Buyer Interview Series Part 1: Ed Montes, EVP/Managing Director, Havas Digital US
Not a day goes by where there isn't an article about the health of the broadband video industry - how viewer consumption is growing, how much ad revenue it's slated to generate (or not), and what content and infrastructure partnerships have been inked. With the lion's share of the industry ad supported, it's time to hear from the people who are in position to make or break projected revenue budgets: the media buyers.
This interview is with Ed Montes, EVP/Managing Director of Havas Digital US; it is the first of a series of interviews that The Diffusion Group's senior analyst, Mugs Buckley, is conducting with advertising's key media buyers.
WHAT TYPE OF ONLINE ADS DO YOU BUY?
We buy pre-rolls, mid-rolls, in-line video ads. The only thing we have not bought much of are ads around user-generated content.
WHO ARE SOME OF YOUR CLIENTS?
Sears, K-Mart, Fidelity Investments, Amtrak, Tyson, Choice Hotels, Volvo, Air France, and Reckitt Benckiser, to name a few.
ARE ALL OF YOUR CLIENTS BUYING VIDEO ADS?
Many of our clients are placing ads in online video.
IS IT A "MUST HAVE" ON THE MEDIA PLAN?
We're definitely see it grow in importance and yes, it is a "must have" on some media plans. What I can say with more certainty is that online video advertising is becoming, and for some clients is, as important as display advertising. What remains a more consistent "must have" are search buys.
WHAT ARE THE SIZES OF SOME OF YOUR BUYS? WHAT ARE THE CPM TRENDS?
A buyer considers two things: scale (will it reach enough people) and the size/cost of a buy. It depends on the overall size of the campaign. For instance, in a large campaign a buy is south of $50K, may not make the plan, unless we're going to do it for the intelligence of the buy or because the CPM is very discounted. On a smaller campaign $50K might be the entire campaign so you will see much smaller video purchases. There is a huge swing for CPM range depending on the content. Everything hinges on the content. We see CPMs ranging from $15-$40 for non-UGV content in-stream units. UGV, the lower-end quality content CPMs tend to be in the single digits. In-banner video is generally on the lower end of the single digit range.
HOW LABOR INTENSIVE IS AN ONLINE VIDEO AD BUY?
Relatively speaking, it is a lot more labor intensive than a broadcast buy. In the online world, there are a lot of steps in the process to create, buy, optimize, build and analyze a video ad campaign.
WHAT DO YOU WANT YOUR SELLERS TO KNOW BEFORE THEY COME AND PITCH YOU?
I'd like sellers to be informed about our clients, their campaigns, and goals so we can build the best possible idea. I want someone to bring me a solution, not just sell me their unsold inventory.
IS THE "BUY" ALL ABOUT SCALE?
I think it's about audience fragmentation, the inverse of scale. People buy TV because they can aggregate a large audience; it is the best mass media vehicle. As TV ratings decline, a buyer has to buy an increased mix of television to achieve the same scale they did previously. Now the consideration shouldn't just be TV, it should be all video.
WHO DOES THE BUYING? BROADCAST BUYER? ONLINE BUYER?
Both online buyers and broadcast buyers do the buying but like anything, it depends on the buy. Pure online purchases (like Hulu, Veoh, YouTube), the online buyers are in the lead. On the network side (such as buying from ABC), it's a little bit different because there are instances where media is bought by network buyers with the assistance of online buyers.
WOULD YOU BUY FROM AN INDEPENDENT WEB STUDIO OR THEIR CONTENT?
I would consider such a buy but it goes back to the issue of scale. Would we buy directly from the programmer or buy from a network? In a world where I'm trying to aggregate reach, they may fall out of the category due to their limited audience size.
QUOTE
"We're bullish on online video, the performance we've seen from it is highly encouraging."
Categories: Advertising, People
Topics: Havas, The Diffusion Group
-
4 More Thoughts on the Super Bowl Ads
The Super Bowl ads are continuing to generate all kinds of buzz and continued chatter. In the spirit of "everything's been said, but not by everyone," here are a few additional broadband-related thoughts.
Doritos user-generated contest is a big winner - Doritos snagged 2 of the top 5 placements in the USA Today Ad Meter popularity rankings, displacing Anheuser-Busch for the first time. The fact that the Herbert brothers of Indiana could have created an ad more popular than all of those by the pros is impressive enough. More interesting though to me is Doritos is steadily morphing its brand into one which its customers control. This was the 3rd time Doritos handed over its Super Bowl advertising to fans to both submit ads and also vote on them. I've written about other brands' UGV contests, but Doritos is clearly the furthest along in embracing this concept. It's a great differentiator for the brand and will only build further momentum in the future.
Hulu's ad: funny but confusing - did you catch Hulu's first-ever Super Bowl ad starring Alec Baldwin as a creepy alien? The tag line was "Hulu: An evil plot to destroy the world. Enjoy." I thought the ad was hilarious and Baldwin's a classic, but I have to say I found myself wondering if this is really the best positioning for Hulu, the premium online video aggregator?
The ad development process usually starts with identifying key brand attributes (e.g. "convenient," "affordable," "wide variety," "hip," etc.). Did the Hulu marketing team start with attributes like "deceitful" or "creepy" or "offbeat?" Seemingly so. Although the spot was fun, it didn't do anything to articulate Hulu's great value proposition. Further, is Hulu now going to pursue this creepy positioning further? If they do, does that make sense for the brand? But if they don't, wasn't the ad a waste of effort, with little continued momentum? I'm not an ad expert, but I'm not clear on what Hulu was trying to do here, other than get some great yucks.
How about some more "behind-the-scenes" and "making-of" video - Ad executives don't seem to understand what filmmakers discovered with DVDs years ago - that the backstory around the final cut is often even more interesting to fans. Since DVDs offer the capacity to provide director's notes, explanations of special effects, outtakes, actor interviews, etc they often do. This stuff is fascinating. Same with broadband; it offers brands the ability to provide a lot more video than just the ads themselves on their web sites, which some did indeed do.
But many others who could have done so, did not. Two that come right to mind: Coke, whose fascinating ad with insects stealing a sleeping man's bottle had some of the best special effects ever. How about some interviews with the computer animation team that did them? That would be fascinating. The other: E-Trade's talking babies. How'd they do that? Would love to know.
Should ads be rated or filtered? Ok, here's something controversial to think about - should Super Bowl ads be rated or filtered somehow? This is supposed to be family entertainment after all, isn't it? Does the woman getting stripped in the Doritos "Bus" ad or the suggestive GoDaddy girls belong in prime-time? I wonder. Or maybe the online galleries should rate the ads somehow? Maybe the racier ones deserve a parental warning? Just a thought.
Ok, that's it for the '09 Super Bowl, on to other topics...
What do you think? Post a comment now.
Categories: Advertising, Sports
Topics: Super Bowl
-
January '09 VideoNuze Recap - 3 Key Themes
Following are 3 key themes from VideoNuze in January:
Broadband video marches to the TV - At CES in early January there were major announcements around connecting broadband to TVs, either directly or through intermediary devices (a recap of all the news is here). All of the major TV manufacturers have put stakes in the ground in this market and we'll be seeing their products released during the year. Technology players like Intel, Broadcom, Adobe, Macrovision, Move Networks, Yahoo and others are also now active in this space. And content aggregators like Netflix and Amazon are also scaling up their efforts.
Some of you have heard me say that as amazing as the growth in broadband video consumption has been over the last 5 years, what's even more amazing is that virtually all of it has happened outside of the traditional TV viewing environment. Consider if someone had forecasted 5 years ago that there would be this huge surge of video consumption, but by the way, practically none of it will happen on TVs. People would have said the forecaster was crazy. Now think about what will happen once widespread TV-based consumption is realized. The entire video landscape will be affected. Broadband-to-the-TV is a game-changer.
Broadband video advertising continues to evolve - The single biggest determinant of broadband video's financial success is solidifying the ad-supported model. For all the moves that Netflix, Amazon, iTunes and others have made recently in the paid space, the disproportionate amount of viewership will continue to be free and ad-supported.
This month brought encouraging research from ABC and Nielsen that online viewers are willing to accept more ads and that recall rates are high. We also saw the kickoff of "the Pool" a new ad consortium spearheaded by VivaKi and including major brands and publishers, which will conduct research around formats and standards. Three more signs of advertising's evolution this month were Panache's deal with MTV (signaling a big video provider's continued maturation of its monetization efforts), a partnership between Adap.tv and EyeWonder (further demonstrating how ecosystem partners are joining up to improve efficiencies for clients and publishers) and Cisco's investment in Digitalsmiths (a long term initiative to deliver context-based advanced advertising across multiple viewing platforms). Lastly, Canoe, the cable industry's recently formed ad consortium continued its progress toward launch.
(Note all of this and more will be grist for VideoNuze's March 17th all-star panel, "Broadband Video '09: Building the Road to Profitability" Learn more and register here)
Broadband Inauguration - Lastly, January witnessed the momentous inauguration of President Barack Obama, causing millions of broadband users to (try to) watch online, often at work. What could have been a shining moment for broadband delivery instead turned into a highly inconsistent and often frustrating experience for many.
In perspective this was not all that surprising. The Internet's capacity has not been built to handle extraordinary peak load. However on normal days, it still does a pretty good job of delivering video smoothly and consistently. As I wrote in my post mortem, hopefully the result of the inauguration snafus will be continued investment in the infrastructure and technologies needed to satisfy growing demand. That's been the hallmark of the Internet, underscored by the fact that 70 million U.S. homes now connect to the 'net via broadband vs. single digit millions just 10 years ago. I remain confident that over time supply will meet demand.
What do you think? Post a comment now.
Categories: Advertising, Aggregators, Devices, Politics, Technology
Topics: ABC, Adap.TV, Adobe, Amazon, Broadcom, EyeWon, Intel, Macrovision, Move Networks, MTV, Netflix, Nielsen, Panache, VivaKi, Yahoo